Advantages and disadvantages
Wooden boxes enclosing the beds improve the appearance of the plantings and make them easier to care for. The box prevents soil from shedding when watering or processing crops. Board fencing makes it difficult for weeds to spread and makes periodic weeding much easier. The soil in such a structure can be filled in layers, forming and maintaining their optimal location.
The main advantages of board beds are:
- maintaining the shape of the beds and preventing them from falling off;
- ease of construction;
- ease of weeding and other care, ease of fertilizing;
- slowing down the penetration and development of weeds and pests;
- creating comfortable conditions for cultivated plants;
- possibility of attaching film to create a microgreenhouse;
- possibility of fastening arches for film;
- aesthetic appearance.
What do board beds look like
? The disadvantage of this solution is its short service life.
When wood comes into contact with soil and moisture, it quickly becomes unusable, rots, and is attacked by fungus and pests. Boards in strawberry, vegetable and root vegetable beds need bioprotection.
Other factors
Paths
You should not make them from gravel, otherwise they will quickly become overgrown with weeds. You shouldn’t make them too narrow (along a path narrower than half a meter, you won’t be able to roll a wheelbarrow during harvesting) and too wide (otherwise too much useful space will be lost).
Subsequence
You cannot plant the same crop in the same place for two years in a row - this depletes the soil and introduces pests that target a specific crop. Therefore, the beds need to be dug up in the fall and sown with new vegetables in the spring.

Compatibility
Many crops grow better side by side - even in the same bed - because one of them releases substances that are beneficial to the other. Worth combining:
- tomato with onion and cabbage;
- potatoes with beans;
- cucumber with cabbage, beets or salad;
- carrots with herbs - salad and dill;
- cabbage with radish and tomato.

Material selection criteria
Wood is an easily processed and relatively inexpensive material for the rapid construction of various structures. Working with boards does not require high qualifications or expensive equipment. If the dimensions are calculated correctly and the technology is followed, the boards fit well together without leaving any gaps. This makes it difficult for weeds and pests to penetrate the garden bed, helps retain moisture in the soil, and reduces water consumption and labor costs for watering.
The following tree species are used to form beds:
- Oak or ash. Dense wood is slightly susceptible to rotting, but is expensive and difficult to process.
- Cedar or larch. The material is well processed and does not rot at all. The disadvantages include the high price.
- Pine. The material is inexpensive and easy to process. Subject to rapid rotting. Requires special impregnation.
Terrace board. Heat-treated wood does not rot. The price is several times higher than that of ordinary boards.
When choosing a material, proceed from the planned service life and area of the beds. So, you can plant oak or cedar in a small garden bed. The high price will be compensated by a long service life and excellent appearance. If you plan to cover many beds with boards, then it is better to choose pine boards and thoroughly impregnate them with bioprotective compounds.
Which wood do you prefer?
Warm beds are a “pie” of several layers of organic matter. By overheating, it increases the temperature at the roots, accelerating the growth of garden crops. In addition, plants receive natural fertilizers, and metabolic processes in the top layer of soil are improved due to the active work of beneficial microorganisms.
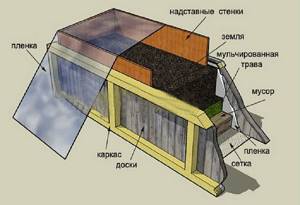
Arranging an organic “pie” is impossible without restrictive sides - the so-called box. It does not allow the layers to “float” during rains, gives the plantings a neat appearance, and does not allow weeds to enter. The box can be made from slate and metal sheets, plastic panels, concrete or brick. However, boards are considered the best option for warm beds. They are easy to process, affordable, environmentally friendly and decorative.
Related article:
The best weed killers in the garden
The box turns out to be relatively light, it can be removed from the ground and moved to a new location, unlike its concrete or brick counterparts. Wood does not heat up on hot days, as metal does, causing the soil to dry out and plants to die. And it does not emit toxins, which is the “sin” of plastic or slate. The main disadvantage of wood is rotting with excess moisture, and any organic matter requires frequent watering.
The solution is to use conifers with a high resin content.
It is advisable to make beds from edged boards. “Gorbyl” and lumber with “wane” are cheaper, but they look aesthetically pleasing only if the house and the adjacent area are designed in the appropriate rustic style. In other cases, the plantings will appear untidy.

Pine
Pine boards are most often chosen for arranging beds. This material is cheaper than others, with good strength and resistance to rotting. Pine is easy to process, thanks to its high viscosity, it holds fasteners well, is resistant to bending deformation, and has bactericidal properties. Due to its low density, it is much lighter than other softwoods. The pine box, measuring 600x100 cm, can be easily lifted and carried by two people.
Related article:
Smart landing is a guarantee of success
However, protection from water and pests will be required. Without special impregnations or painting, pine walls are subject to destruction and are unlikely to “last” more than 3–4 seasons. In addition, due to the high resin content, wood is capable of self-ignition. The softness of sapwood, which simplifies the processing process, also has a downside - mechanical stress leaves scratches and dents on the material, accelerating decay.
Features of wood processing
There are several types of compounds that protect wood from rotting.
Impregnation products are widely available in stores in Moscow and other cities. These compounds penetrate deeply into the structure of the tree and protect it from rotting, mold, insect pests and rodents. When choosing an impregnation, you must take into account how it changes the color of the treated wood: some substances give the boards pink or green shades. If the appearance of the garden matters, then it is better to choose a colorless impregnation or natural brown tones close to the color of the soil. There is no point in overpaying for the fire-retardant properties of complex impregnations used for wooden building structures. Fire does not threaten the garden; the bioprotective properties are quite sufficient.
The next group of products is paints and varnishes. They must be water-based so that potent components do not get into the soil and into the vegetables and berries being grown. When painting boards, be sure to leave the ends unpainted. Varnish or paint creates an airtight layer on the surface of the wood, and a board deprived of the ability to “breathe” will rot much faster than an unpainted one.

Varnish is used to treat board beds
And finally, the traditional method of protection: coating with lime mortar. It protects the tree quite well and is inexpensive. Lime has one drawback: its fragility. It will have to be repainted every year.
Protecting wood from moisture
The wooden box for the garden bed is treated with antiseptics before assembly. Otherwise, there will be unprotected areas at the joints that will begin to rot. You can coat wooden parts with liquid paint or impregnation - a difficult-to-wash-out antiseptic for use in harsh conditions (for structures in contact with the ground).
But there are other ways:
- The cheapest solution is used motor oil. But apart from being cheap, the product has no advantages, although it is popular. Exhaust is a concentrate of carcinogens that, when released into the ground, poison everything that grows on it.
- You can cover the boards in places of contact with organic matter with bitumen diluted to paint. However, the environmental friendliness of the method is also questionable.
- Copper sulfate simultaneously protects against rotting and harmful insects. A ready-made solution is applied to the wood, which can be bought at flower shops. The disadvantage of this method is that lumber treated with vitriol must be dried outdoors in the shade for 7 to 30 days. So, you will have to prepare in advance.
Related article:
Features of the fight against dandelions in the garden: how to remove the weed

- A mixture of propolis and sunflower oil in a ratio of 1:3, respectively, is effective. But if there are a lot of boxes, the costs become significant. In addition, the mixture is flammable and wood soaked in it is a fire hazard.
- You can use the so-called “Finnish composition”. It includes: 700 g of wheat flour, 1500 g of iron sulfate and slaked lime, as well as 400 g of table salt. The flour is diluted with water to the consistency of liquid sour cream, and then, stirring constantly, the remaining ingredients are added. It is advisable to use the composition warm and apply twice.
For additional protection from moisture, the inside of the box is lined with spandbond (agro-fabric). The material is attached to the walls using a furniture stapler. However, not all adherents of the organic method agree with this decision. Some argue that, on the contrary, moisture forms under the film, which does not evaporate and, as a result, only accelerates decay.
Related article:
How to arrange warm beds at the dacha
Spunbond also prevents weeds from germinating, so its use may be advisable if the “pie” has good drainage.

Wood burning as an alternative to impregnation
When making wooden beds with your own hands, you want to achieve maximum environmental friendliness at every stage. Otherwise, there is no point in gardening - it’s easier to buy vegetables and spices at the nearest supermarket. Impregnations protect wooden fencing well, but one can only guess about their safety.
Another thing is the ancient method of burning wood, which today is again gaining fans. When treated with fire, a layer of coal is formed on the surface, like a barrier preventing the penetration of living organisms: insects, bacteria and molds. Firing is best done with a gas burner for roof repairs.

A heavily burnt top layer is cleaned with a stiff brush or a Karcher. At the same time, the wood shows its texture and gets less dirty. Then the surfaces are treated with technical linseed oil or drying oil.

Drying oil creates a water-repellent barrier that prevents coal from washing out
Texture after brushing – brushing:

The box will last from 5 to 10 years if the oil layer is restored annually. You can also varnish the wood.
Related article:
What to make the walls of the beds from

Nuances of the layout and size of the beds
How to make beds correctly and choose the optimal shape and dimensions for them? The boards do not bend, so the only shape of the beds available is rectangular. When determining the shape and size of boxes, we proceed from the following principles:
Height of beds made of boards. Calculated based on the type of bed. For ordinary ones, 150-200 mm is enough, this is equal to the thickness of the layer of fertile soil. For the “warm bed” technology, the box is made significantly higher - up to 700 mm. A high bed made of wood will allow you to place several layers in the desired order. The higher the box is made, the more measures will have to be taken to ensure that it does not burst open during seasonal temperature fluctuations.
- Width. Determined by the method of processing plants. When working manually, it should be convenient for the gardener to reach the far wall or the middle of the box if passages are provided on both sides. The most common width is from 600 to 1200 mm. When using tools with extended handles, the width can be increased. In this case, it is also necessary to take measures against bursting.
- Length. It is determined based on the general plan of the garden and the ease of movement around it. The standard length of boards when delivered from a sawmill is 6 meters. Usually the length is made a multiple of this size: 3, 2, 1.5 meters. This helps reduce the amount of waste.
Form. On open ground, it is most convenient to make beautiful beds in the form of rectangles. In stationary greenhouses and greenhouses, the shape is determined by the size of the structure and the ease of passage and passage of a garden wheelbarrow through it. The passage between the beds should be no narrower than 400 mm.
Triangular boxes are less common. They are usually made in the corners of vegetable gardens or large greenhouses to increase the efficiency of land use.
Recommended Settings
Naturally, the summer resident himself decides what size “plantation” is more convenient for him to choose. Therefore, we are talking only about the optimal dimensions, which are determined on the basis of the practical use of such structures.
Height
It is with this parameter that the most difficulties arise when calculating the most acceptable size. Its value is determined based on where exactly the artificial plot is located.
- When placing the frame on fertile soil, without isolation from it, the optimal height of the sides of the artificial bed is 18±4 cm.
- If the plot is set up in a place unsuitable for growing plants directly in the soil (isolated structure), then at least 30.
- Many gardeners grow potatoes on their plots. For this (and similar) crops, the height of the sides will have to be slightly increased, taking into account the depth at which the tubers develop. As a rule, in this case, there are 2 - 3 boards on the sides of the frame, which are attached one above the other.
Separately, it is worth mentioning the so-called compost structures. They are mainly installed in regions with rapidly changing weather. For what? For example, the dacha is located not just outside the city limits, but at a considerable distance. If weather forecasters warned that frosts are expected overnight, will everyone be able to go to the site to cover the seedlings planted in open ground?
Compost, placed under a layer of soil (and it remains relatively warm), preserves the root system from freezing. For such a design, the sides should be at least half a meter, sometimes higher.
Length Width
The first parameter is determined arbitrarily, but the optimal width (cm) is considered to be from 90 to 120. You just need to correlate this value with the height of the sides. There is only one criterion - whether it will be convenient for the gardener to reach the middle of the garden bed.
Manufacturing procedure
Here, a detailed description of all technological operations, as well as recommendations for choosing a tool, is not required. The pictures explain everything well. Anyone can knock down a frame from boards to specified dimensions with their own hands.
What to consider
When making a high bed isolated from the ground, it is necessary to carry out a number of additional measures. This mainly concerns work on arranging the “bottom” of the frame.
Protection from rodents. To do this, a metal mesh is placed on the bottom.
Elimination of weed germination. Quite often there are recommendations for using P/E film. The simplest and cheapest option, but in this case you will have to think about how to ensure good drainage. After all, this material is a waterproofing agent, and stagnation of water in the garden bed is fraught with rotting of the root system of the plantings. A more acceptable solution is geotextiles. Perhaps the reader will come up with something different, but the meaning is clear.
General recommendations
The board has a significant drawback - it is susceptible to rotting. Especially if it is used for an artificial bed. Regular watering of the plot means constant contact of the material with moisture. The method of protecting the frame from rotting is at the discretion of the owner. The most common methods are impregnation with used machine oil, special purchased preparations, and so on.
You just need to understand that contact with artificial materials (only natural ones) is contraindicated for all garden crops. Covering boards with plastic, for example, is not an option. In general, the problem of increasing the shelf life of wood is a separate topic, so the author limits himself only to drawing attention to the need to solve it.
When assembling frames for high beds, it is not advisable to use nails as fasteners. After all, such board structures can last for more than one year; This means they will have to be disassembled/assembled regularly. In this regard, a good solution is to fix individual frame elements with self-tapping screws.
In order not to complicate your life at the beginning of the next season, racking your brains over which specific boards are fastened together, they should be marked. For example, 1-2, 1-4. In the spring it will be clear that bed No. 1 is being assembled from these elements. And the diagram drawn up during the initial installation will tell you on which side of the frame this or that board is placed.
Everything else - choosing a place to install high beds depending on the illumination of the area, wind roses, and the like - is no different from the rules for arranging traditional plots on the site.
When is it appropriate to use raised beds?
At the beginning of the article, it is partially noted why such designs are convenient. But, in addition to making it easier to process the beds, they also allow you to solve a number of other everyday problems.
- When planting plants that require different soil characteristics. Each of the plots can be loaded with exactly the soil mixture that is needed for the normal development of a particular crop.
- If there are difficulties with arranging high-quality drainage on the site.
- Possibility of installation in any place, even unsuitable for gardening due to the properties of the soil.
- If necessary, insulate plots. In relation to artificial beds, the solution to this issue is significantly simplified.
Manufacturing nuances
How to make a bed from boards with your own hands? The construction of a fencing box does not require highly qualified workers or the use of expensive equipment. Materials you will need:
- boards 20-40 mm thick;
- block 40*40mm;
- bioprotective impregnation;
- painting tool or sprayer;
- wood screws.
You will also need tools:
- manual or electric carpentry tools: saw, jigsaw;
- screwdriver;
- a set of measuring instruments: a tape measure of sufficient length, a ruler, a marker, a level;
- earth-moving tools: shovel, wheelbarrow.
It is mandatory to use personal protective equipment: thick clothing, shoes, gloves, glasses. When applying impregnation, you should use a respirator.
Preparatory work
The choice of location for the garden bed is carried out taking into account the sun-loving (or shade-loving) culture. It is not necessary to have fertile soil: it can be brought and poured into a box. The area must be cleared of debris, turf, and roots of perennial weeds. Digging up the base of the box will help improve the moisture permeability of the soil.
Next, the area is marked according to the dimensions of the box. To make sure the box is square, you need to measure and compare its diagonals. They must be equal. Before installation, boards, corner and intermediate beams, sawn to size, should be impregnated with a bioprotective compound.
Making a box
On the cleared and leveled base, corner bars are driven into the ground at the corners of the box. They should sink 10-15 cm. Next, lay the first row of boards. They are attached to the corner bars. If the box has only one row of boards in height and is small in size (1-1.5 m in length), then you can do without corner bars. In this case, the boards are attached to each other.
After 1.5 meters of length, intermediate bars are driven in and boards are attached to them. This will prevent the box from expanding and help maintain its beautiful appearance.
Next, install the second row of boards, check them for level and also attach them to the bars with self-tapping screws. The operation is repeated until the design height is reached.
The soil is covered with geotextile and secured to the sides with a construction stapler. This will protect the soil in the box from weed roots and pathogens.

Making a box
Fine crushed stone or pebbles are poured onto the geotextile layer in a layer of up to 5 cm. It will act as drainage.
Next, the box is filled with fertile soil, not reaching 3-5 cm to the top side.
In areas where moles and shrews are common, a fine galvanized mesh is rolled out under the geotextiles and also attached to the sides.
Filling rules
When filling the box layer by layer, proceed as follows:
- 10 cm permeable layer: mulch, bark, shavings, etc.
- Organics: compost; rotted farm animal manure or bird droppings.
- Second permeable layer;
- Second layer of organics. Mineral supplements are also added to it.
- 10-15 cm of good fertile soil.
The layers should not be mixed. The soil should be well watered and left for a couple of days for the layers to settle. The prepared bed is covered with a dark covering material: polyethylene or spunbond. The technology is often used in strawberry beds.











