Actinidia is a member of the genus of woody vines and part of the actinidia family. In the wild, such a plant can be found in Southeast Asia, the Himalayas and the Far East. This genus includes approximately 70 species. Almost every person knows a fruit of this species, the delicious sea anemone - this is kiwi. This liana comes from China, but its fruits appeared in Europe only in 1958. The name of this liana was derived from the Greek word, which translates as “archer”. Today, in temperate latitudes, species are cultivated that are related to the sea anemone, but their fruits, as a rule, are not very large and less shaggy when compared with kiwi. Among the cultivated species cultivated by gardeners, the leader is Actinidia kolomikta: this garden actinidia is highly resistant to frost. Actinidia acute (arguta) is the largest species of this genus; the height of such a vine can reach up to 30 meters.
Features of actinidia
Actinidia is a deciduous vine that is a perennial. The leaf blades are entire, in some cases they are leathery, but sometimes they are also thin. Actinidia is highly decorative due to its variegated foliage, since such plants can be seen quite rarely in mid-latitudes. The shoots and stems of such a vine need support. The scars of the leaf blades contain buds. The flowers are mostly solitary, but can also form small groups of three; they are collected in the leaf axils. Quite often, actinidia have white corollas, but in some species their color is yellow with a golden tint or orange. The flowers of most species are fragrant, but in some species they have a pleasant smell, for example, polygamous actinidia.
What are the differences between female actinidia and male actinidia?

This dioecious plant has both male and female specimens. You can find out which sex of the actinidia you have grown when it blooms for the first time; this is determined by the structure of its flowers. But what are the differences between a male specimen and a female one? The flower of a male plant has a large number of stamens, but there is no pistil. The flowers of a female plant have a pistil in the central part, which is surrounded by stamens that have sterile pollen that is not capable of pollination. Pollen gets to female specimens from male specimens with the help of bees, bumblebees and wind. It is on the shoots of the current year that buds appear, and they are located in the leaf axils. The plant blooms for about a week and a half, then the female specimens develop ovaries, which eventually form into pale orange or greenish-yellow fruits. Since such a vine is dioecious, to obtain fruits, it is necessary that at least two copies are grown in the garden, so that they will have the opportunity to cross-pollinate. The fruits of such a vine are quite a valuable dietary and food product; they contain a large amount of ascorbic acid, sugars and other biologically active substances. Such fruits are eaten fresh, and are also used to make drinks, jam, wine, and are also dried. The dried fruits of this plant are similar to very large raisins. Over the past few decades, the popularity of actinidia among gardeners has grown significantly and therefore it is quite possible that after some time it will be as widespread a crop as strawberries, currants or raspberries.
How to plant actinidia correctly. Actinidia care
Description and features
Actinidia is a perennial vine that has entire leaves. The plant is highly decorative because the foliage is variegated in color. The stems and branches of the crop need support. Flowers can be solitary or collected in groups. The corolla is usually white, but yellow or orange flowers are also found.
Male flowers
A characteristic feature of the plant is the absence of a pistil against the background of a large number of stamens.
Female flowers
Such flowers, in addition to stamens with pollen, which do not participate in pollination, contain a large pistil in the center.
Planting actinidia in open ground

What time to plant
It is necessary to plant actinidia in open soil at the beginning of spring or autumn. To do this, you need to purchase a bush from the nursery, the age of which will be from 2 to 4 years. The planting site must be chosen with special care, because with proper care, such a plant can grow in one place and bear fruit for more than 30 years. But this is only if the gardener strictly adheres to the rules of agricultural technology for a given crop. This liana is shade-loving, but it requires sunlight to ripen the fruits. In this regard, the best place for planting it will be a sunny area, which will be in the shade in the afternoon. Actinidia has an extremely negative attitude towards proximity to an apple tree, but it can be planted next to currants. This vine cannot be grown on clay soil. The soil should be moist, loose, well-drained and non-alkaline. If the groundwater is shallow, then to plant this vine you will need to make a hill of soil. It is very good if the site is located on a slope or on a hill, since there the liquid does not stagnate in the root system, but flows down itself. It should also be taken into account that this plant requires mandatory support, for example, it could be a fence or the wall of a building, but it is best to use a special trellis for actinidia. Using this design, you can form a plant, for example, in the shape of an arch; the point is that the fruits are located in the upper part of the crown, and therefore, when grown near a building, they will have to be collected from its roof.
Spring planting

Planting should be done in the first weeks of spring before sap flow begins. If you are planting actinidia agruta, you should keep in mind that this is a fairly large vine, and therefore a distance of 150–200 centimeters should be maintained between plants. When planting actinidia kolomikta, a distance of about 100 centimeters is left between the specimens. If this vine is used as decoration for the wall of a building, then it must be planted at a distance of 50 centimeters, and organic matter must be added to the prepared trench. Before proceeding with the actual planting, the seedling will need to be prepared. To do this, it is necessary to remove all dried and injured branches and roots; the root system should be immersed in a clay mash before planting. The planting pit is prepared half a month before the planting day. Its size should be 0.5x0.5x0.5 m, at the bottom a layer of pebbles, broken bricks or small pebbles should be made for drainage. Please note that the use of building crushed stone is prohibited, since it contains lime, which is so unloved by this plant. After this, the pit must be filled with nutritious soil mixed with peat (humus or compost), and 250 grams of superphosphate, 120 grams of ammonium nitrate and 35 grams of potassium sulfate or wood ash must be added to it. You cannot add fertilizers to the soil that contain chlorine, for example, potassium chloride, as this may cause actinidia to die. After 14 days, the soil in the hole will settle, and you will need to make a hill in it from simple garden soil. The seedling is placed on this hill so that its root collar is flush with the soil surface. Then the hole must be gradually filled with earth, which should be well compacted. The planted actinidia needs to be watered abundantly; for this, 20–30 liters of water are taken per bush. The surface of the tree trunk must be covered with a layer of mulch (compost), the thickness of which should be 40–50 mm. Until the seedling takes root, it must be protected from direct rays of the sun; for this it is recommended to cover it with cloth or paper. Cats simply love the smell of actinidia, and therefore the vine must be protected from them. To do this, it is necessary to dig a metal mesh around the plant to a depth of five centimeters, the height of which should be at least 50 centimeters.
Autumn planting
In autumn, the vine is planted in open ground 15–20 days before the first frost, and only seedlings no older than 2–3 years should be used, otherwise the plant will not be able to survive the first wintering, as it will take a long time to take root. It is necessary to plant actinidia in open ground in the autumn in the same way as in the spring.
HOW TO PLANT ACTINIDIA. Growing actinidia. How to grow actinidia.
Which support is suitable?

This vine does not have aerial roots, so it is not capable of harming the structure. In this regard, it can be safely planted near the walls of buildings, using them as a support. It is very often used to decorate gazebos. If there is no support, the plants will become tangled, which makes caring for them much more difficult, and the number of fruits may be reduced. Experienced gardeners choose classic forms of pergolas and arches, which can be metal, wood or concrete, as supports. Also, galvanized wire can be stretched between two concrete posts that are not very high, and in this case 3 or 4 rows are made according to the principle of a grape trellis, this will allow the actinidia to grow horizontally. As the shoots grow, they should be tied to a trellis. In regions with cold winters, removable trellises are often used. They are made from a metal angle, it is inserted into pipes that should be dug into the ground. Before frosts begin, such a trellis should be pulled out of the pipes and carefully placed on the surface of the area, while there is no need to remove the vine from it, but it must be well covered. In spring, such trellises return to their usual place.
3. Planting and care
When growing actinidia as an ornamental foliage plant, it is enough to place several male vines; to obtain fruits, it is worthwhile to plant one male vine for every 3 - 4 females. For some varieties, the presence of plants of the opposite sex is not required - this information should be clarified with the seller.
Lianas with male flowers have brighter leaf colors; many modern varieties have been bred from them, serving as garden decorations.
↑ Up,

To grow kiwi, it is better to choose a well-lit location - if there is a lack of light, the leaves of ornamental varieties will fade, and the flowering of fruit-bearing vines will become scarce or not occur at all. Fruit ripening in insufficient lighting occurs at a later date; in some cases, the berries will remain unripe.
Actinidia loves warmth and when grown in the conditions of the Middle Zone, it is better to place the plants on the south side of buildings and structures. Having heated up in the sun during the day, the walls will give off heat to the vine at night. Sunlight should reach the site in the first half of the day. Most vines will like it if the base is in lacy shade, and the top can receive enough sunlight. Actinidia loves high air humidity.
It is interesting that this species does not tolerate close proximity to apple trees; such “neighbors” as currants and many legumes have a positive effect on the condition of the plants.
Flooded areas and areas with shallow groundwater are not suitable for growing vines. If there is no other place, then plants are planted on the top of some hill.
Since the vine attracts the attention of cats with its smell, it should be surrounded with a small fence. The fact is that cats can sharpen their claws on the trunk of plants and they can die, bleeding juice.
↑ Up,

3.1.How and when to plant a vine
Planting in the garden is carried out in spring or autumn, and planting holes should be made ahead of time - in the fall or a couple of weeks before planting the vine. The fact is that during this period the walls and bottom of the hole will become dense and will allow plants to be placed at the required depth, without subsidence of the soil.
In the case of autumn planting, plants should have the opportunity to adapt to open ground before the onset of frost. For spring planting, it is worth using the time when the snow cover has just melted, and the plants have not yet begun to flow sap. Saplings with an open root system should only have swollen buds, but not unfolded leaves.
↑ Up,

Plants that are 2-3 years old are suitable for planting. Younger specimens are still too weak and may die, and adult plants can hardly tolerate transplantation. It takes too much time for a large bush to adapt its root system.
Plants purchased from a store with a closed root system can be planted in a container for a long period from spring to autumn.
The distance between the holes when planting several specimens should be about 1.5 - 2 m - the vine develops quickly and fills the free space. If you need to get a dense decorative wall, then the distance between the holes is reduced to 50 - 90 cm.
The width and depth of the planting holes should be about 50 - 60 cm so that the seedling fits along with the root system.
If the soil is too dense, then a drainage layer in the form of river pebbles or ordinary broken brick is placed at the bottom of the planting holes - it will allow moisture to be quickly removed from the roots. The height of the drainage layer can be 10 - 12 cm. Crushed stone cannot be added to the hole - its alkaline reaction will not suit the vine.
↑ Up,

A nutrient layer is placed on the drainage, which should contain a sufficient amount of well-rotted organic matter and mineral complex fertilizers. Plants respond well to the addition of wood ash. Plants do not like fertilizers containing chlorine.
Planting methods will be different for bare-root plants and potted seedlings. If the vine’s root system is closed, then the bushes are simply transferred to the planting holes along with the root ball. In order for the soil to move well away from the walls of the pot, the plants are watered abundantly a day before planting. When planting, you should pay attention to the fact that the root collar of the plant should remain flush with the soil surface.
If the seedlings were purchased with bare roots, then it is possible to assess the condition of the root system - cut off old and rotten branches with sharp pruners, leaving only healthy tissue.
A clay mash is prepared for plants - rooting preparations and a little potassium permanganate are diluted in water. Clay is added to the water, bringing the solution to the consistency of liquid sour cream. The root system is lowered into the finished mash and the plants are kept in this way for 2 - 3 hours.
↑ Up,

At this time, small earthen mounds are made at the bottom of the planting holes. The seedlings are lowered into the holes, straightening the roots, lowering them down and installing bushes on the top of the mounds. Plants are sprinkled with soil without deepening the root collar.
After filling the holes, the soil is carefully compacted to remove possible air pockets. The bushes are watered abundantly with settled or rain water - at least 20 liters of water per plant.
The bases of the vines are mulched with straw, sawdust or pieces of tree bark. During the week, the plants are shaded, protected from direct sunlight. Water the vine for another 3 to 4 weeks so that the soil never dries out.
↑ Up,

3.2.Soil for shrubs
Actinidia prefers neutral or acidic soils with sufficient nutrients. The soil should easily allow moisture to pass through after watering, and also allow the root system to breathe, absorbing oxygen.
You should not plant bushes in heavy loams with high density. Such lands retain water after watering or rain, which leads to rot in the root system. River sand is mixed into such soil - it makes the soil looser and prevents it from caking.
For additional nutrition, it is worth adding leaf and turf humus to the soil, as well as, if possible, well-rotted horse or cow manure.
↑ Up,

3.3.Growing in open ground
Of course, the tall stems of actinidia will need support. Without support, long shoots become tangled and flowering and fruiting suffer. The height of such plants often does not exceed 1.5 - 2 meters.
It is not necessary to arrange special trellises for the vines - the stems can perfectly shade and decorate the wall of a gazebo or veranda. It is interesting that actinidia always wraps around the supports counterclockwise. The trellises should be no more than 10 cm in diameter, otherwise the plant will not climb along them.
↑ Up,

It is better to place fruit-bearing plants on special arches about 2.5 - 3 meters high. This is due to the fact that the most abundant flowering and formation of berries occurs closer to the top and their collection will be difficult. When grown on a garden arch, the fruits will fall down on their own as they ripen.
Trellis for grapes with horizontally stretched wire are also well suited for such plants. On such a wire shoots are launched at a height of 50, 100 and 150 cm above ground level horizontally.
Plants in the garden will also need proper pruning, timely watering and fertilizing. After each watering, the ground around the vine is loosened and weeds are removed, and the layer of mulch is renewed. This liana cannot tolerate drying out of the soil - in such conditions, not only can you get fruit, but you can’t even expect flowers and buds.
↑ Up,

3.4.Pruning and formation of actinidia
For the onset of abundant flowering and the formation of berries, the plants will need competent formative and sanitary pruning.
The bushes are trimmed for the first time at the age of 4 - 5 years; in the first 1 - 2 years, the planted plants are allowed to develop at their own discretion. There are sanitary, rejuvenating and formative pruning.
↑ Up,

During sanitary pruning, all old, dying or frost-damaged branches are removed, and shoots directed into the crown are also removed. When the flowers are very thick, fewer flowers are formed, since the strong branches remain in the shade; in such conditions, fungal diseases often appear.
Sanitary haircuts are carried out from early spring to autumn, as needed. In the spring, frozen shoots are removed in early spring, as soon as it becomes clear which branches did not survive the winter.
Actinidia are often formed in the same way as grapes, and this pruning is carried out in the fall. Spring and summer pruning can cause serious harm - during this period there is active sap flow and damage to large trunks leads to weakening of plants. In the first year after pruning, only 2 strong shoots of the first order are left, which are directed along the trellis in different directions. The next year, several of the strongest branches of the second order are left on the shoots, which will bear fruit.
At the end of summer, it is worth removing the unripe tops of the vines - this will allow the remaining part to ripen faster and be overgrown with tree bark, which protects from frost. During this pruning, from 1/3 to half the height of the shoots is removed.
Every 5 - 7 years, a rejuvenating radical pruning is carried out, during which old branches that are 8 to 10 years old are cut off, leaving only 30 - 40 cm of growth from the surface of the earth. For such shoots, replacement young branches are prepared.
↑ Up,

The stumps remaining after pruning must be treated with garden varnish. Pruning is carried out with a sharpened and sterilized garden tool - a knife or pruning shears. You should not prune plants during the period of active sap flow - they can die, bleeding juices.
Grafted plants require special pruning - all stems appearing on the rootstock should be removed, otherwise within a few years they will completely replace the grafted part and the plant will go wild.
↑ Up,

3.5.Feeding and watering
When growing in the garden, it is enough to fertilize 2 - 3 times per season. As fertilizers I use both organic substances - manure or humus, and ready-made mineral compositions.
For the first time, you can apply mineral fertilizers in early spring by simply scattering granules directly on the snow. At this time, you can apply nitrogen compounds to help the plants form sufficient green mass. Organic matter can also be placed on the snow, but care must be taken to ensure that the fertilizer does not touch the plants themselves.
The second feeding is carried out with the appearance of the first buds - potassium-phosphorus mixtures are added.
↑ Up,

As a third top dressing, it is worth using potassium fertilizers, which strengthen the root system and help plants survive the winter in open ground. Carry out the third feeding after fruiting.
You cannot feed plants with fresh organic matter - such fertilizers weaken them and are susceptible to many fungal diseases.
Water actinidia in the morning or evening. Moisture on leaves during the day can cause sunburn. When watering, add 40-50 liters of water to each adult plant so that the moisture penetrates deep to the roots.
For irrigation, always use warm water - rain or well-settled tap water. When the soil dries out, the bushes begin to shed their leaves, the leaves are restored late and often die from the onset of night frosts.
↑ Up,

3.6.Transplant
It is not recommended to change the location of adult plants unless absolutely necessary - with age, they form a fairly large root system and replanting is difficult for them. You should immediately choose a permanent place for the bushes.
If it is still necessary to move the plant, then it is worth minimally damaging the roots and keeping the earthen lump at the base of the vine undestroyed.
Transplantation is carried out in the spring, before flowering. For planting, prepare holes of sufficient depth and width that can accommodate actinidia along with the root system.
↑ Up,

In order to carefully move the vine, prepare a piece of plastic film, which is spread near the bush. The plant is dug in a circle, gradually going deeper under the roots. The dug up specimens are placed on film and transferred to a new location.
After planting, the flower is watered generously with warm water. Transplanted plants should not be exposed to direct sun for 5 to 7 days.
The soil at the foot of such vines should remain moist, but not swampy, for a month. About what the plant. managed to take root in a new place, one can judge by the new shoots and leaves that appeared.
↑ Up,

3.7. Care in autumn, preparation for winter
Actinidia kolomikta has the best frost resistance - these are the plants that can most often be found in central Russia.
Young plants do not have proper winter hardiness and will need shelter for the first 2 to 3 years. Adult vines overwinter in the middle zone without additional shelter.
In order to prepare plants for winter, in October - November the shoots are removed from the trellis or laid on the surface of the ground along with the structure, if it is collapsible. The plants are covered with a layer of dry leaves on top or covered with cut spruce branches at least 20 cm thick. The cover is removed in early spring, as soon as the snow cover melts in the given area.
You can use a small frame made of mesh - chain-link or a special garden plastic mesh - as a shelter. Plant shoots are tied and surrounded with a net, the entire internal volume of which is filled with dry leaves. From above, such a shelter is additionally wrapped with non-woven material.
↑ Up,

Actinidia care

During the growing season, actinidia must be watered in a timely manner, weeds must be removed, pruned, fed, and the health of the vine must be monitored and, if necessary, treated for diseases or pests destroyed. At the same time, any type of actinidia must be cared for in the same way. It is recommended to moisten such a plant in the morning and evening by spraying; this procedure is especially important in hot weather. During prolonged drought, the vine begins to shed its foliage. To prevent this, the soil should be moistened once a week, with 60 to 80 liters of water poured under 1 bush. If all the leaves of the vine do fall off, then the young leaf plates that appear in their place will not be able to get stronger before frost and will freeze. The surface of the soil near the bushes should be loosened quite often, but not to a very great depth. While loosening the soil, weeding is also done.
Fertilizer
If you feed the plant with mineral fertilizers, this will lead to an increase in frost resistance and an increase in the yield of the vine, and the growth of young shoots will also be activated. At the very beginning of the spring period, for every 1 square meter of soil, 20 grams of potassium and phosphorus and 35 grams of nitrogen fertilizers must be applied. The plant should be fed the second time during the formation of the ovaries; for this, 10–12 grams of potassium and phosphorus and 15–20 grams of nitrogen fertilizers should be added for each 1 square meter. When all the fruits have been collected (around mid-September), the vine needs to be fed again. To do this, 20 grams of phosphorus and potassium fertilizer should be added for every 1 square meter. Fertilizers are purchased in granules, which should be distributed over the site and buried 10–12 centimeters into the soil. Once this is done, water the actinidia generously.
Actinidia pruning

If you care for the plant correctly, this leads to stimulation of stem growth, and the buds also begin to awaken. Very often the result is a strong thickening of the crown. If the crown is excessively thick, this will negatively affect the frost resistance and productivity of the plant. Therefore, it is very important to carry out formative pruning in a timely manner, but only plants that have reached 3–4 years old can be subjected to it. The plant needs to be trimmed during the summer, and those branches that remain should be distributed along the trellis, pointing them in the direction you need. In order for the wood to ripen better by winter, it is necessary to pinch the tips of the shoots, which will slow down their growth. If the trellis is horizontal, then a two-arm cordon is made from the stems; for this, it is necessary to direct 2 stems, located at the same level and in the same plane, in opposite directions and fix them in this position; the remaining shoots of this level must be removed. Next year, second-order stems will grow on these horizontal branches, and ovaries will form on them. These shoots should be tied to a vertical guide; as they grow, they themselves will begin to curl around it. To replace old skeletal branches, you will need rejuvenating pruning; it is needed for plants that are 8–10 years old. After such pruning, only a stump should remain from the actinidia, the height of which should be from 0.3 to 0.4 m. You cannot prune the vine at the beginning of the spring and at the beginning of the autumn, the fact is that at this time the actinidia has a very strong sap flow, and if damaged, it can leak juice, which will lead to its death.
Actinidia pruning part 1
After harvesting the fruits

When the vine is 3 or 4 years old, its first fruits appear, but it begins to produce good harvests from the age of seven until old age. Thus, actinidia can bear fruit for 40 years or even longer. If you care for the plant correctly, you can collect about 60 kilograms of fruit from one specimen per season. The fruits do not ripen at the same time, but they do not fall from the bushes for a long time. Fruit harvesting begins in mid-August, and in some cases the harvest ends only in mid-September. When the vine is freed from fruits, it needs feeding, which will allow the plant to survive the winter normally.
Care in autumn and winter

Young seedlings that have been growing in the garden for no more than 2 or 3 years must be removed from the support and well covered using spruce branches, peat or fallen leaves. The thickness of the covering layer should not be less than 20 centimeters, while experienced gardeners advise placing rodent poison under it. The mice do not touch the stems, but they make their nests in them. In April, cover should be removed from young bushes. Adult actinidia are subjected to sanitary pruning from the middle to the end of September, while their stems are cut by ½ or 1/3 of their length, and all branches that contribute to thickening of the crown must also be cut out. Mature vines do not need to be covered for the winter.
SHELTER OF ACTINIDIA FOR WINTER.
How actinidia is pruned: cultivation and care
The main indicator of the rooting of the sprout of such a vine is the active germination of branches in the first year of the plant’s life. Basic care consists of frequent watering and periodic loosening of the soil.
Cats like this sprout. For this reason, the planted seedling must be protected from cats for about a couple of years. To do this, you can use a chain-link mesh that can be wrapped around the stem of the plant.
Depending on the type of vine, a bush can be created in different varieties.
For example:
- Forming a bush in a fan form. This formation can be achieved using 5 seedlings, which are evenly distributed on the surface. In order to obtain such a formation, it is necessary to pinch such a plant at 70 cm in August. Such plants are used for 3 years, and after that they need to be changed.
- Formation of a two-armed bush. In this case, vertical shoots are created. Such sleeves bear fruit for about 20 years and only after 20 years do they need to be changed.
As for pruning, it is carried out at the end of autumn or after the snow melts.
Only frozen and damaged branches are removed.
Reproduction of actinidia
There is nothing complicated in propagating actinidia, especially since the gender and varietal characteristics of the parent plant are inherited, but only if you propagate it vegetatively. When growing from seeds, you will not be able to determine what gender the seedling is, and in this case the seedlings rarely inherit the varietal characteristics of the mother plant. However, it should be taken into account that plants grown from seeds are distinguished by higher endurance, but they, as a rule, begin to bear fruit only at the age of seven. Moreover, those actinidia that were grown using the vegetative method produce their first fruits at the age of three or four.
Reproduction of actinidia by arc layering

It is very easy to propagate such a vine using arc layering. In the spring, after the end of sap flow and the blossoming of young foliage, it is necessary to find a well-developed and sufficiently long growth shoot; its top should be bent to the surface of the earth and fixed in this position. In the place where the shoot is pinned to the ground, it should be sprinkled with soil, and the layer thickness should be from 10 to 15 centimeters, then the resulting mound should be well watered and covered with a layer of mulch (sawdust or humus). It should be taken into account that the top of the stem must remain free. Provide the shoot with timely weeding and watering, while the young shoot that has grown from it should be systematically moistened with a sprayer. By autumn, the cuttings should take root and can be planted in a permanent place. You can also transplant the cuttings next spring.
Actinidia. Choosing a reproduction method
Actinidia propagation by cuttings

Actinidia can be propagated by green cuttings. With this method of propagation, you can quickly and easily obtain many seedlings. Cuttings are harvested in June, at which time the fruits grow very quickly, and the stems begin to become woody and change their green color to brown. You need to select several annual strong branches that reach 50–100 centimeters in length; they need to be cut off from morning to lunch. The ends of the cut stems should be placed in a container with water, this will prevent the branches from withering. Then the shoots should be cut into several cuttings, the length of each of them should be from 10 to 15 centimeters. Remember that each segment must contain 2 internodes and 3 buds. The top cut should be straight, and it should be located 40–50 mm above the top bud. The cut at the bottom should be made at an angle of 45 degrees, and it is made directly under the lower bud. The lower leaf plates and their petioles must be carefully removed, while those plates located on top are shortened by ½ part. The prepared cuttings need to be planted in a greenhouse or greenhouse, while the bed is made in advance and watered well. The soil should be slightly acidic or neutral; river sand and humus (2:1:2) should be added to it, as well as complex mineral fertilizer, which does not contain chlorine (100 grams of substance per 1 square meter). The cuttings are planted at an angle of about 60 degrees, the row spacing should be 10 centimeters, and a distance of 5 centimeters should be maintained between the plants. The cutting must be buried in such a way that its middle bud is flush with the surface of the substrate. The soil surface around the planted sections must be compacted. Then they are watered, and when the water is completely absorbed into the ground, its surface is covered with gauze rolled up in 2 layers. Before the cuttings sprout roots, they need to be very well moistened with water from a spray bottle 2–5 times a day directly through gauze. If the weather is rainy, then the gauze can be removed from the cuttings, and this is done in the morning and evening. Half a month after landing, the shelter is removed for good. For wintering, the cuttings need to be covered with dried leaves. In early spring, before the buds open, the rooted cuttings must be dug up and planted in a permanent place.
Important tips about Actinidia kolomikta
Reproduction of actinidia by lignified cuttings

Lignified cuttings are harvested in late autumn. They are tied into bundles, which are placed vertically in a box filled with sand. There they will be stored until spring. To store cuttings, a temperature of 1–5 degrees is required. The preparation of such cuttings can be done in the last weeks of winter, and it must be done before the sap begins to flow. The cuttings are planted in a greenhouse or greenhouse; they need to be watered once every two days. Next, they need to be cared for in the same way as green cuttings.
Combined cuttings are also suitable for rooting. In the first weeks of summer, it will be necessary to cut off the growing stem of the current year with the heel (part of the annual branch adjacent to it). Such cuttings should be planted in a greenhouse or in a garden bed. They must be protected from direct sunlight and provided with daily watering. In this kind of cuttings, rooting occurs quite quickly, and therefore already next year they can be planted in a permanent place.
Actinidia propagation by seeds

Seeds must be extracted from ripe fruits that have not been damaged. They should be kneaded, and the resulting mass should be placed in a mesh bag. It is thoroughly washed under running water, after which the remaining seeds in the bag are laid out on a paper sheet. To dry, they are placed in a shaded place. Preparing seeds for planting should begin in the first ten days of December. To do this, they are placed in a shallow container, into which water is poured so that it rises 20 mm above the seeds. Soaking the seeds will last 4 days, and the water must be systematically replaced with fresh water. After this, the seeds need to be poured into a nylon stocking, which is placed in a box filled with damp sand. The container with seeds should be placed in a place where the temperature will remain between 18–20 degrees. Once every 7 days the stocking must be removed from the sand. Allow the seeds to air, just a few minutes will be enough, then they should be rinsed under running water directly in the stocking. After this, they must again be placed in a container with damp sand. Be careful not to let the seeds dry out. In January, this box, along with the seeds and sand in it, should be wrapped in cloth, and then it is buried in a very deep snowdrift. The seeds will stay there for 8 weeks. If there are no deep snowdrifts on the street, the seeds along with the box will need to be placed on the vegetable shelf of the refrigerator. They will stay there for 8 weeks, then the box is taken out and put away in a place where the air temperature fluctuates between 10–12 degrees. Remember that seeds should not be placed in heat, as after cold they may go into a dormant period. After stratification, seeds should continue to be washed once a week and ventilated. After several seeds have hatched, you can start sowing them. To do this, use containers filled with turf soil mixed with river sand, and they need to be buried only 5 mm into the substrate. Emerging seedlings need regular spraying from a spray bottle, and they also need to be protected from direct sunlight. After the seedlings have 3 or 4 true leaf blades, they are planted in a greenhouse; as a rule, this time occurs in mid-June. The first flowers of such plants will appear at the age of three to five, then it will be possible to transplant them to a permanent place after determining the sex.
Reproduction methods
Actinidia is propagated in the usual and familiar ways: by seeds, cuttings, dividing the bush, layering.
Cuttings
Reproduction is carried out in different ways: rooting with lignified or green cuttings.
The order of planting green cuttings:
- Dig grooves 50 cm deep.
- Lay drainage from broken red brick or crushed stone.
- Pour a base layer of sand and high-moor peat with the addition of a small amount of humus.
- Add a rooting layer consisting of sand, perlite and peat.
- The cut cuttings are planted to a depth of 3 centimeters.
- The soil is compacted and watered abundantly.
- Cover the bed with film to create a greenhouse effect.
- After the roots have formed (20 days), the plant is transplanted into a bed with an interval of up to 40 cm from each other.
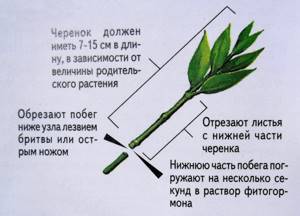
Actinidia is transplanted to a permanent place after 2-3 years.
For propagation, you can use annual woody cuttings, which are harvested in the fall. Store planting material in the basement, refrigerator, or instilled in an unheated greenhouse.
In April, they are planted in the ground under cover at a distance of 40 cm from each other. The first year actinidia grows in a “school”; the vine is planted in a permanent place the following spring.
Seeds
Growing a plant from seeds until the first harvest can take up to 4 years - this is the longest propagation method.
Seeds must be prepared before planting: kept in the refrigerator for two months and in a cool room two weeks before planting.

When the actinidia seeds have sprouted, you can plant them
Sowing is carried out according to a 2x2 cm pattern, to a depth of no more than 0.5 cm. The container is covered with film until sprouts appear. Two true leaves are a signal to dive into separate containers or a spacious box.
In the first year, actinidia is grown indoors or buried in the ground, protected from domestic animals. The plant spends the second and third years in school. Weak shoots are discarded.
Planting in a permanent place is carried out in the 3rd – 4th year of cultivation.
Dividing the bush
The plant can be propagated by division. The old bush is dug up in the spring before the buds swell and carefully divided into 2-3 parts. Each division should have well-developed roots and 1-2 formed vines.

In autumn, division of actinidia is carried out no later than a month before the onset of frost.
Layerings
In spring, the annual vine is pressed to the ground and covered with soil. As it grows, add a mound of earth to a height of 15 cm.
The liana remains in this state for 2 growing seasons. In the autumn of the second year of cultivation, the young plant is separated from the parent bush and transplanted to a permanent place.
Graft
Grafting is used to produce varietal plants. The operation is carried out in the spring and no later than mid-June. Plant buds or annual cuttings. The method is labor-intensive and not always successful.

Pests and diseases of actinidia

Diseases
Actinidia has very high resistance to diseases and pests. If you properly care for the plant and do not forget about the rules of agricultural technology when growing it, then such problems may not arise with it at all. In some cases, such a vine can become infected with a fungal disease, which causes spots to appear on its foliage, for example, phyllosticosis, powdery mildew, etc. Actinidia is also susceptible to infection with diseases such as gray and green mold, and fruit rot, while actinidia arguta suffers from them somewhat more often. Cut off all infected parts of the vine (leaf blades, stems, fruits); for preventive purposes, it is recommended to spray the plant with a solution of Bordeaux mixture (1%), when the buds appear, the second treatment is carried out half a month after the first. In order to get rid of powdery mildew, you need to spray the plant with a solution of soda ash (0.5%), and it is treated a second time 1.5 weeks after the first spraying.
Pests
At the very beginning of the growing season, the swollen actinidia buds can be damaged by leaf beetles. When the larvae of these insects appear, they will begin to devour the leaf plates, of which only veins will remain. Less commonly, caterpillars of the raisin moth settle on the vine; they gnaw large holes in the foliage. Bark beetles and lacewings can also settle on such a plant. Therefore, it is very important in the spring to carry out preventive spraying of actinidia and the surface of the area around it with Bordeaux mixture; this will help destroy overwintered pests and pathogens. In the fall, the same treatment should also be carried out with the same agent in order to destroy pathogenic microorganisms and pests that have settled in for the winter.
Actinidia or Arctic kiwi
Actinidia: varieties
Actinidia: video about growing vines
Small-fruited varieties are considered easier to grow. The fruits of these varieties are very similar to gooseberries. Actinidia is used not only as a fruit plant; thanks to its attractive appearance, this vine is widely used in landscape design. There are many varieties of actinidia.
- Actinidia Arguta belongs to the tall vines. As it grows, it wraps around the tree trunk and rises higher and higher. From the crown of one tree it can move to another. The actinidia variety Arguta has fruits with a pineapple aroma.
- Actinidia Giraldi can grow up to 25 meters in height. It grows quickly and is often used to landscape all kinds of structures. The fruits of this Actinidia variety are relatively large.
- Actinidia Kolomikta is most suitable for the climate of the central zone of our country. Compared to other varieties, this is a relatively low vine, up to 7 meters high. The fruits of the Actinidia variety Kolomikta are small, only about 2 centimeters, and they have a pleasant smell.
Polygamous actinidia is the shortest, up to only 5 meters in height. The fruits of this variety are similar to the fruits of kolomikta, but until they ripen, they have a sharp, burning taste.
Actinidia varieties with photos and descriptions
There are a large number of species of actinidia in the wild, but only 3 of them are cultivated by gardeners: actinidia kolomikta, arguta and purpurea. They also grow interspecific actinidia polygamous, Giralda and hybrid. A large number of different varieties of these subspecies and species are also cultivated. Below will be a detailed description of them.
Actinidia arguta

Of all the cultivated species, this is considered the most powerful. In the wild, it can be found in the Far East, and the height of such a vine can vary from 25 to 30 meters. The trunk reaches 15–18 centimeters in diameter. The pointed, ovoid-shaped leaf plates reach 15 centimeters in length and have a finely toothed edge. This dioecious plant is decorated with fragrant white flowers, reaching a diameter of 20 mm; they can be collected in racemes or single. The dark green, spherical fruits can be eaten; they have a slight laxative effect. The diameter of the fruits reaches 15–30 mm, while they weigh about 5–6 grams. Fruit ripening occurs in the last days of September. Popular varieties:

- Self-fertile . This frost-resistant variety ripens relatively late, because its fruiting period begins from mid to late September. Rich green, elongated, cylindrical, fragrant fruits weigh 18 grams. From one bush they harvest from 10 to 12 kilograms of fruit.
- Primorskaya . This self-fertile variety requires male plants. Resistance to frost is average, and resistance to pests and diseases is high. Soft, smooth green leaf plates are of medium size. The fruits are elliptical in shape, olive in color, weigh 6.6–8.3 grams, the pulp is very tender, covered with thin skin, it has an apple smell and high taste.
- Large-fruited . This dioecious variety is resistant to drought and frost. Medium ripening fruits. They have an elliptical shape, dark green color with blush, weigh 10–18 grams, and reach 2 centimeters in length. The pulp is slightly aromatic and has a honey taste.
In addition to these varieties, gardeners often grow such varieties as: actinidia Estafeta, Mikhneevskaya, Ilona, Zolotaya Kosa, Vera, Sentyabrskaya, Lunnaya, etc.
Actinidia kolomikta

This plant is very frost resistant. Its height can be 5–10 m. The trunk reaches two centimeters in diameter. The ovoid leaf plates can reach 7–16 centimeters in length, they have a sharply serrated edge, and the veins have light red pubescence. The petioles are painted pale red. In male actinidia, the leaf blades have a variegated color, namely, in July, the upper part of the leaf blade turns white, then light pink, and then deep crimson. In autumn, the foliage also looks very impressive, as it turns purple-red and pink-yellow. This liana is dioecious. Fragrant white flowers on male specimens are collected in racemose inflorescences of 3–5 pieces, and on female specimens they are single. The length of the green fruits is from 20 to 25 mm, they can be eaten; in the sun they may appear bronze or light red. The fruits begin to ripen in August. Popular varieties:

- Pineapple . This dioecious plant, characterized by rapid growth, is one of the most productive varieties. The length of the oval fruits is about 30 mm, they are green in color and have a red side. The pulp is very tasty with a pineapple flavor.
- Doctor Szymanowski . This variegated plant of medium fruiting period is winter-hardy. Green fruits reach 25 mm in length and weigh about 3 g. The pulp is tender, sweet-sour taste with a pineapple-apple smell.
- Gourmet . This medium-ripening variety was born relatively recently. The length of large fruits can reach 3.2 cm, while they weigh 4–5.5 grams. The taste is sweet and sour pineapple.
Also popular among gardeners are varieties such as actinidia Moma, Narodnaya, Waffle, Priusadbnaya, Prazdnichnaya, Slastena, etc.
Actinidia polygama

The trunk diameter of such a plant is about 20 mm, it reaches a height of 4–5 m. It is externally similar to Actinidia kolomikta. The elliptical, oblong leaf blades are pointed towards the apex and have a serrated edge. On the surface of the green plates there are specks of silver color; in autumn, the color of the foliage changes to yellow. White fragrant flowers are usually solitary and dioecious, but they are also bisexual. The fruits weigh about 3 grams and can be eaten. Popular varieties:

- Apricot . The late ripening variety has moderate resistance to frost, and high resistance to diseases and pests. Such a plant is self-sterile (male specimens are required). The fruits are flattened on both sides, they reach 35 mm in length and weigh 6 grams. The sweet-sour pulp has a balsam smell.
- Gorgeous . This variety is highly resistant to diseases, pests and frost. The green-yellow fruits have a strong odor and weigh up to 3.5 grams. The pulp is slightly sour.
- Patterned . This variety is late. The elongated cylindrical orange fruits have longitudinal stripes on the surface that are barely visible. The smell and taste are peppery and fig.
Actinidia giraldii

Some scientists believe that this plant is a variety of Actinidia arguta, but its fruits are much larger and sweeter. In the wild, this species is extremely rare, so it is listed in the Red Book. Therefore, if you decide to cultivate this vine on your site, you will help preserve this rare species. Popular varieties:
- Juliana . Late variety. The fruits are green, laterally compressed, weigh 10–15 grams. The smell of the pulp is pineapple-apple, it is sweet.
- Alevtina . The green, barrel-shaped fruit is laterally compressed and weighs 12–20 grams. The sweet pulp has a pineapple-apple-strawberry smell.
- Native . This variety is late. The short, barrel-shaped fruits are laterally compressed and weigh 7–10 grams. The pulp has a strong pineapple smell.
Actinidia purpurea

The birthplace of this tree-like powerful dioecious plant is China. This liana is shade-loving, and it is distinguished by lush flowering and abundant fruiting. The large sweet fruits are purple in color and ripen in the last days of September. This species has only one drawback - low resistance to frost. At the moment, only the Purpurnaya Sadovaya variety is available: dark burgundy oval-shaped fruits reach 25 mm in length and weigh 5.5 grams, the smell of sweet pulp is delicate marmalade.
Actinidia hybrid
This subspecies was born thanks to the breeder I.M. Shaitan from Kyiv. It was he who crossed actinidia purpurea and arguta. The result of this was the emergence of completely new varieties with high resistance to frost and very large fruits, which is characteristic of Actinidia arguta, as well as with the taste, smell and bouquet type of flowering and fruiting of Actinidia purpurea. After some time, specialist Kolbasina continued the works of Shaitan. Popular varieties:
- Kievskaya Large-fruited . This is a late variety. Green, large, oval-shaped fruits weigh about 10 grams. Their tender flesh is very sweet.
- Candy _ This variety is late. The oval-shaped fruits are green in color and weigh about 8 grams. The sweet pulp has a fruity caramel aroma.
- Souvenir . The color of the fruits is red-green, they weigh about 8 grams. The sweet pulp has a candy-fig-fruit aroma.
Every year the following varieties of this subspecies become more and more popular: actinidia Hybridnaya Sausage and actinidia Hybridnaya-10.
Actinidia - Actinidia - types, varieties, use - part 1
Characteristics and types
This perennial plant belongs to the genus of woody vines that shed their foliage in winter. It is the leaves, changing their color several times during the season, that give it an extraordinary decorative effect. The flowers of the vine are snow-white and not very large in size. Later they turn into yellow-green or orange fruits. Actinidia is a dioecious crop, therefore, in order to produce fruits, male and female specimens must grow on the site.
There are 75 species of this vine in the world. The most famous species is Actinidia deliciosa or kiwi, which is grown in New Zealand, Italy, Greece and Chile. In other species, the fruits are smaller and not always tasty, so they are used more for decorative purposes. Their habitats are Southeast Asia, the Himalayas and the Far East. Previously, it was believed that actinidia could not grow in a temperate climate, but in fact there are several species of this perennial that successfully winter and develop in central Russia . These include:
- Actinidia kolomikta. The most winter-hardy species, the length of which can reach from 5 to 10 meters. Edible green fruits begin to ripen on this dioecious plant in August. Their length is 2−2.5 cm. This type is most decorative. Its leaves are initially white-green, then they turn pink, and then acquire a crimson hue. In autumn they turn yellow-pink and red-violet, which is no less beautiful.
- Actinidia arguta. A very powerful dioecious plant, reaching as much as 25-30 meters in length. Its flowers have a pleasant aroma, and the fruits, whose diameter is 1.5-3 cm, can be eaten.
- Actinidia polygamum. This is a rather rare self-fertile species. Its flowers are distinguished by their ability to self-pollinate, and ripe fruits are bright orange in color and very pleasant to the taste. The length of the vine is 4-5 meters, it is distinguished by high productivity and a long lifespan.
- Actinidia Giraldi. It is similar in appearance to argut, but its fruits are larger and sweeter.
- Actinidia large-fruited. It was bred by crossing species of argut and purple actinidia. The result was a fairly winter-hardy species, suitable for growing in central Russia.
Properties of actinidia

The composition of a fully ripened actinidia fruit includes fiber, starch, carotene, sugars, pectin substances, vitamins, mineral salts, phenol carbonic and organic acids, nitrogen-containing compounds, saponins, alkaloids and other substances that the human body needs. They contain vitamin C, and there is much more of it than in lemons, oranges and black currants. These fruits also contain vitamins A and P, and their seeds contain a large amount of fatty oils.
Experts advise eating such fruits for diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, anemia, pulmonary diseases (including tuberculosis), rheumatism, vitamin deficiency, gonorrhea, scurvy, lumbago, colitis and caries.
Other parts of the vine are not without healing properties. For example, the bark contains cardiac glycosides and tannins, due to which it has a sedative, tonic, expectorant and hemostatic effect.
Actinidia is often used for belching, heartburn and other problems with the digestive system; it also has a mild laxative effect and improves the digestion of meat.
Based on this plant, the drug “Polygamol” was developed; it has a general strengthening property, it is also able to support cardiac activity and increase diuresis. For angina pectoris, actinidia tincture is used. Infusion and decoction prepared from the roots are used externally for radiculitis, painful joints and gout. The peel and juice of the berries improve appetite and have a wound-healing effect.
This plant is also used in the treatment of colds, bleeding, and also in getting rid of parasites. An ointment is made from the berries, which is used after bone fractures, and also for massages.
Contraindications

Any new product or drug should be used with caution. Actinidia has no special contraindications. However, those who suffer from varicose veins, thrombophlebitis, and also people with high blood clotting should avoid eating its berries. If you eat a lot of such fruits, it can cause the development of intestinal disorders.
Healthy recipes

There are many very useful recipes with actinidia, for example:
- Infusion of fruits . Dried fruits should be placed in a container with water. They are cooked over low heat for 60 minutes. The cooled infusion must be strained. The infusion is consumed after meals in small portions; it helps prevent cancer.
- Ointment made from berries , which has a restorative effect. Fresh berries must be ground very well. They are combined with crushed mustard seeds and a fatty base (for example, you can take lard). This ointment is used after fractures and during massage.
- Bark decoction . 20 grams of bark must be crushed very well. Then it is combined with 1 tbsp. just boiled water and keep in a water bath for 30 minutes. The cooled infusion must be strained. If metabolic processes in the body are disrupted, drink this infusion 2 or 3 large spoons 3 times a day.
- Infusion of flowers and foliage . Take 20 grams of crushed leaf blades and flowers. The mixture must be combined with 1 tbsp. just boiled water, then keep it in a water bath for a quarter of an hour. The cooled infusion must be strained. You need to drink the infusion 3 times a day, 1/3 tbsp. for angina and rheumatism.
Actinidia pureed with sugar is a source of vitamin C for the whole winter
Actinidia: description of the bush

Actinidia plant: photo of a bush
Actinidia is a perennial deciduous vine. It has green heart-shaped leaves. In some species of actinidia, the tips of the leaves are painted white, which makes them noticeably more beautiful. In April, the actinidia vine blooms. Its flowers are white with a soft pink tint; most of them are odorless, but there are varieties whose flowers have a pleasant aroma.
Actinidia fruits are edible. They are small in size, oblong in shape, sometimes covered with fluff. The pulp of actinidia fruits is juicy, sweet and sour in taste, with a pleasant aroma. There are varieties of actinidia, the fruits of which have the aroma of strawberry or pineapple. Actinidia fruits are eaten fresh, jam, compotes, wine are prepared from them, and they are dried. When dried, they are very reminiscent of raisins.
Actinidia fruits are very useful. They contain a lot of vitamin C; in terms of its content, they can compete with rose hips, black currants and citrus fruits. Actinidia bark, leaves and flowers have healing properties and are used to treat many diseases.











