There are different opinions on the question of when to start planting seedlings in the ground.
Some rely on personal experience or advice from older relatives; for others, a good example is neighbors who receive an excellent harvest year after year. As for specialists, their numerous disputes do not subside, since everyone has their own point of view. But if we summarize the various opinions, it turns out that for most of the territory of Russia, spring is the best period for planting “young trees” of almost all fruit trees.
The fact is that the peculiarity of our climate is such that many seedlings planted in the fall do not have time to “take root” well. One of the reasons is that it takes at least 2 months for the plant to independently extract moisture from the soil with all the substances necessary for full development.
Unfortunately, early frosts do not allow this time. The result is “freezing” or drying out of the “young animals”. Therefore, the recommendation for autumn planting of seedlings has many opponents.
Let's take a closer look at the procedure for spring planting fruit tree seedlings in the country house or in the garden of your home.
Site layout
Some landing features must also be taken into account in cases where the territory has already been developed. The principle of “where there is free space” does not apply here. What to consider:
Type of seedlings. Each plant is characterized by a certain height, characteristics of the crown and root system. If you do not take into account the specifics of development, then there is a possibility that the trees will subsequently “interfere” with each other. For example, taller ones will shade short ones that grow intensively sideways and will be intertwined with branches.
Compatibility. Gardeners who do not have sufficient experience do not take this factor into account. But there are special tables with recommendations on which plants can be planted nearby and which ones should not be planted. At any summer cottage (and this is what we are talking about, since a professional doesn’t need tips), in addition to fruit trees, there are also beds with their own plantings, and various shrubs (fruit, ornamental).
Place in the garden. If there are any buildings on the territory or it is shaded by something (for example, other trees growing on the adjacent one), then it is advisable to place the seedlings so that they are illuminated by direct rays most of the day.
Deadlines by region
The decisive factor in choosing the timing is the climate of the area. You need to familiarize yourself with preliminary forecasts in advance in order to roughly plan planting work and prepare planting material.
Related article:
Pruning cherries using the Stop Leader system
Bare-rooted seedlings should be planted immediately after purchase. You can delay planting a little if you place the tree in the shade and sprinkle the roots with soil. For plants with a closed root system, the planting period lasts longer, since the roots are in the ground and their adaptation is faster. Such trees can be planted in late spring and even early summer, if it is not very hot.

Region and planting period:
- southern regions – March-April;
- Moscow and the region , middle zone - from mid-April to mid-May;
- Siberia, the Urals, St. Petersburg and the north of the Leningrad region - from the third ten days of April to the third ten days of May.
When planning, you need to take into account that it is not recommended to plant or replant on the days of the full and new moon.
Preparation of "planting" holes
Since we are talking about the spring planting of tree seedlings, then it is necessary to prepare the place in advance, in the fall (although this is not necessary). In this case, it is necessary to take into account the characteristics of the soil. Depending on this, the sizes of the holes are selected. There are various recommendations. For example, if the soil is soft and fertile, then the side of the conventional “cube” of the hole is about 70 cm. On loams and sandstones it increases to 1 m.
You need to understand the meaning of landing. In black soil, the hole does not have to be wide and deep. The roots of the plant will “find their way” themselves, and the soil is already a nutrient medium. If the soil is “depleted,” then enriched soil will have to be poured into the hole, so its dimensions should be larger.
During the work process, the earth is “stored”, for which the top layer of the excavated soil (fertile) is placed separately from the “inner” one, since the latter will have to be “fed” (mixed with compost, humus).
A separate conversation concerns areas where underground water layers come close to the surface (read about how to determine the groundwater level). The plant should not be buried on them, otherwise there is a risk of root rotting. In such cases, compost is used, a mixture of soil with peat or black soil, which is poured in a heap.
The bottom of the hole “softens”. To do this, it is dug up with a shovel at least half the length of the bayonet.
And most importantly! Planting immediately is not recommended. The hole should “settle” and erode for at least 10 – 12 days.
How to save planting material
Since it is not always possible to purchase planting material at the time of planting, it is purchased in advance. The question of safety also arises when the weather did not allow landing on time. In order for the seedlings to remain viable and be able to take root successfully, they need to create proper storage conditions. There are several ways.
Prikop for frost-resistant breeds
This storage method is chosen for winter-hardy tree species and varieties. It allows you to create conditions such that the plant does not take root and does not freeze. To do this, in an area without stagnant moisture, in a vegetable bed after harvesting, or at the site of a future planting hole, dig a trench, directing it from east to west. The length and width depend on the size and number of plants, the depth is 0.5-0.7 m. The wall of the northern edge is dug at a right angle, and the southern edge - with a slight slope.
Related article:
Popular types and varieties of juniper
Before this, the seedlings are soaked for 4-5 hours, having first removed all the leaves. Then they inspect the roots, cut off damaged and dry areas, remove growths, and tie the branches if there are many of them. Each tree is placed with its roots facing north and its top on a flat edge. This location protects from cold northern winds. If there are a lot of seedlings, you can lay them in two rows. The roots are straightened and covered with a 20-centimeter layer of sand or peat.
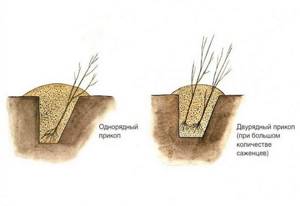
The plants fall asleep completely after frost - a mound is formed on top. In winter, you can pour snow on it and put spruce branches. With the arrival of warmer weather, the mound is removed, and the entire trench is dug up in April. There is no need to cover it with film or slate - awakening may occur earlier, which will lead to a decrease in immunity.
Related article:
Figs – Crimean black and Abkhazian purple
If there are few seedlings, then instead of digging, you can use a simpler option - after soaking, they are placed in any container, the roots are covered with damp soil and stored in a cool room at 0-5 ° C. Seedlings in a coma of earth, after removing the leaves, can be stored in the basement, in a cool room at the same temperature.
Planting a seedling
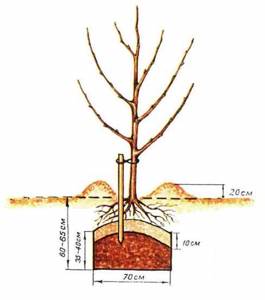
First, a support is installed at the bottom of the hole, after which water is poured. After it is absorbed into the soil, a mixture of earth with humus or something else (this has already been said) is poured in with the expectation that a tubercle will form. The seedling (with straightened roots) is placed on this mound, its base is sprinkled and lightly pressed, after which it is spilled with water. This work is carried out in several stages: a layer of soil - light compaction - watering.
It is necessary to take into account that the root collar should be flush with the surface after the soil “subsides”. Therefore, when installing a plant in a hole, it rises above the ground by about 50 mm.
After planting is completed, the hole around the perimeter is surrounded by a bank of earth so that the sides of such a unique bowl are formed. In this case, during subsequent waterings, water will not spread over the area.
Time
Anyone, even someone who is not a specialist in the field of plant growing, has heard about the so-called “lunar cycles”. Every year special calendars go on sale, aimed primarily at people who are involved in one way or another in caring for plantings, be it beds on the site or house flowers on the windowsill.

They contain all the necessary information (lunar days, phases, zodiac signs in which the “heavenly Goddess” is currently located) and recommendations for planting various types of plants depending on these factors. Similar information can be found in almost any “tear-off” calendar.
It is not worth working with seedlings on any free day. The correct choice of planting time will determine how the seedling will “take root” and develop, and what kind of harvest can subsequently be expected. These rules should not be neglected, especially since these are laws of nature, and all of them have been tested many times in practice. For example, it is best to plant trees in the ground before the full moon. Anyone who really wants his work to have the desired effect needs to be guided by data from the lunar calendar.
But that is not all. For example, several days a month are suitable for planting seedlings. Which to choose? Here you should also ask about the weather forecast or just look out the window (if the event is planned for today). The best weather is calm, and when the sky is “covered” with clouds. Seedlings (especially the root system) are easily exposed to external influences (scorching rays, gusts of wind), and this must be taken into account.
There is one more rule. You need to “pick it up” so that the shoots have not yet started to grow, but the soil has already thawed. At this time, if all the above conditions coincide, you can begin planting.
How to plant a pear
The vast majority of pear varieties do not require any special care or soil composition. However, pear seedlings adapt and grow much better on humus-rich soils, loose soils, and well-lit areas. Drought is contraindicated for young plants. In the first years of planting fruit seedlings, it is necessary to provide abundant and frequent watering. The pear tree begins to bear fruit at the age of 3–8 years.
Active hybridization of species has led to the fact that a fairly diverse number of unusual species have now been bred. Among the most popular varieties, it is worth noting such as “Lada”, “Nectarnaya”, “Cathedral”, “Allegro”, “Dibrovskaya”.
Purchase of seedlings
To ensure that the tree will develop well and bear fruit, you need to pay attention to the following points:
- “young trees” must be adapted to local conditions, so you should not buy imported trees;
- The best age for a seedling is considered to be 2 years;
- you should carefully inspect the barrel. There should be no mechanical damage, burns, or signs of disease;
- the root system has 4–5 branches, no less. Their optimal length is about 25 cm. If they look shrunken and break easily, then you should refuse the purchase.
How to care for seedlings

Watering vegetable seedlings
The soil in the container with seedlings should always remain barely moist - neither the soil should dry out nor water should stagnate in it. To make it easier to maintain constant soil moisture, watering is carried out from a sprayer, and the container must be kept on a tray from which excess water is drained. The grown seedlings are watered with a watering can with a divider (shower nozzle), or even better, use the bottom method of moistening, watering into a tray - this stimulates the development of a branched root system in the seedlings.
Water for irrigation is taken settled or filtered, at room temperature, the plants are watered according to the principle “little by little, but often.”

Temperature for vegetable seedlings
According to the criterion of “heat requirements of seedlings,” vegetable crops are divided into three categories:
- cold-resistant, which prefer a lower temperature on average of about 13 ºC, that is, 14-18 ºC during the day and 6-10 ºC at night. These include all types of cabbage (kohlrabi and cauliflower prefer a temperature a couple of degrees higher);
- moderate plants that require 16-18 ºC during the day and 12-14 ºC at night - celery, onions and leeks, beets, lettuce, potatoes;
- plants that require heat, for which a comfortable daytime temperature is 20-24 ºC, and a night temperature is 10-16 ºC - eggplants, peppers, cucumbers, pumpkins, zucchini and squash, melons and watermelons, tomatoes, beans.
The temperature can be adjusted if you are using a greenhouse for seedlings. To do this, adjust the amount of sunlight falling on the plants, and also use ventilation. Seedlings grown at a constant and optimal temperature for the culture are distinguished by good health and subsequently higher productivity, while even a small and short-term decrease in temperature can lead to a delay in the growth of seedlings, and an increase in temperature causes the seedlings to elongate their stems and shrink their leaves.
Fertilizer for seedlings
With the first leaves, the plant runs out of nutrients from the seed, from this moment it is necessary to start adding seedling fertilizer to the mixture. The first fertilizer is especially important if you are using a sterile starting mixture (peat/perlite/vermiculite). Unlike potted plants, which can be given slow-release fertilizers, seedlings require a liquid and fast-absorbing fertilizer.
Seedlings are very sensitive to temperature, especially during fertilization. Cool soil reduces the absorption of nutrients by plants and inhibits the activity of beneficial bacteria in compost fertilizers. In order for fertilizing seedlings to be successful, it is necessary to apply fertilizer at room temperature or a little warmer.
The roots of seedlings are very delicate and sensitive to high concentrations of nitrates and minerals from the fertilizer, so it would be optimal to apply weaker solutions, but more often - once every 7-10 days.

Hardening of seedlings
You can begin hardening of seedlings and acclimatization from the appearance of the first leaves. Give the seedlings a small draft by simply passing your hand over the greenery several times a day. Open the window for several hours a day, move the trays into direct sunlight, starting with an hour a day. Adaptation of seedlings to open ground also includes cool nights and more moderate watering without heating the water. All this is carried out without fanaticism, only for healthy plants and taking into account their type - off-season cabbage, celery, lettuce, chard can withstand even short-term frost, and tomatoes, peppers, eggplants and cucumbers are very sensitive to low temperatures.










