How to fight weeds in the garden
In any garden, in addition to vegetables and berry crops, weeds actively grow - wild plants that take away water, nutrients and even sunlight from cultivated plantings.
Any weeds that appear must be destroyed. If you do not pay attention to them, then in a very short time the garden may become overgrown, and you will no longer be able to get a harvest. In general, methods for killing weeds can be divided into 2 categories:
- Chemical method. Cultivated plantings or soil prepared for them are treated with special solutions that prevent the growth of weeds. The good thing about this method is that no weeds appear on the site after treatment with herbicides. However, chemicals against weeds also have a disadvantage; most often, only “empty” land can be treated with chemicals, in which vegetables and other crops have not yet been planted.
- Mechanical method. In this case, weed control comes down mainly to weeding the soil - harmful plants that have emerged from the ground are pulled out by the roots, not allowing them to grow. The method is very reliable and allows you to destroy existing weeds, but it requires significant and constant effort, since the weeds grow back quickly and in large quantities.
You can also permanently destroy weeds by mulching and covering the beds. The greatest effect can be achieved by combining all of the above means, in which case the fight turns out to be purposeful and truly effective.
Precautionary measures
The use of weed control chemicals requires compliance with the following rules:
- Do not apply on windy days to avoid contact with garden crops.
- Keep the spray head close to the ground.
- Remember that herbicides need 6 hours to dry.
- Spraying should be carried out in dry weather, preferably a day before the rain starts.
- If there is light rain, add a soap solution - this will allow the chemicals to linger on the leaves.
- Do not work with unprotected hands.
During weed control, herbicides may come into contact with vegetables and fruits. Wash them thoroughly before eating.
Is the weed really that bad?
Even malicious weeds do not bother you as long as there are few of them. But as soon as they feel at ease, they begin to capture new territories. Not only free, but also occupied by other plants, crowding them and depriving them of nutrition. They kill growing seedlings and deprive tall plants of living space.
Malicious weeds are often more viable than cultivated plants.

The vitality of plantain is the envy of many plants.
They freeze less and can withstand heat and drought, so they often emerge victorious in the battle not only for a place in the sun, but also in the depths of the earth. Many plant lovers know that plants growing nearby have one effect or another on each other. Often the “fight” occurs at the root level, when various toxic compounds are used. Even grapes, which have their own “good” and “bad” neighbors, are susceptible. You can read about this in my article “Grapes: the pros and cons of joint planting with other plants.”
There are especially dangerous weeds, the proximity of which does not benefit many cultivated plants. These are ragweed, henbane, hemlock, speedwell, bitterweed, quinoa, ranunculus, dandelion, field sow thistle, bedstraw, creeping wheatgrass, fragrant chamomile, gooseberry, hellebore and wild rosemary.

"Green fire" or weed invasion
Weeds become carriers of diseases and “incubators” for pests. They rob us of the time we were supposed to have for rest. Even such a phrase, understandable to everyone, as “green fire” appeared.
Let's look at some of the most effective options for getting rid of malicious weeds.

Dandelions bloom on the lawn in May
Herbicide treatment
This is the fastest and most effective method, which gives excellent results, but has contraindications and requires great caution. The choice of drug depends on the type of uncontrolled growing plants
The agricultural market offers different types of pesticides, which are divided into several groups according to various characteristics.
Ability to move through plant tissues
System
When it gets on any part of the plant, the destructive substance quickly spreads both throughout its entire above-ground part and into the root system, which causes its complete death, including every leaf and every root.

Contact
In this case, the effect of the drug occurs only at the point of direct contact.
According to the spectrum of action
Continuous action
In this case, the drug destroys everything that is within the radius of its impact, including cultivated plantings and weeds. The use of such preparations is justified in the case when it is necessary to obtain an area completely cleared of vegetation, in which there will not be a single blade of grass.
Example - “Tornado”, “Antiburyan”. They can be useful when laying paths, laying paving slabs on a site, laying a reservoir, preparing land for a lawn.
Selective action
They are able to get rid of unwanted plants without causing harm to the planted ones. Effective for maintaining a smooth, well-groomed lawn. The product and its concentration can be selected individually depending on the type of weed, their strength and quantity.

The most popular are “Hurricane”, “Roundup”, “Agrokiller”, “Fusilade”, “Lapis Lazuli”, “Lintur”. The drug "Tornado" can also be used as a selective agent, but it should be remembered that it, along with the drug "Antikiller", is more powerful than others. They are recommended for use in the fight against the most stubborn and powerful weeds, such as horsetail, wheatgrass, all types of weeds, hogweed, plantain, and dandelion.
With the help of the drug "Agrokiller" you can even cope with thickets of bushes and trees to clear a neglected area.
Chemicals
They are divided into continuous and selective herbicides. By spraying an area with continuous herbicides, you will destroy all the plants that grow on it. It is important to understand that the most popular herbicides among summer residents act only when applied directly to the leaves and stems during the active growing season of plants. That is, they are useless to use on bare ground or in late autumn, when the plants are already in their pre-winter “half-asleep”.
Selective herbicides leave a certain group of plants, destroying all others (conditional and unconditional weeds). For example, when treating a lawn, such preparations are safe for cereal grasses (bluegrass, fescue, bentgrass) and deadly poisonous for unwanted “guests” of the lawn: dandelion, plantain or all kinds of umbelliferae. If you need to specifically destroy individual weeds in dense plantings, then it is best to use special strong-acting preparations. They are equipped with a brush with which you can apply them to the sheet plates. Of course, a weed “marked” with poison will not die immediately, but will fade away for several days as the drug takes effect.

Chemicals, electricity or weeding: which is more effective against weeds? More details
Chemicals and products

Herbicides are the most common chemicals used in weed control. Among their many types, there are selective drugs (they are dangerous for certain plants) and continuous action drugs (they destroy all plants in a row).
Chemical preparations with a selective effect should be used only in areas with plantings of one type of plant to which the preparation will not cause any harm. It will completely destroy only the weeds that grow around.
Chemicals with a general effect are capable of destroying all vegetation to which they are applied deliberately or accidentally.
It is very important to strictly adhere to the norms and dosages indicated in the instructions or on the packaging, and precautions when working with drugs (for example, using rubber gloves)
It is recommended to use chemical solutions only in dry and windless weather to avoid their spread to ornamental, vegetable or fruit and berry plantings, which will completely die after such treatment. Dry weather is necessary for the drug to fully carry out its chemical effect on plants, and its effectiveness is not reduced due to the ingress of water or raindrops. In order for the solution to penetrate all organs and parts of weed crops, it takes an average of 3-6 hours. At low concentrations the drug loses its effectiveness, and at high concentrations it increases several times.
Over a certain period of time after chemical treatment (from 5 to 30 days), gradual death of weeds may occur. During this period, it is not recommended to carry out any work on the treated area (for example, digging up soil or mowing grass). This control method allows you to destroy not only the above-ground part of harmful plants, but also most of their roots.
Once in the soil, herbicides do not accumulate in it, but break down into safe substances that can no longer harm the environment. Approximately five days after treating the beds, you can begin planting or sowing various crops. One of the main substances in chemical preparations is glyphosate. This substance does not have a negative effect on the germination of seeds or animals, but it poses a real threat to fish and insects.
Among gardeners and summer residents, the following products are considered the most common: “Glyphos”, “Tornado”, “Lapis Lazuli”, “Rap” and “Agrokiller”.
The advantages of these control methods are that they obtain excellent results in a very short time (from 3 to 6 hours) and for a long period, and the disadvantages are that the wrong choice of means or inaccurate dosage of the drug can destroy crops, as well as cause harm to animals and humans.
For those who do not welcome chemical treatment and are distrustful of such “harmful and dangerous” drugs, it is recommended to prepare your own homemade “chemical” remedy. A herbicide prepared with your own hands from improvised means available in almost every home is very effective and is capable of maximally destroying harmful weeds. It contains: 900 ml of water, 60 ml of vodka (or moonshine) and forty milliliters of liquid dishwashing detergent. If you treat weeds with such a solution in hot sunny weather, then vodka (or rather, alcohol) will destroy the protective waxy surface of the plants and they will die from dehydration under the influence of sunlight.
Weed control in the garden in autumn. Weed control in autumn - how effective is it?
- Useful tips
Fighting weeds in the fall is simply necessary. This time is especially suitable for the destruction of horse sorrel, wheatgrass or bindweed. And to achieve the best result, you should do this immediately after harvesting from the beds.
Don't pull out small weeds!
Don't pull out very fine grass, otherwise you might miss a lot. Give the weeds a chance to sprout and grow properly. Do not forget that weed killers only affect their greenery. Excellent chemical preparations against unwanted plants are Roundup, Hurricane, Utal, Tornado.
Note! Before spraying weeds, there is no need to cultivate the soil; even loosening should be avoided. All this is due to the fact that you can hit the roots with a shovel, and the chemical will be less accessible to the plants. Accordingly, weed control is considered unsatisfactory.
What is the best day to start removing weeds?
To control weeds in the fall, it is better to choose a dry and windless day. Naturally, in this season there are not so many of these days, so try to at least make sure that there will be no rain in your area after treatment for at least 2-3 hours.
The drug concentration standards must be calculated strictly individually; all instructions are written on the packaging. Please note that the effect of the drug decreases sharply even at a temperature of +10 degrees. So it is better to treat the soil against weeds in September or October. As soon as the root system of the plant turns brown, the area should be dug up and the still living roots should be pulled out.
Use a second try
If you used few chemical weed killers or held the event before it rained, then you weren’t able to deal with the annoying grass the first time. You must wait until the plants grow a little again and gain strength and then treat them with drugs.
What to do in the spring with an area that has been treated with chemicals
In the spring, you will be able to grow any crops in this area without any problems, do not worry - all the harmful components will have time to evaporate. If you decide to get rid of weeds in a densely saturated area, then all the roots of the grass will not have time to rot before spring, so you can grow crops on this soil only if you first feed the soil with fertilizers.
When are chemicals not effective?
Let's look at the effect of drugs using Roundup as an example. It cannot help you in the fight against annual weeds. These include chamomile, shirita, pikulnik, etc. By destroying all weeds in the fall, you will not ensure a spring without this weed, since their seeds are contained in the top arable layer of soil. Often these uninvited guests are dealt with manually. It is very tedious and lengthy, but effective.
Continuous action herbicides against weeds
The word "herbicide" is translated from Latin as "killing grass." These are drugs that have a suppressive effect on plants we don’t need. These chemicals are toxic to the environment. Therefore, it is better to use them in extreme cases and in areas where cultivated plants do not grow.
What are herbicides - classification
According to the mechanism of action, drugs are divided into 2 groups.
- Continuous action, when all types of plants are killed upon contact with the drug. They are better suited for continuous processing in vacant lots, near fences;
- Selective action - destroys certain types of weeds without affecting neighboring plantings.
Contact herbicides act only on the above-ground part of the plant, while continuous herbicides penetrate into the plant and gradually affect the leaves, stem and root system.
The effect of using continuous action drugs may not be noticed immediately, but within 7-10 days. So, 1-2 days after their use, the leaves first turn pale, then they dry out, the stem also dries out, and lastly the roots die.

Advantages and disadvantages of chemical weed killers
The advantages of using herbicides on the site are:
- High efficiency;
- Convenience and speed of use;
- Large selection and affordable price;
- The ability to simultaneously get rid of harmful insects and rodents.
But there are also disadvantages, among them:
In case of accidental contact with cultivated plants, they also die; The soil microflora is disturbed; The drugs are toxic; if precautions are not followed, there is a risk of poisoning. Therefore, precautions must always be taken when working with herbicides.

Means for killing weeds and plant roots
Continuous action herbicides with the active ingredient glyphosate include the following:
- Roundup is a systemic herbicide with continuous action; when used, all plants are killed without showing any selectivity. Price for 50 ml 280 rub. The bottle should be diluted in 3 liters of water.
- Agrokiller – when used once in recommended dosages, does not cause a significant deterioration of soil microflora. The cost of a 40 ml bottle is 130 rubles. The drug is diluted at the rate of 30-40 ml per 3 liters of water.
- Tornado - successfully used to exterminate annual and perennial weeds. The product is sold in a spray bottle, which is convenient for use, as well as in 50 ml bottles costing 90 rubles each, which is dissolved in 3 liters of water.
- Ground is one of the strong herbicides with continuous action. Sold in bottles of 50 and 100 ml, the cost is 75 rubles, respectively. and 130 rub. For treatment, 60 ml of the drug is diluted in 10 liters of water.
- Hurricane - quickly decomposes in the soil, is safe for honey insects, and does not have a negative effect on the soil. The cost of a 50 ml bottle is 120 rubles, the product consumption is 75-100 ml per bucket of water.
- Lapis lazuli is a selective herbicide, the safest of all herbicides. Available in powder form, in sachets of 20 g. The active substance is metribuzin, an aqueous solution is used to exterminate weeds
Prices may vary depending on the manufacturer, as well as the region of sale, which may have its own markup and trade markup. Although the products presented can be found at a lower price on the Internet.
How to apply herbicides
Herbicides are very effective weed killers. However, when using them, it is necessary to take into account some points.
Different dosages are used to treat different areas, for different weeds, this should be remembered, so before diluting the drugs, carefully read the instructions for use. Areas with weeds should be sprayed in dry, windless weather 5-6 hours before the expected rain, or after rain or watering after the plants have dried.
All herbicides are highly poisonous, so when working with them, take precautions and wear protective clothing.
Agrochemistry
Herbicides
This is one of the most effective methods of weed control today. Herbicides are ideal if the field is heavily overgrown or if there is a large area to be treated. These drugs are divided, in turn, into several types: continuous and selective action, systemic, contact and soil type. Let's look at the most popular herbicides used in agriculture today.
Roundup
This is probably the most popular herbicide today. Its advantage is safety: Roundup does not harm the soil or livestock. Cultivated plants can be planted immediately after treating the soil with this herbicide.
Roundup is effective against most weeds: they are defeated within 8-10 days. Over the designated period of time, the weeds die completely, withering. The principle of action of the herbicide is aimed at suppressing the synthesis of amino acids in weeds.
Tornado
This product is most often used to destroy weeds in orchards and vineyards. Tornado is effective against both annual weeds and perennials.
This is a continuous action product, so it is important that no cultivated plants get in its way.

The product causes the death of weeds 7-10 days after spraying.
Instructions for using Tornado can be found at this link.
Hurricane
This herbicide effectively controls annual and perennial weeds. It is good for developing new land plots and cultivating the soil around greenhouses. Great for killing weeds on the lawn.
Completely destroys weeds 2-3 weeks after spraying. The composition acts on the plant from the inside, gradually bringing it to complete withering. Hurricane can be used throughout the growing season: from early spring to late autumn.
We recommend that you read the instructions for the Hurricane product in this material.
Glyphos
Another reliable weed killer. Glyphos is safe because it destroys weeds by affecting the synthesis of their amino acids. A positive effect is observed when destroying both perennial and annual weeds.
Saltpeter
A chemical such as ammonium nitrate is highly effective against weeds. It is recommended to use the product only if the weeds have really grown greatly. This method is good because ammonium nitrate burns the grown weeds, while itself settling in the soil, and then acting on cultivated plants as a fertilizer.

In order for the substance to cope with weeds, it is necessary to dilute 3 kg of saltpeter in a bucket of water, and then spray the weed thickets with the resulting solution.
Methods of fighting with folk remedies are described in this article.
The chemical method helps when the mechanical method is powerless: in case the area is heavily overgrown with weeds, or when no other methods help. It is effective to apply herbicides simultaneously with the application of fertilizers. But this method can only be used for small areas of the garden. If during the herbicide treatment the substance gets into empty areas, then the latter can be sown only after a few weeks.
Traditional methods of weed control
There are several ways to control weeds in the traditional way:
- Preventive, based on a thorough check of planting material to select seeds and roots of weeds.
- Biological, implying the inclusion of living organisms in the process.
- Cultural, using the natural properties of cultivated plants.
- Drip irrigation.
- A mechanical method consisting in manual or mechanized removal of weeds from the cultivated land area.
- Mulching, where the soil is covered with polyethylene or plastic to prevent light from reaching it, resulting in the reduction of unwanted vegetation.
- Chemical, in which the soil is treated with a special preparation that selectively affects growing plants.
Weeding
Weeding
Although labor-intensive, weeding is the easiest and most reliable way to remove weeds. The disadvantage of the method is the need to regularly repeat the procedure, which makes the person caring for the garden constantly tied to it.
Weeding can be done in several ways:
- hoe;
- with a pitchfork;
- mechanized equipment.
After weeding, it is important to collect all the plucked unnecessary herbs and their roots so that they do not take root and continue their parasitic effect on cultivated plants.
Covering material
As you know, the necessary conditions for plant growth are the presence of soil, moisture, air and light. Thus, by removing one of the listed factors, you can safely achieve the destruction of unwanted vegetation.
Strawberries in covering material
Therefore, before planting on the site, it is recommended to cover it with material that does not allow air and light to pass through. The following materials can be used:
- cardboard;
- roofing felt;
- black film;
- linoleum.
The method of eliminating weeds using covering material consists of performing the following procedures:
- Covering a plot of land.
- Waiting for a month.
- Removing the covering from the ground and removing weak shoots using a rake.
This method of weed control is often used not only on empty plots of land, but also on planted crops, and the materials usually used are black film, which is laid between the rows.
Some plants, for example, strawberries, are completely covered with film, and the bush is placed in a special nest, shaped like a slot. At the same time, the film not only protects from unnecessary vegetation, but also retains moisture and attracts sunlight.
Drip irrigation
The essence of the fight against unnecessary plants using drip irrigation is to saturate only useful plants with moisture, while weeds are left without nutrition.
In practice, this method can be carried out by running a hose along the rows with planted crops, with holes made in the place where they are planted.
Mulching
Mulching with straw
The following are usually used as mulch:
- fallen leaves;
- compost;
- straw;
- dry grass;
- crushed polyethylene waste.
Any of the above materials should be thoroughly crushed and laid around the cultivated plants in a layer of 7 cm. The resulting mixture retains moisture, allows air to pass through and maintains the optimal temperature necessary for the growth and development of the root system. If the weeds have already grown, it is recommended to destroy them using any mechanical method and only then begin mulching. In this case, the layer of crushed mass increases to 18 cm.
Weed control on the site in the fall. What danger do weeds pose?
Weeds are dangerous and worst enemies of cultivated plants. They appear in the garden with the arrival of spring and multiply throughout the entire growing season of cultivated plants. There are several ways how weeds get to a summer cottage, one of which is through the ground. Spores of some weeds live in the soil constantly and begin to actively germinate when favorable conditions appear, for example after rain. There is a high probability of parasitic plants entering the garden through organic fertilizers.

You need to be very careful that the manure or compost that you import for feeding undergoes the necessary thorough processing. Weed vectors can also enter the garden through poor planting material purchased at a spontaneous market. Therefore, to avoid unpleasant consequences, it is better to buy seedlings or seeds in special stores.
And finally, the ideal carrier of weeds is the wind. One gust of it is enough to re-infect even the most perfectly cleaned area with weed seeds.
How to remove all weeds from the beds forever is still unknown to either agronomists or experienced breeding scientists. It has been scientifically proven that weeds take half of the fertilizers and fertilizers from the soil, this
leads to nutritional deficiency of cultivated plants and reduces their productivity.

Parasitic plants are a habitat and breeding ground for insect pests, and also release harmful substances into the soil that cause various diseases.
Even burning plants in the fall does not help in the fight against weeds in the country. Unfortunately, weeds adapt very well to unfavorable environmental conditions, are resistant to frost, high humidity and drought, and quickly recover even after mechanical damage is caused to them. Even the use of radical measures helps eliminate the problem with weeds only for a while.

Folk remedies
Before the advent of herbicides, our grandparents got rid of weeds using improvised means. Some of these techniques are successfully used today.
Salt
Cheap, accessible and always effective solution. To remove incipient weeds, you should sprinkle the areas where they grow with ordinary salt or pour a concentrated solution at the rate of 500 g per square meter of area. Atmospheric precipitation will soon bring everything to its logical conclusion. The negative side of this method is the unsuitability of the treated areas for further farming. Therefore, this method is used when preparing an area for artificial turf, as well as to combat overgrowing of garden paths.

Soda
A concentrated soda solution gives a powerful alkaline reaction; in such an environment, the development of weeds is suspended. To achieve maximum results, grated laundry soap is added to the composition.

Alcohol
It is believed that this method was invented by the Americans. It involves the use of medical alcohol diluted with water in a ratio of 1 to 10, and the resulting solution is poured generously onto the ground.
Of course, getting rid of grass this way is not cheap, but the technique has an important advantage over other methods - it does not kill crops and does not disturb the healthy microflora of the soil. Only row spacing can be treated; a bucket of the resulting solution is enough for 2 acres of land.
The effect lasts for one year.

Vinegar
There are several recipes for using vinegar against weeds:
- 5 glasses of 6% vinegar are diluted in 2 liters of water;
- 9% vinegar is mixed with lemon juice at a ratio of 3: 1;
- add 2 tbsp to 1 liter of water. l. salt and 5 tbsp. l. table vinegar, apply hot.

Homemade herbicide soap
If desired, you can make herbicidal soap at home. For this you will need:
- 1 liter of vinegar;
- 150 g coarse salt;
- 1 bar of laundry soap, grated.
All components should be stirred, diluted with water and shaken until smooth. Treatment is carried out on problem areas. To achieve a sustainable effect, you will need to re-water the soil after 7-10 days.

Boiling water
Proper pre-sowing preparation of the area will help remove weeds from your dacha. Before planting seedlings, you should pour boiling water over the substrate generously. This method allows you to destroy not only the seed material of the weeds, but also clear the soil of larvae of insect pests and pathogenic microorganisms.

Biological methods
EM drugs
Preparations with effective organisms are a good alternative for those who do not want to use chemicals. It is necessary to trim the weeds and water the soil with the prepared solution, as a result of which the rhizomes of the plants in the soil will begin to rot and be processed. The procedure is carried out in the fall after harvest.
The most well-known means are “Vostok EM-1” and “Shine-3”.
Watch the video on how to make a solution with the EM preparation.
Saltpeter
Ammonium nitrate is a universal fertilizer obtained by mixing nitrogen and hydrogen, which is also used to control weeds. 3 kg of saltpeter is dissolved in a bucket of water and the resulting solution is sprayed on the plants. This burns weeds without harm to the soil and humans, while the residue goes into the ground and becomes an excellent feed for useful crops.
Mulching
Mulching is covering the soil around crops with various materials. This method has a number of advantages:
- reducing the number of pest plants;
- protection of the earth from overheating, hypothermia and drying out;
- improvement of internal microflora, for example increased activity of earthworms;
- decorating function.
Hay, straw, sawdust and wood shavings, fallen leaves, pine needles, humus, compost or peat are used as mulch. They not only protect the soil, but also act as fertilizer.
Mulching can also be carried out using inorganic materials: film, expanded clay, pebbles, crushed stone, cardboard or paper.
Sideration
The soil does not tolerate emptiness, and if the garden beds are left clean after harvesting, pests will soon grow on them. To prevent this from happening, sow green manure - they suppress the viability of weeds and also serve as a natural fertilizer for the land.
What grass should I plant to prevent weeds from growing? White mustard, oilseed radish, buckwheat and rye will do an excellent job with this mission. However, the latter also suppresses useful crops, so do not place them nearby.
Compacted plantings
Here we also follow the principle “the land should not be empty.” To prevent the appearance of weeds, we plant crops close to each other, combining them correctly:
- late cabbage gets along well with cauliflower, tomatoes, onions and beans;
- cucumber feels great next to tomatoes and cabbage;
- Chicory, onions, cucumbers, carrots and beets are friends with each other.
And these are just some of the successful combinations. There are also bad neighbors: for example, cucumbers and potatoes, onions and legumes.
Folk methods and remedies
Before the invention of chemical compounds and the advent of black film, beloved by summer residents, weeds were fought not only with hands and hoes, but also with the help of improvised means. Many of these methods are still used successfully today.
Salt
Available, cheap and very effective. You can use a saline solution or sprinkle the ground with regular coarse salt at the rate of 1.5 kg per 1 sq.m. - natural precipitation will do its job on its own. The disadvantage of the method is the unsuitability of the cultivated land for further farming, but, for example, to combat overgrowing of paths or prepare an area for artificial turf, this is a very simple and effective method.

Soda
The strong alkaline reaction of strong soda solution works well against plant growth. To enhance the effect, you can add grated laundry soap. But it should be remembered that even in this case it will not be possible to grow anything useful on this soil for a long time.

Alcohol
The method attributed to the Americans
It is quite expensive (it requires a dilution of medical alcohol in a ratio of 1:10), but it has an important advantage - it does not kill crops

Only row spacing is subject to treatment; 2-2.5 acres will require 11 liters. The effect continues for the current year.
This is interesting! The use of strong alcohol against weeds has a long history in America. A month before sowing, the land here was treated with ethyl alcohol. This caused rapid growth of weeds, which were easily weeded out even before sowing. The method was also mastered in Russia, where 1 liter of vodka was simply poured into a bucket of water!
Vinegar
- There are several recipes for use.
- 5 tbsp. 6% vinegar is diluted in 2 liters of water (volume per 2 acres).
- 9% vinegar + lemon juice in a ratio of 3:1.
- Pour 2 tbsp into 1 liter of water. salt and 5 tsp. table vinegar, use hot. This recipe is considered the most reliable.
Homemade herbicide soap
You will need:
- 1 liter of vinegar (best strength - 15-20%)
- 150g coarse salt;
- 1 piece of laundry soap (100g), grated.
Mix everything, dilute and shake until smooth. Treat problem areas; for a sustainable effect, repeated procedures are required with a break of a week.
Burn the grass with fire!
A rather exotic method is when the planted seeds are attacked by pest plants with a sliding flame of a blowtorch even before the seeds germinate.
It is important to comply with two conditions - do this before the first shoots and do not stay in one place for a long time. After the procedure, abundant watering is carried out
Avoid voids
A holy place, as the saying goes, is never empty. This fully applies to the vegetable garden. If the bed is free of onions, plant greens, radishes or any green manure. Permanently empty spaces are well saved by ground covers. Both beautiful and reliable.
Read more in our article: Green manure - purpose, which is better, advice on agricultural technology
It is better to cut off the top of the weed than to dig deeper and cut the rhizome. In the first case it will weaken, in the second it will have the opposite effect. If you touch the root, then remove it entirely.
Planting compaction
To avoid leaving room for weeds, some crops can be planted more densely. An option for experienced people, since thickened plantings can destroy not only weeds, but also everything planted. Such seedlings are often affected by rot.
Fencing
If you managed to clear a certain area of weeds, you can isolate it with a dug ditch or old slate dug 20-25 cm into the ground.
Paying attention to row spacing
After weeding the garden bed, many people often ignore the spaces between the rows where the grass gets trampled underfoot. However, this does not prevent them from developing in the ground and from time to time “raising their heads” to sow seeds. These places can be covered with mulch, covered with gravel, and treated using the methods described above.

Freezing
Dig the beds deeper than usual in winter and do not level the ground. Freezing before snow falls will destroy more weed seeds than usual.
It’s still not worth hoping that weeds will leave your garden and your work alone once and for all. There are especially persistent plants, for which it is almost impossible to order the way to your site (quinoa, wheatgrass, hogweed, plantain, sow thistle, etc.). But a combination of mechanical and chemical methods of dealing with them can give an excellent effect, and you will be able to put your plot in order with much less time and physical effort.
The best methods and folk remedies for weed control
Now the industry has simplified weed control by inventing black covering material and special chemicals. Before that, gardeners used what was at hand. Moreover, these methods of control are still effective and are quite often used in their areas. They are easy to use, they can be used equally in the garden and in the country house to eradicate weeds in the beds, without chemicals or weeding, as well as on the lawn and even in the cemetery.
How to Kill Weeds with Vinegar, Salt and Detergent
This method is the most popular of all other folk remedies. Moreover, you will receive a non-toxic, but quite effective product.
To do this you will need 9% vinegar, table salt and dishwashing detergent.
First, mix vinegar and salt: for 1 glass of vinegar you will need 1 tbsp. l. salt, mix them thoroughly until the salt dissolves. Then add a few drops of detergent, mix everything thoroughly again to obtain a homogeneous substance, and pour the liquid into a spray bottle and spray dry weeds, preferably in the evening or in cloudy weather.
You can get rid of weeds forever in places where no planting is planned (between paving stones or near other road surfaces) by sprinkling these places with salt. But first, water this area well, then sprinkle with salt, and water again. Or immediately dilute 0.5 cups of salt in hot water and pour on the weeds.
Traditional methods for weed control
- Soda . Make a very concentrated solution of soda, add a spoonful of liquid soap to it and pour it over the area where the unwanted grass has grown. But remember, it is unlikely that you will be able to quickly grow anything useful in this place, since the strong alkaline reaction well prevents plant growth.

- Boiling water – if there aren’t too many weeds, it’s good to pour boiling water over them. Instead of boiling water, you can burn out especially “tenacious” weeds with hot fat. For example, if you fry cutlets in a frying pan, there is some fat left, pour it directly onto the core of the weed.
- Alcohol is an expensive method, but it has the advantage that it does not kill crops. Dilute 70% medical alcohol 1:10 and treat the beds.
- Burning out with fire . Pest plants are burned with a sliding fire using a blowtorch. This method is used before the first shoots appear, without staying in one place for a long time, immediately after this they are watered abundantly with water. Better suited for cultivating furrows between beds.
- Freezing . In the fall, after harvesting, dig up the beds to the depth of a spade bayonet, while simultaneously removing plant roots. Frosts will destroy most of the seeds.

Preventative techniques
It is easier to prevent the appearance of weeds than to fight wild plants. I’ll share my preventive techniques:
- No fresh organics. I fertilize the beds only with well-rotted manure. The fact is that fresh seeds contain a lot of weed seeds with excellent germination (horses and cows feed on grass with inflorescences). I let the manure sit for 2-3 years, then I use it for its intended purpose. When organic matter is stored in thick layers, decomposition occurs intensively - the mass heats up so much that the seeds in it die.
- Root watering. I try to water, where possible, only at the root. Wild plants need not only fertile soil and sunlight, but also moisture. If it is deficient, they die. Of course, watering leaf by leaf or using a hose is faster and easier. But with such watering, the appearance of weeds on the ridges is inevitable.
- Spring and autumn processing. I’ll share with you my grandfather’s old method - before the start or at the end of the season, water the empty beds with boiling water. From such an impact, the seeds of wild plants will “cook” and will not germinate.
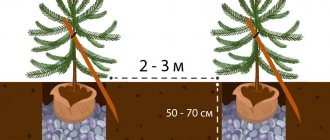
- Natural fencing of garden beds. Sometimes you have to fight not only wild plants, but also cultivated plants. Gardeners know how raspberries, lemon balm and mint, horseradish and Jerusalem artichoke can grow. I try to fence plantations with these plants with slate, plastic, metal sheets, digging them 0.5 m into the ground.
You now know several effective ways to rid your area of weeds. The safest are folk and mechanical. The fastest way is to use herbicides. But it’s easier to prevent the dominance of wild plants on the site - do not forget to lay mulch, sow green manure, cultivate the site in spring and autumn, and resort to prevention.
Mechanical struggle for purity
Mechanical work with weeds means manual or mechanized weeding. The method is long, very labor-intensive and familiar to all gardeners. The success of such a fight depends on the type of grass. If, for example, garden purslane with its poorly developed roots can be pulled out easily and without residue, then thistle or wheatgrass cannot be completely destroyed by hand, no matter how hard you try.

Resorting to mowing the above-ground part without rhizomes can only be effective if the procedure is carried out at least three times in a short period of time. Then the root will dry out and stop trying to sprout, but this does not apply to all weeds.
Rules for successful hand weeding:
- You can’t wait for the roots to get stronger and the plant to come into its own—the “freeloaders” need to be removed as quickly as possible.
- It is better to use a pitchfork rather than a shovel - a cut root may not only not die, but also produce several new shoots.
- The better the roots are removed, the less likely it is to recur.
- It is necessary to begin removing grasses before they are inseminated.
- Weeding after rain is easier than after watering.
- There are days in the lunar calendar (depending on the passage of the Moon in the zodiac circle) when it is better not to touch the weeds, otherwise they will grow with renewed vigor, and the work will be useless.
General recommendations
An excellent option that can defeat wild species is compacted plantings. Empty spaces in the beds can be sown, for example, with lettuce, parsley or spinach. They grow well and very quickly fill all the space allotted to them.

You can also use green manure, such as mustard or alfalfa. However, it is not worth planting strongly growing crops close to the main plantings - there should be enough space and light for everyone.

Experienced gardeners recommend cutting off malicious invaders of beds right above the ground. As a result of these actions, they will be greatly weakened, and their roots will die off entirely over time. The main thing is not to cut these roots, trying to pull them out of the ground, but to leave them whole. Otherwise, the remaining roots will sprout again.
Sometimes it is advisable to protect the area “cleared” of debris with something dense - non-woven material, slate scraps, etc. This creates a barrier for the penetration of creeping rhizomes, for example, like those of nettles, into the ridges. It is also recommended to cover the spaces between the beds or fill them with something - expanded clay, small stones, old linoleum, boards, etc.