Growing earthen pear
Jerusalem artichoke can be considered an economical crop, suitable for growing on a personal plot. The plant does not need to be planted every year; it is unpretentious in its care. Jerusalem artichoke only needs moist soil without stagnant water, and then it will definitely delight you with its seedlings and harvest.
Before planting a vegetable, you need to prepare the soil. They do this in the fall. Loose soil with a slightly alkaline environment is suitable . The preceding crop can be winter and spring grains, annual grasses, and legumes. It is not recommended to plant in soil where sunflowers previously grew. The soil must be dug to a depth of 30 centimeters and fertilized. Manure, humus, as well as phosphorus and potassium fertilizers are suitable as fertilizers. It takes about 125 days for the tubers to ripen, provided that there are no frosts during the season . In the spring, when the soil warms up, it is necessary to harrow the soil and hill up when the plant reaches a height of 20 centimeters. Further care completely replicates the conditions for growing potatoes.
A vegetable can grow in one place for about 30 years, and there will be a harvest every 3-5 years, but then the root crop begins to shrink.
Vegetables are planted in open ground in the pre-winter period 15-20 days before the first frost. The area must be illuminated. Jerusalem artichoke practically does not need watering (only in particularly dry times); each bush requires 1.5 buckets of water.
In mid-summer, the Jerusalem artichoke should be shortened and the flower heads should also be cut off. It is worth noting that Jerusalem artichoke is afraid of pests such as mole crickets, slugs and wireworms, so appropriate treatment of the bushes is necessary. Also, if not properly cared for, a plant can be susceptible to diseases such as white rot, Alternaria blight, and powdery mildew.
Photo of roots in section
Nuances of crop care
If the soil in which the Jerusalem artichoke is planted is fertile enough, the plant can easily do without any care at all. But in order to regularly get a bountiful harvest, you still have to spend a little time and effort on it.

Regular weeding has a positive effect on the yield of Jerusalem artichoke
Before emergence (usually this happens 15–20 days after planting the tubers), the bed needs to be loosened shallowly. If the summer is rainy, seedlings that have grown to 15–20 cm are earthed up, deepening the furrows. In addition, practice shows that regular weeding has a positive effect on the size of tubers. There is no need to cover the emerging seedlings, even if there is a threat of frost. Plants can tolerate temperatures down to -5ºС.

Hilling Jerusalem artichoke helps avoid the development of rot in wet weather
Jerusalem artichoke does not require regular watering. Natural precipitation is enough for him. But if the weather in summer is abnormally hot and dry, you can moisten the soil once a week, spending 10–15 liters per adult plant. It is also advisable to water the bed every 7–10 days in August, at which time tubers are forming.

If there is no abnormal heat outside, natural precipitation is enough for Jerusalem artichoke
If the bed for Jerusalem artichoke has been prepared in compliance with all recommendations, the plant will be provided with the necessary macro- and microelements for the next 2–3 years. Later in the spring it is fed with nitrogen. 15–20 g of urea, ammonium sulfate, ammonium nitrate are distributed over the bed in dry form or dissolved in 10 liters of water. The recommended dosage should not be exceeded. Excess nitrogen in the soil reduces the plant’s immunity, provoking the development of many fungal diseases. Once every 2–3 years in the spring, while loosening the soil, rotted compost or humus is distributed on the garden bed.

Humus applied to the garden bed helps to increase soil fertility
In mid-summer, fertilize with phosphorus and potassium. You can use simple superphosphate and potassium sulfate, an infusion of sifted wood ash, or any complex fertilizer (Zdraven, Kemira-Lux, Agricola).
Video: tips for growing and caring for earthen pears
Jerusalem artichoke rarely suffers from diseases. But heavy rainfall combined with low temperatures throughout the summer can provoke the development of fungal diseases - rot, Alternaria, powdery mildew. In the first case, the bases of the stems and leaf petioles turn black and become slimy to the touch. Gradually they become covered with a layer of fluffy grayish coating with small black inclusions. Powdery mildew is easily identified by a white coating on the leaves and stems, similar to spilled flour. Alternaria is characterized by brownish-beige spots with a yellow border.
Photo gallery: Jerusalem artichoke diseases

Root rot, like its other types, can be cured only in the earliest stages of development

Powdery mildew seems like a harmless coating that can be easily wiped off, but in fact it is a dangerous disease.

Leaves affected by Alternaria quickly dry out and fall off.
For prevention, Jerusalem artichokes are dusted with tobacco crumbs, sifted wood ash, and crushed chalk once a month. Having discovered suspicious symptoms, you need to immediately cut off even the least damaged parts of the plant. Any fungicides are used to treat fungal diseases. Time-tested remedies are copper sulfate and Bordeaux mixture, but there are also many more modern copper-containing preparations (Abiga-Pik, Kuprozan, Topaz, Skor, Bayleton, and so on). Usually, if the disease is noticed at an early stage, 2-3 treatments with an interval of 5-8 days are sufficient. In severe cases, the source of infection is eliminated, the soil in the place where the diseased Jerusalem artichoke bush grew is disinfected by spilling a bright pink solution of potassium permanganate.

Bordeaux liquid can be purchased at any specialty store or prepared yourself
Among the pests, damage to Jerusalem artichokes can be caused by mole crickets, slugs, and the larvae of the cockchafer. They gnaw through the tubers, eating them out from the inside, as a result of which rot quickly develops. You can protect plantings quite effectively using homemade traps. Deep containers filled with bait are dug into the soil - any porridge with honey or sugar for mole crickets and pieces of cabbage and potatoes for slugs and larvae. Once every 3-4 days it needs to be changed, while simultaneously getting rid of any pests. In case of mass invasion, insecticides are used. To combat mole crickets, Medvetox and Diazinon are used; Groza, Meta helps against slugs; Fury and Confidor-Maxi effectively destroy the cockchafer.
Photo gallery: pests dangerous to Jerusalem artichoke

Slugs feed on the pulp of tubers, leaving a sticky silvery coating on the surface

Mole crickets move by digging tunnels in the ground, in the process they often damage plant roots and tubers

To combat cockchafer larvae, you can use any general insecticide.
In addition, strong, pungent odors repel pests. Therefore, it is advisable to plant spicy herbs, marigolds, and nasturtiums near Jerusalem artichokes. Many of these plants are also good honey plants that attract bees to the site.

Marigolds are not only beautiful, but also useful flowers; the smell of their leaves repels many pests
Jerusalem artichoke is harvested at the end of September or October. There is no point in rushing to dig up tubers. Those that are removed from the soil ahead of schedule will no longer ripen. The harvested crop is not stored for a long time, so some can be left for spring. Wintering the tubers will not harm the tubers in any way; on the contrary, it will have a positive effect on their taste. The stems of such plants are cut off in early November, leaving “stumps” 10–12 cm high.

There’s no point in delaying harvesting until frost, but there’s no point in digging up tubers ahead of schedule either.
The maximum shelf life of Jerusalem artichoke is 30–40 days. To do this, the tubers are placed in boxes so that they do not come into contact with each other or the walls, and covered with sand, peat, and sawdust.

The only significant drawback of Jerusalem artichoke is its short shelf life.
Video: Jerusalem artichoke harvest
History of appearance
The homeland of this useful root vegetable is North America. Initially, it was a wild plant that was cultivated by local Indian tribes. The first Europeans to try Jerusalem artichoke were the British and French. Later, Jerusalem artichoke penetrated into Belgium and Holland, where, trying to give it the taste of an artichoke, it was boiled in wine and butter. The spread of potatoes in the eighteenth century caused a certain cooling of Europeans towards this vegetable. Interest in the vegetable was returned by the French researcher of the New Age Boussingault J.B.
In Russia, the Jerusalem artichoke also appeared in the eighteenth century, but did not gain much popularity. Only in the Soviet era did Vavilov N.I. began to actively promote this crop as a fruitful one. He emphasized the important properties of the vegetable: unpretentiousness and frost resistance. This was the reason for the active development of Jerusalem artichoke on collective farms. But the problem with further cultivation was storage - it cannot be stored for a long time, like potatoes or carrots.
In the nineties, the earthen pear began to be cultivated in the southern regions to create medicines and additives for the food industry. They also began to pay attention to Jerusalem artichoke as an ornamental plant. Increasingly, it began to appear in park areas of large cities. The Jerusalem artichoke is also used to enrich poor soils.
Today Jerusalem artichoke is equally known throughout Europe and in Russia. It was brought from North America in the 17th century as a medicine. It began to be used as food only in the 19th century.
The root of the Jerusalem artichoke, which tastes similar to turnips or cabbage stalks, is edible. The Jerusalem artichoke is characterized by frost resistance and high yield. For this reason, Jerusalem artichoke is considered a weed in many countries. It blooms in mid-autumn, and during the first frosts the tubers ripen.
More than three hundred varieties of Jerusalem artichoke are known , but it is quite difficult to distinguish them externally. An important distinguishing characteristic is the volume of green mass, productivity, and decorativeness. The varieties most often grown in Russia are:
- Interest - a late variety, characterized by a greater need for moisture, good yield, and rapid germination. The variety is resistant to frost. This variety has white smooth tubers. Mainly cultivated in the southern regions.
- Leningradsky is a late variety characterized by good yield. The tubers are white, elongated, medium size. They are stored well in the ground until frost sets in. Cultivated mainly in the north-west of Russia.
- Volzhsky 2 is a vigorous variety that is resistant to drought and frost. The root crop is white, pear-shaped, with purple splashes.
- Early ripening is an early variety, does not require much light, and is frost-resistant. It has a compact root system with white round tubers.
- Pasko is a late, vigorous, bushy variety. The roots are white, round, and can weigh up to 80 grams.
- Solnechny is a late variety, characterized by productivity with medium-sized white ellipse-shaped tubers.
- Nakhodka is a late variety with white tubers with pink veins. Cultivated in the southern regions.
Also popular are varieties such as: Patat, White, Red, Vadim, North Caucasian.
Choosing a variety

The most popular varieties of Jerusalem artichoke are:
- 'Kyiv white',
- 'Red',
- 'Spindle-shaped',
- 'Patat',
- 'Maikopsky',
- 'White',
- 'Precocious',
- 'Nakhodka',
- 'Dietary',
- 'Volzhsky-2',
- 'Vadim',
- Leningradsky',
- 'North Caucasian',
- 'Interest' (three times the potato yield).
By crossing Jerusalem artichoke with sunflower, breeders created a new plant - sunflower (especially productive - sunflower 'Vostorg').
Latin name - Helianthus tuberosus L.
Family - Asteraceae.
View - Jerusalem artichoke.
Predecessors are annual grasses and leguminous crops.
Lighting – light-loving.
Watering is moisture-loving.
Soil – sandy and loamy soils.
Planting - tubers and seeds.
Jerusalem artichoke (earthen pear) is a herbaceous plant. It looks somewhat like a sunflower. But it differs from it in that it forms tubers in the soil. Its homeland is North America. Today it is grown in Canada, Japan, England, Germany, the Netherlands, the USA, Australia and Russia. It grows both in the northern regions and in the subtropics.
Features of the plant
Jerusalem artichoke is a storehouse of vitamins, and in the spring it can be dug up and used as a healing remedy against vitamin deficiency.
- This is an unpretentious crop and can produce a harvest in any soil;
- Tubers are not afraid of weeds and pests;
- Grows well both in the shade and in the sun;
- Almost does not accumulate nitrates;
- The calorie content of the crop is equal to potatoes.

Biological features of Jerusalem artichoke
Jerusalem artichoke - a crop for the garden without worries:
- grows on any soil, except salt marshes and highly acidified ones,
- does not require maintenance,
- does not get sick and is not damaged by pests; very rarely and slightly damaged only by white rot in the lower part of the stems,
- does not accumulate nitrates and nitrites in tubers and ground green mass,
- Jerusalem artichoke is a short-day plant; in the southern regions (the day exceeds 12 hours), flowering occurs late, the seeds do not ripen.
Jerusalem artichoke has edible flowers, young leaves and roots. Moreover, the harvest of root crops is perfectly preserved in the soil. It can be partially removed in the fall and in the second half of the spring, when vitamin deficiency is especially noticeable.
Jerusalem artichoke still has one drawback - it is poorly stored. Unlike potatoes, Jerusalem artichoke tubers do not have a cork layer that protects the product from spoilage. This property was the reason for replacing Jerusalem artichoke with potatoes.
Healing properties and chemical composition of Jerusalem artichoke
The root vegetable has medicinal properties and has many useful substances, among which the following is especially worth noting.
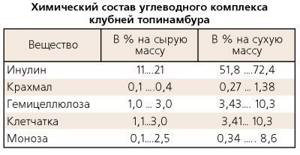
Firstly, the plant is rich in amino acids and proteins . Contains a large amount of vitamins C and group B. Jerusalem artichoke is rich in iron. In terms of its content, it can compete with carrots and beets. Jerusalem artichoke also contains significant amounts of inulin and fructose . Inulin is an excellent prebiotic, read more about probiotics and prebiotics. Fructose is a sugar substitute and, like glucose, is involved in metabolic processes. Fructose is able to penetrate all cells without the use of insulin and enriches cells with energy. This causes a decrease and stability of glycemia. Therefore, it is recommended for diabetes mellitus , when glucose is poorly absorbed. Eating Jerusalem artichoke lowers blood sugar levels. In addition, fructose is an antioxidant and antitoxin. This has a positive effect on blood vessels and reduces susceptibility to infections.
List of amino acids that form medicinal properties:
- Arginine helps stimulate the immune system, provides muscles with nutrition, increases the synthesis of growth hormone, reduces the amount of subcutaneous fat, and helps rejuvenation.
- Valine has a calming effect, balances the nervous system, reduces the body's sensitivity to heat or cold, and increases muscle coordination.
- Histidine is a component of hemoglobin, used in the treatment and prevention of allergies, anemia, and prevents hearing loss.
- Lysine, one of the more common amino acids found in protein, affects the breakdown of fats, converting them into energy. Affects the growth process.
- Isoleucine acts as a sugar regulator and provides energy to the body.
- Methionine is involved in reducing depression, reduces cholesterol, and prevents the formation of fatty deposits in the liver.
- Leucine helps protein synthesis, is necessary for tissue nutrition, and prevents amino acid molecules from being destroyed.
- Tryptophan stimulates the formation of growth hormone, helps normalize sleep, and relieves fatigue.
- Phenylalanine is responsible for the production of thyroid hormone and is important for the formation of endorphins.
Jerusalem artichoke is rich in potassium, magnesium, calcium, silicon, fluorine and chlorine. A lack of potassium can cause neuralgia. Magnesium affects the transmission of nerve impulses and muscle contraction. Silicon can accelerate redox processes, affects the condition and strength of bones, and prevents atherosclerosis.
Jerusalem artichoke is rich in fiber and pectin and a large amount of carotene. Also rich in iron and manganese. Iron is part of hemoglobin, affects respiratory processes, and can prevent anemia. Manganese affects the functioning of the sex glands and blood formation. This root vegetable is a good alternative to pills and drugs from the pharmacy. But this culture can have both benefit and harm, for example in case of individual intolerance .
Secondly, pear roots are an effective remedy for a number of diseases. First of all, they help with disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, are recommended for those suffering from diabetes , and help the body fight viruses and infections. Effective for headaches and high blood pressure. Able to increase hemoglobin levels and remove toxins from the body.
Thirdly, due to its high inulin content, Jerusalem artichoke helps lower blood sugar and is recommended for patients with diabetes . You can consume two to three tubers a day not only for people with diabetes, but also for those at risk. In addition to the tubers, the leaves may also be suitable for medicinal purposes. They are recommended to be added to salads, and the benefits of this dish will be undeniable.
Inulin contained in Jerusalem artichoke is a special substance that affects the reduction of glycemia. Inulin does not dissolve in the digestive system. This means that it retains all its nutritional and beneficial properties throughout the digestion process.

In the large intestine, inulin is fermented, facilitating the proliferation of beneficial bifidobacteria. Thus, inulin performs important functions in the human body:
- Contains nutrients and vitamins;
- Protects the intestines from diseases and tumors;
- Strengthens the immune system;
- Promotes the synthesis of vitamins;
- Regulates glycemia;
- Reduces the amount of fat and cholesterol.
Fourthly, the vegetable will be useful for residents of large cities with not very good ecology. The plant helps remove heavy metal salts and also helps cope with microbes and viruses.
Fifthly, all varieties of this unique plant have beneficial properties. The most useful is squeezed Jerusalem artichoke juice. It promotes the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, reduces acidity, and helps with small wounds. It is better to take this drink a few minutes before meals, half a glass three times a day.
Sixth, this vegetable is a good remedy for urolithiasis, stroke and obesity.
Seventh, Jerusalem artichoke will be useful during pregnancy. It shares all its beneficial properties with the developing fetus of the child. The root vegetable is also known for its laxative properties, and is used by women for constipation, especially in the last trimester . The amino acids contained in the product affect the growth of the baby's muscle mass, therefore, the product is recommended for breastfeeding. Jerusalem artichoke has anti-inflammatory and immunostimulating properties that can protect both mother and baby from infections during breastfeeding. Although, in this case, the intake of Jerusalem artichoke should be supervised by a doctor.
Eighth, earthen pear is often used to strengthen the immune system. By using it regularly for various diseases, recovery occurs much faster.
Ninth, Jerusalem artichoke leaves are used for arthritis and osteochondrosis.
Tenth, the root vegetable is quite suitable for baby food. Its benefits for the digestive system are that it improves intestinal function, copes with dysbiosis, strengthens the immune system, and helps fight infections. Jerusalem artichoke is especially recommended for children with low hemoglobin.
You should not get carried away with raw Jerusalem artichoke, as this can cause flatulence. There are practically no other prohibitions, with the exception of individual intolerance to the product. These are the only contraindications for use.
Other beneficial properties of Jerusalem artichoke
Jerusalem artichoke, according to many studies, contributes to:
- strengthening the immune system
- protecting the body from parasites and pathogens
- normalization of intestinal function
- strengthening and restoration of the mucous membranes of the body, damaged due to various reasons

It speeds up the healing process in sick people and helps remove heavy metal salts from the body. They say that this plant helps maintain potency in men. For women, it is important that it improves skin condition.
Application of earthen pear
- A decoction of Jerusalem artichoke is used in the treatment of: pyelonephritis, cystitis, anemia, diabetes. Pour two tablespoons of leaves into a glass of boiling water and leave for two hours, strain and drink a few minutes before meals.
- Juice from tubers is used in the treatment of patients with tuberculosis, as well as high blood pressure and gastrointestinal diseases. It is a remedy for constipation, heartburn, has choleretic properties and protects the liver, and is also recommended for overweight. A little juice is diluted with water in equal parts and taken 20 minutes before meals.
- Jerusalem artichoke syrup has healing properties. The tubers must be crushed through a meat grinder or using a blender, and then squeeze out the juice, pour into a saucepan and heat to a temperature of 60 degrees. Keep on fire for ten to fifteen minutes. Cool everything and repeat the heating procedure. Heat three to four times until the syrup reaches a thick consistency. At the end of cooking, add lemon juice. The finished syrup is stored in the refrigerator.
- The infusion is used in the treatment of blood diseases. Powdered tubers are poured with boiling water and infused. It is recommended to drink a liter of infusion per day for a month.
- An infusion can also be made with alcohol. The leaves are poured with alcohol or vodka: a liter of vodka per 0.5 kilograms of leaves. The infusion should be kept in a dark room for two weeks. Then strain and take two tablespoons before meals three times a day. This infusion strengthens the cardiovascular system and helps reduce blood sugar.
- To treat and prevent diabetes, you can make coffee or tea from Jerusalem artichoke.
- Jerusalem artichoke baths help with arthritis and osteochondrosis. For the bath, you need to choose the healthiest leaves, chop them, make a decoction and pour it into the bath. Should be taken eight times a day for 15 minutes.
Jerusalem artichoke flowers also have healing properties. They are crushed, dried and brewed with boiling water. The infusion should stand overnight. Then it is filtered. You need to drink half a glass three times a day before meals. This remedy will help with anemia.
Use in cosmetology
It is also used as a cosmetic product that promotes rejuvenation and healing of the skin. This product also treats fine wrinkles on the face. The tubers need to be grated and mixed with linseed oil. Keep the mask on your face for 15 minutes. The positive effect will occur after 10-15 sessions.
- For oily skin, the mask is made with the addition of honey, and after the session you need to wash it off with green tea and wipe your face with an ice cube.
- You can wipe your skin with Jerusalem artichoke juice - it will get rid of pimples and blackheads.
Jerusalem artichoke is used for peeling to remove age spots. The juice of the root vegetable is mixed with grapefruit essential oil and sea salt. The mixture is applied to the skin in the décolleté area with massaging movements and then washed off with water. This procedure is recommended to be carried out once every two weeks.
On a stuffy and hot day, a tonic will help - mineral water with Jerusalem artichoke juice. Spray the skin with this tonic, then it will not dry out and peel.
To improve the condition of hair, use root juice mixed with burdock oil. The mixture must be rubbed into the roots of the hair, gradually distributing it over the entire length.
Jerusalem artichoke is recommended in the autumn-winter and spring periods. It helps protect the body from diseases, viruses and infections. The vegetable also allows you to keep your body in good shape and tone. To do this, it is enough to eat 1-2 tubers of the plant daily or drink its juice.
The culture also has purely decorative properties - its sunny flowers not only decorate the area, but can lift your spirits and create a favorable atmosphere.

Photo of leaves and roots
The benefits of Jerusalem artichoke for diabetes. How to use Jerusalem artichoke if you have diabetes?
IMPORTANT: Insulin is produced industrially from Jerusalem artichoke.
Patients suffering from diabetes are recommended to consume 2 - 3 Jerusalem artichoke tubers per day to reduce sugar levels. It is advisable to do this 10 - 15 minutes before meals three times a day. RECIPE: Salad with Jerusalem artichoke for diabetics. You need to take several Jerusalem artichoke tubers, chop them finely and mix with 3 eggs pre-boiled and cut into cubes and 100 g of canned corn from a can. The result is a tasty and very healthy salad, especially for people with diabetes.
Jerusalem artichoke is a natural source of insulin, it is useful for diabetics
Insulin contained in Jerusalem artichoke also helps remove toxic and harmful substances from the body, promotes the normal functioning of the digestive system, and stimulates the regular and without stagnation of bile.
Use in folk medicine
Jerusalem artichoke is used by folk healers in the treatment and prevention of many diseases.
- For cardiovascular diseases, the Jerusalem artichoke tuber was crushed and filled with water. Cooked in a water bath for about 15 minutes. Take 2-3 doses of 100 milliliters.
- To treat heartburn, use freshly squeezed juice from the root vegetable.
- For anemia and low hemoglobin, an infusion of Jerusalem artichoke flowers is used.
- Used for diseases of the pancreas.
- Deposition of salts in joints is treated with a decoction of the stems and tubers of Jerusalem artichoke. The raw material is filled with water and brought to a boil. They take baths with this decoction.
- Compresses are used to treat purulent wounds and skin lesions.
- Jerusalem artichoke juice is recommended to be used against rhinitis and runny nose.
- If vision deteriorates, the juice of the plant is mixed with honey and taken 20 milliliters for a week.
Jerusalem artichoke is essential for diabetes due to its inulin content . Inulin prevents blood sugar levels from rising and prevents diabetes. Root vegetables have this property, both raw and boiled. In modern medicine, drugs based on Jerusalem artichoke have been developed:
- “Neovital” contains, in addition to dry Jerusalem artichoke, stevia powder, reindeer antler. The drug promotes metabolic processes in the body and strengthens the immune system.
- “Inulin” helps reduce sugar and ensures the production of insulin. Recommended for patients with diabetes.
- "Alga Helianthus" includes flax seeds, sea brown algae, Jerusalem artichoke. The drug helps remove toxins and waste from the body. Improves heart function.

Jerusalem artichoke powder
Use in cooking
Thanks to its pleasant taste, Jerusalem artichoke is used for preparing first and second courses. It can be boiled, stewed, fried and evaporated. It is also used raw, since tuberous sunflower is a salad product. In terms of its taste, it goes well with boiled eggs, canned corn, carrots and vegetable oil. This salad is an excellent option for breakfast - minimum calories, maximum benefits and a boost of energy and vigor for the whole day! Jerusalem artichoke goes well with sauerkraut and apple.
There are many recipes with Jerusalem artichoke; pancakes are also made from it. It should be grated, add flour and egg, mix everything and fry in vegetable oil.
Pear puree soup is healthy and tasty. The tubers are cut into circles and sautéed with onions. Vegetables should be placed in the broth and cooked for 15 minutes with the lid closed. For thickness, you can add a little flour to the broth. Then, you need to add cream to the boiling soup and beat everything with a blender.
For people suffering from diabetes, we recommend coffee made from this miracle plant. The tubers are dried, all the juice is squeezed out, and all moisture is removed, and the pulp is crushed and fried. The resulting product is ground in a coffee grinder and then brewed in the usual way.
Jerusalem artichoke can simply be fried - it tastes like potatoes, which is why chips made from this vegetable are popular among young people.
A quick and healthy recipe for making Jerusalem artichoke will not only save time, but also saturate the body with the necessary substances. Especially recommended for diabetes. Jerusalem artichoke tubers need to be washed well, grated and simmered a little. Place the resulting slurry on a baking sheet and pour in the beaten egg, semolina and milk. Bake at 185 degrees for 20-30 minutes.
Jerusalem artichoke caviar has good taste. Grind the tubers into puree using a meat grinder or blender. Add spices and salt to the resulting puree. Mix with tomato paste and fried onions and carrots. Place the resulting mixture in a clay pot and simmer in the oven for an hour at 175 degrees. The resulting product is ready for use, but it can also be preserved.
Description of Jerusalem artichoke
The Jerusalem artichoke is similar to a sunflower in its external structure of the ground part. It is called (like the sunflower) a sunny flower for its ability to turn the inflorescence after the sun.
The underground part of the plant consists of a tap root and underground shoots - stolons, located at a depth of 15-20 cm. At the ends of the Jerusalem artichoke stolons, tubers, pear-shaped in external shape, are formed. Their appearance can also be fusiform, oval, round, and almost always tuberculate.
The ground stem of Jerusalem artichoke is annual, straight, reaches a height of 2–4 m, rounded-cylindrical, rough due to numerous short hard hairs, dark green, very dense. In autumn cultivation, the stem of Jerusalem artichoke is cut into a stump 7-10 cm high.
Jerusalem artichoke leaves are large, rough, petiolate. They densely cover the stem. The leaf blade is dark green, heart-shaped or ovate. The developed large leaves are slightly drooping.
The inflorescence of Jerusalem artichoke is a basket. The flowers are yellow or orange-yellow. The marginal flowers are ligulate, unisexual, sterile. In the center of the inflorescence are tubular bisexual, self-pollinating or cross-pollinating. The earthen pear blooms in September and blooms until November, depending on weather conditions and the growing region.
The fruit of Jerusalem artichoke is an achene, small, grayish-brown in color. Inflorescences are often cut off to obtain larger tubers. When grown for decorative purposes, they produce elegant bushes that bloom until late autumn.

Jerusalem artichoke, or tuberous sunflower (Helianthus tuberosus). © Raw Edible Plants
Technical Application
Certain varieties of Jerusalem artichoke are used as fodder and for technical purposes. The stems and leaves of the plant are the raw materials for the production of silage. They gather in early autumn. Jerusalem artichoke tubers are used in hunting farms. It is an indispensable feed for hares, moose, and wild boars. Also, the vegetable is often planted along roads, clearings and forest edges as a fodder belt. Jerusalem artichoke has a positive effect on the milk production of cows and pigs. There is more milk and higher fat content. The same effect is observed when feeding birds - they begin to lay eggs 2-3 weeks ahead of schedule.
Planting Jerusalem artichoke and preparing for it
The unpretentiousness of Jerusalem artichoke also extends to the place where it is grown. The culture successfully takes root in both sunny and shaded areas. But practice shows that under direct sunlight, the tubers become smaller and lose their characteristic sweetish taste.

The Jerusalem artichoke harvest is more abundant in an open area than in the shade, but direct sunlight is not the best option for it.
The plant also has no special requirements for soil quality. Any soil is suitable for it: light sandy and heavy clay. The only thing that Jerusalem artichoke categorically cannot tolerate is acidifying soil. In such a substrate, the tubers begin to rot very quickly. Therefore, it cannot be planted in lowlands, in wetlands and where groundwater comes closer to the soil surface than 1.5 m. In saline or acidified soil, the plant takes root, but you cannot expect abundant harvests. The ideal option for the crop is a fairly light but fertile substrate.
When choosing a location, you need to take into account what grew in the garden before. Bad predecessors for Jerusalem artichoke are sunflowers and garden strawberries. The earthen pear grows well after potatoes, all types of cabbage, cucumbers, and zucchini. It is also worth remembering that the height of Jerusalem artichoke reaches 3 m or more. It may well shade nearby beds. Therefore, most often a place is allocated for it in the far corner of the site or along the fence.

Sunflower is a bad predecessor for Jerusalem artichoke; plants from the same family suffer from similar diseases and pests
Planting Jerusalem artichoke differs little from the procedure for planting potatoes familiar to any gardener. But the optimal time comes a little earlier - in the last ten days of April or early May. Although there are also supporters of autumn planting of tubers. They endure winter without problems, and harvest within a year.

Preparing a bed for Jerusalem artichoke differs little from a similar procedure for other crops
The bed itself is prepared in advance. If you plan to plant in spring, start in the fall. The selected area is cleared of plant debris, dug up, and fertilizer is applied at the same time. It is advisable to increase the fertility of poor soil with humus or rotted compost (5 l/m²). Otherwise, a complex mineral fertilizer - Nitrofoska, Azofoska, Diammofoska (about 50 g/m²) is sufficient. An additional additive for acidic soil is dolomite flour, powdered eggshells, fluff lime (200–400 g/m²).

Nitrophoska, like other complex fertilizers, contains nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium - these are the main macroelements needed by any plant
For planting, only absolutely healthy tubers with a diameter of 6–8 cm (about the size of a chicken egg) are selected. To disinfect, they can be soaked in a pale pink solution of potassium permanganate for 2–3 hours the day before the procedure; to increase immunity and increase productivity, they can be soaked in water with the addition of any biostimulant (Epin, Zircon, Heteroauxin, succinic acid, aloe juice). Those tubers that have noticeably dried out are placed in a container with water at room temperature for 2–3 days, changing it daily.
Jerusalem artichokes are planted in furrows or individual holes 7–12 cm deep (the lighter the substrate, the deeper the tubers need to be buried). The distance between them is 50–60 cm, between the tubers in a row is 35–40 cm. When forming a “scene”, Jerusalem artichokes are planted in a checkerboard pattern, leaving 20–25 cm between them. If there are reasonable doubts about your own eye, it is better to mark the bed in advance . A little humus, a handful of sifted wood ash and a little onion peel are added to each hole to repel pests. The tubers are placed sideways. The hole covered with earth is watered abundantly, using 2–3 liters of water. The substrate must be well compacted. When planting in autumn, the bed is mulched with fallen leaves or peat chips.

Jerusalem artichoke is planted in almost the same way as potatoes.
Jerusalem artichoke has the ability to “spread” through the garden like a weed. To avoid this, it is recommended to dig a container into the garden bed. Its walls will limit the area of distribution of tubers.
Interesting Facts
- The product is not only a storehouse of healing properties, but also has the unique property of enriching the soil.
- The tall and dense stems of Jerusalem artichoke can protect against wind and weeds, so it is often used as a hedge in personal plots.
- In Russia, Jerusalem artichoke was not immediately accepted as a food product. For a long time it was grown strictly for medicinal purposes.
- For many people during the Second World War, Jerusalem artichoke was a life-saving product and did not allow them to die of hunger.
- In one place, Jerusalem artichoke grows and produces crops for several decades. At the same time, the soil will not become poorer.
- Americans often replace potatoes with Jerusalem artichoke. Jerusalem artichoke with bacon and vegetables became their favorite dish.
- The French serve it with cheese, anchovies and olives.
- One Jerusalem artichoke bush can produce a harvest of two buckets of good mature tubers.
- Ground pear can be a good substitute for wheat flour.
- This vegetable serves as a raw material for biofuels.
How to select and store Jerusalem artichoke?
To select this healing product, just a visual analysis will not be enough. The product should be picked up and its quality determined tactilely. Roughness and hairs on the skin will indicate quality. Also, the tubers must be firm. Root vegetables should not have damage or dents on the skin, much less wrinkles.
Jerusalem artichoke requires a special approach to storage. The earthen pear should not be stored for a long time due to its thin skin, which is not resistant to damage. Tubers can be stored for two to three weeks in food paper in the refrigerator.
Jerusalem artichoke for children
Considering the numerous beneficial properties of Jerusalem artichoke, the question necessarily arises of how good it is for children to consume. So, he is good for children, even very good. Thanks to the use of this product as food for a child:
- digestion will improve
- dysbiosis will not occur in the intestines
- blood counts will improve, in particular hemoglobin
- the body's resistance to infections will increase

Moreover, dishes made from Jerusalem artichoke do not cause any negative reactions in children.











