You can grow rose hips from seeds at home without seedlings. The grains are collected in August, when the fruits are not yet ripe, and are immediately sent for stratification in a dark, cool and humid place. They can be sown in open ground before winter and then mulched with sawdust. In the spring, when shoots appear, regular watering should be provided. After two leaves appear, they are picked and continued to be watered, feeding if necessary.
Is it possible to grow rose hips from seeds?
Growing rose hips from seeds is carried out in two ways:
- Planting rosehip seeds in open ground in the fall.
- Spring procedure in April-May after stratification.
Growing rose hips from seeds in open ground is possible immediately after harvesting in August. If you delay and purchase seed, for example, in early October, you can also plant it in the ground. To do this, make several rows and bury the seeds 1–2 cm, mulch and wait for the first shoots next spring. This method is used for growing wild species, as well as winter-hardy varieties.
The second option (spring planting) can be considered universal, since it allows you to grow both wild and cultivated rose hips. Seeds are purchased in autumn or winter and sent for stratification in the refrigerator (for at least three months). Then they are germinated and planted in the ground in the second half of spring, when the soil has time to warm up to +8–10 degrees °C.
Proper care of rosehip seedlings
Caring for planted rosehip seeds is not difficult. To grow them, it is necessary to regularly remove weeds and periodically loosen the soil, which improves the air supply to the root system of plants, and consequently improves their growth.
Do not forget also about the need for regular watering and proper feeding of seedlings. The latter is carried out with various organic compounds and a small amount of mineral fertilizers.
Timing of sowing seeds
To grow rosehip from a seed, it needs to be planted on time. The timing depends on the growing method:
- For direct sowing in the ground - immediately after collecting the seeds (late August - early September).

- If you collect material for artificial stratification, at the end of summer it is placed in boxes with soil and taken to a cool place, for example, in a cellar or in a refrigerator.
- In spring, sowing in open ground is carried out at the end of April or at the beginning of May. In the south it is 1–2 weeks earlier, in Siberia and the Far East - on the contrary, later.
Rules for planting rose hips
By adhering to the rules for planting rose hips, you can grow luxurious bushes of this plant in your area.
Video: planting rose hips
Selecting a location
The planting site should be on a hill. Rose hips do not like soil with high acidity. The place should be well lit by the sun and hidden from direct winds. The lack of groundwater in the area will not harm the plant, but will only have a beneficial effect. Since a crop can grow on a site for up to 30 years, it is important to foresee in advance the possibility of such a long stay of the bush in one place.
Before planting, the area must be thoroughly cleared of weeds. It is better to plant ornamental fruit crops in isolation from other plants in the garden. A suitable place for this may be the area along the fence.
Soil preparation
Experienced gardeners recommend planting legumes or cereals on the site two years before planting shrubs. You can dig up such a place in the second year in the fall after the first mowing. The site is maintained in this form until spring and deep digging is carried out only in May. Before autumn, you should clear the soil of weeds, keep it clean, and carry out small digging several times during the summer before planting the seedlings. Planting is usually carried out in October-November. Acidic soils must be limed.

How to grow rose hips from seeds at home
Growing rose hips at home consists of several stages. The seeds of this plant are covered with a very dense skin. To destroy it, it is necessary to keep the planting material in a humid environment in cool conditions. First, the seed is sent for stratification, then for germination, and then planted in the ground.
Seed preparation and stratification
The first stage of breeding rose hips with seeds is stratification, i.e. imitation of wintering. To do this, take seed purchased in a store or collected yourself and mix it with fertile, light, well-moistened soil. This can be universal soil for seedlings or your own mixture of surface soil, black peat, humus and sand (ratio 2:1:1:1).
Instead, you can use wet sand, which is pre-calcined. If you are not sure, you can also disinfect the soil mixture by watering it with a weak solution of potassium permanganate. Other ways are to put it in the freezer for a week or keep it in the oven for 15–20 minutes at a temperature of 130–150 degrees.
Sequencing:
- The container with the seed is kept at room temperature for several days so that the rosehip seeds have time to swell.
- Then cover it with a tight lid or film. Place in the refrigerator on the bottom shelf with vegetables.
- In this form, the seed for cultivation is kept for one to three months (if necessary, longer), until planting as seedlings or in open ground.
- During storage, the soil must be monitored and periodically sprayed with a sprayer.
If possible, it is better to arrange a two-stage stratification for growing plants. At the first stage, planting material is kept in soil or sand for four months (from late August to late December) at a temperature of 12–15 degrees. On the second – another four months (from the first days of January to the last ten days of April) in the refrigerator at a temperature of +3–5°C. It is under such conditions that maximum germination is observed.
Attention! Seeds of wild rose hips can be sown directly into the soil (at the end of August), where they will undergo natural stratification.
The fruits are planted to a depth of 2 cm, and sawdust, straw, pine needles or other mulch are placed on top.
How to germinate rosehip seeds
Before sowing, rosehip seeds can be germinated. This is an optional but desirable step. In order for the grains to smoothly emerge from cool conditions and become active for growth, they are wrapped in a damp cloth and left in a bright room at room temperature (18–20 degrees Celsius). As soon as the sprouts hatch, they can be planted in an open bed (at the end of April) for further cultivation.
How to plant rose hips with seeds
To grow plants, choose an open, sunny place with fertile soil. The area is cleaned, dug up, and if necessary, fertilizer is applied (a bucket of compost or humus per 1–2 m2). To plant grains, proceed as follows:
- Carefully level the surface with a rake or other tool.

- Several shallow (up to 3 cm) grooves are formed at a distance of 5 cm from each other.

- Plant seeds to a depth of 2 cm at intervals of 5 cm.
- For the winter, mulch with sawdust, peat, straw or other mulch (in the case of autumn cultivation).
Aftercare
To successfully propagate rose hips by seeds at home, it is necessary to provide proper care:
- In early spring, the mulch is removed.
- They install a frame with film or agrofibre to provide a normal microclimate for the seedlings.
- Regularly water the plantings with warm, settled water. The soil should remain slightly moist - it should not dry out.
- Also, for normal cultivation, you need to pick the crops on time. As soon as the seedlings have 2 leaves, they are transferred to a permanent place.
- After the night temperature stops falling below 10–12 degrees Celsius, the film can be removed.

Picking is done in the early stages of cultivation, when each seedling has at least two leaves
In the first year of cultivation, it is not necessary to give fertilizers (if the soil is fertile enough). If the soil is depleted, you can apply urea or other nitrogen fertilizer, observing the dosage (15–20 g per 10 liters for watering 1 m2 of crops). It is also very important to keep the soil moist during the first stage of growing. To do this, you need to water regularly and also use mulch, which will protect the soil from drying out and temperature changes.
Important! Despite the fact that rose hips are a frost-resistant plant, seedlings are carefully prepared for winter in the first 3–4 years of life.
For successful cultivation, plantings are mulched with sawdust, humus, and straw (layer height 5–10 cm). When the bushes grow up, they can be wrapped in agrofibre for the winter and dry leaves sprinkled inside.
Features of rosehip propagation by cuttings
Rose hips can be propagated by cuttings, which is most often carried out in summer or spring. This is the easiest way to propagate a crop. It guarantees complete survival of the cuttings. The procedure is carried out in late May-early June, when the shoots turn green. During this period, summer residents make biological preparations in the form of apical rosehip branches, the length of which is 8-10 cm. The cut on it should not be more than 4 cm. When cutting the shoot, it is necessary to remove the lower leaf plate.
Expert opinion
Stanislav Pavlovich
Gardener with 17 years of experience and our expert
Ask a Question
Note! Growing cuttings occurs in water, which is enriched with stimulating solutions. Summer residents advise using the drugs “Kornevin” or “Emistin” for the development of the shoot.
The sprout is placed in a vessel with water so that it stands 6-7 cm deep. It is better to keep the cuttings in a sunny place where there is room temperature. Summer residents will also need to monitor the microflora of the liquid so that pathogenic microorganisms do not begin to multiply in it. The stimulating solution will need to be changed periodically. When small shoots appear at the cut site, the plant will need to be transplanted into the ground. treated with peat. When the root system is formed, the crop can be transplanted to an open area.
If, after growing in water, the rosehip root immediately becomes stronger, then you can skip the step of planting it in a pot and immediately place the plant outside. The soil will first need to be treated with mineral fertilizers based on nitrogen, potassium or phosphorus. Cuttings should be planted at a distance of at least 50 cm. During the first time after transplantation, gardeners will need to regularly water the crop. When autumn comes, the amount of watering can be reduced by 2 times.
See also What fertilizers can be used to feed blueberries
When and how to collect seeds for sowing
To grow a rosehip bush, it is important to know the timing and rules for collecting rosehip seeds. The material must be harvested from unripe berries - as soon as they begin to turn red. The timing may vary depending on the characteristics of the variety and the climate of the region. In some cases it is the end of July or the beginning of August, in others it is the last days of summer.

Seeds for cultivation are collected from those fruits that have just begun to ripen
All grains must be thoroughly washed and cleared of pulp. They are then laid in a single layer in a ventilated area and dried for several days. The grains can be sent for stratification for subsequent planting in the spring or sown in a garden bed to overwinter in natural conditions.
Important! Planting material should not be stored without soil, even in the refrigerator.
The grains are immediately planted in fertile, light soil or in calcined sand: otherwise they may not germinate next spring. Those. The sooner you start stratification, the better.
Caring for rosehip sprouts
The first rosehip shoots look like small strawberry leaves. When they appear, it is time to take care of the soil moisture. For the first month, rose hips should grow in moist soil. The soil should not be allowed to dry out, which will lead to the inevitable death of the plant.

Basically, caring for shrubs is not particularly different from caring for roses. Likewise, it is necessary to regularly loosen the soil so that the root system can breathe. You also need to apply fertilizer. For example, you can dilute urea in water in a ratio of 1 tbsp. l. for 5 l. water.
If the soil is highly acidic, then in the spring you need to add lime to improve the condition of the soil. It is also important to weed seedlings in time so that they do not take away useful microelements from the ground. Weeds can greatly obscure the sprouts. Then the rosehip will stretch out and will not have the proper strength.
Young seedlings may develop pests that need to be eliminated as quickly as possible. The most common are:
They love young rose hips because the stem is soft and juicy. If pests are not eliminated immediately, they will destroy valuable seedlings in a matter of days. Organophosphorus preparations should be used against sawflies. To scare away leaf-eating caterpillars, you need to spray young leaves with a decoction of wormwood (boil 1 kg of wormwood in three liters of water for 15 minutes. Dilute the infusion to 10 liters and spray the tops). Gentle preparations that can be purchased at a plant protection store can help against aphids.
Propagation by seeds
- This method is inexpensive and simple, but time-consuming. The downside is that with such propagation the characteristics of the mother bush are lost. But such a splitting of characters is observed only in some varieties, and this allows this method to be used in most cases.
- The seeds of the plant germinate very poorly, since they have a hard shell, and the embryos are located deep inside the seed. Germination requires a fairly long stratification, but even so, seedlings appear only in the second or third year.
- It is important that the seeds are in the right condition. If they are overripe or ripe, then stratification does not work. Experienced plant growers recommend collecting immature, yellowish seed material for propagation. This material is of sufficient quality and can be used for germination. Almost half of the seeds will sprout.

Stratification
This process is mandatory and necessary for the seeds to wake up and then sprout. You can purchase ready-made seeds, or you can prepare them yourself.
- If you purchase seed material in a store, it should be placed in light, fertile soil for several days. The seeds should swell.
- Cover the pot with film or a lid and put it in a cool place, maybe in the refrigerator. The stratification process can last from 3 to 4 months or more.
- There is another way: seeds, which were previously removed from the fruit, are placed in a container with pre-calcined moistened sand and covered with film or a piece of glass. The mini-greenhouse is sent to a cold place for long-term stratification. Periodically, in both cases, the film or glass is removed, the soil is moistened and the soil is ventilated.
- Watering should be done only by rain, so that the seeds are not washed deep into the ground.
Step-by-step guide to growing plants outdoors
When can you plant - autumn or spring?
Rose hips are planted both in the spring, before the beginning of the growing season, and in the autumn.
. For planting, one-year and two-year-old seedlings are used. Planting steps include:
Determining a landing site
When choosing a location, you should take into account not only the aesthetic appearance of the garden plot, but also the needs of the plant for its normal development and productivity. To do this, plant the bushes in a well-lit place with fertile soil.
.
The ideal soil for it is loam and slightly acidic soil. It is not recommended to plant the plant in wetlands where groundwater is close.
Preparing the soil before planting a bush
The main requirements for the soil are thorough cleaning of weeds and accumulation of nutrients. The soil in the selected area needs to be dug up to 20 cm.
Then dig holes for planting, the width and height of which should be half a meter. At the bottom of the depression, make a small hill of fertile soil.
How to plant ornamental shrubs correctly
In order for the bush to take root well, you need to cut off its roots by a couple of centimeters, while their length should be at least 25 cm. Before planting, immerse the seedlings in a mash of peat and manure
. Water the planting holes well with water.
Then lower the seedlings, straighten the roots and carefully sprinkle with soil so that no voids form. Then compact the soil around the young bush, water it and mulch it with peat.
It is important that the distance between bushes varies from 60 to 120 cm
.
In order for the bush to take root well, you need to trim its roots - their length should be at least 25 cm
Subtleties of rosehip care
Rosehip is not a capricious plant, but if you want the bushes of the crop to delight you with high yields and beautiful views, then you need to make an effort.
Optimal watering
The plant has a high level of drought resistance and does not require constant watering. The bushes need sufficient nourishment from periodic rains. But if the weather is dry and hot, which lasts for several weeks in a row, then one watering per month will be enough.

During the season, you can water the plant 3-4 times. For one time you need 3 buckets of water. The volume of water can be increased for a fruit-bearing bush.
Fertilizer selection
Particular attention should be paid to young bushes. It is during the period of bush formation that it is necessary to fertilize. You can start the procedure from the second year after planting.
The plant needs to be fed with nitrogen fertilizers 3 times a year:
- For the first time - in early spring.
- The second time - in the summer during the period of active growth of shoots.
- The last time was in September.
Next, organic matter is sufficient as fertilizer (3 kg of humus or compost for a bush). You need to fertilize once every 2 years. Do not forget about loosening the soil after fertilizing. Afterwards, it is recommended to sprinkle the area around the trunk with sawdust or humus.

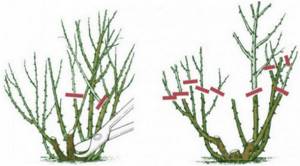
Trimming
The first thinning of the bush should be carried out 2–3 years after planting. The optimal number of branches on a bush for good yield is 15–20. The branches should be no older than 7 years, otherwise they will be of no use - with age they begin to bear fruit poorly. It is good if the bush consists of branches of different ages.
Old and weak shoots are pruned in the spring. It is not recommended to carry out the procedure in the fall, since the plant may not survive the winter period due to fresh cuts on the bush. This is especially true for regions with harsh winters. When pruning rose hips, it is important not to turn the procedure into shortening the bush. This can lead to an increase in growth, which will not bring any benefit.
Pest and disease control
Rosehip is a fairly vulnerable plant to disease.
More often, bushes are affected by the following diseases:
- powdery mildew;
- rust;
- gray, brown, black and dark purple leaf spotting;
- stem cancer.

To protect the bushes, the following measures must be taken:
- regular inspection of the plant and identification of the first signs of disease;
- pruning affected branches;
- regular cleaning of fallen leaves and shoots;
- if the disease has spread widely throughout the bush, it is necessary to spray with fungicides.
Pests affecting the crop:
- aphid;
- mole;
- mites;
- scale insects;
- moths.

Homemade tinctures can be used to combat insects.
For example:
- tobacco tincture - 200 g of tobacco per 10 liters of water;
- tincture with garlic - 200 g of garlic per 1 liter of water;
- wormwood decoction - 1 kg of wormwood per 3 liters of water (boil for 15 minutes, then dilute with water - 10 liters).

To combat caterpillars, you can smear the branches of the bush with kerosene or machine oil. Timely leaf removal and pruning can also protect rose hips from unwanted pests.
Preparing for winter
Rosehip is frost-resistant, so it does not require special attention before the onset of winter. But tree trunk protection will never be superfluous. You can insulate this place using mulching materials - straw, fallen tree leaves. In regions with harsh winters, the bush can be wrapped in burlap.











