What is the difference between cypress and cypress
Despite the similarity of names, cypress and cypress have certain differences, since they are 2 completely different trees, although they belong to the same family. You can distinguish them from each other by the shape of the branches and cones. Cypress branches are flatter, and the cone contains only 2 seeds covered with scales. Cypress cones are much larger in size, and the number of seeds in them is much higher. Its needles are not flat, like those of cypress, but edged, vaguely reminiscent of a pencil to the touch.
Botanical description of the plant
A shrub growing in natural conditions reaches a height of 30 m. The coniferous crop is compared to cypress, but its branches are smaller. The shrub comes from Asia and has been grown since the mid-18th century. Because of its beauty, cypress is often used in landscape design.
The plant has thick needles that resemble scales. Its cones are small, containing several seeds. The shrub is resistant to cold, especially its North American species, so it does not need to be covered for the winter. Coniferous crops do not tolerate drought, and this feature must be taken into account when growing. The crown of the shrub is in the form of a cone, the branches are spreading, medium in size. The trunk is brown or brown, the yellow-green leaves have a pointed shape. The plant is valued for its decorative properties and resistance to frost .
Cypress root system
The root system of the cypress tree is located predominantly horizontally, growing greatly in breadth over time. At a young age, the roots of this tree grow quite actively; over time, this process slows down.

However, this factor must be taken into account when planting, so neighboring seedlings are planted at a distance of at least 1 or even 2 m from each other, so that mature trees do not compete with each other.
Landing
Red Star cypress prefers to grow in sunny areas, although it can develop in partial shade . Choose a planting site in a small depression so that moisture stays in the soil longer. Plants are planted in loam for the same reason. Planting in open ground to a permanent place is carried out in the spring, when the soil warms up to a temperature of +12°C.
Important! Buy seedlings in specialized nurseries or a shopping center. This will allow you to choose a plant that matches the varietal characteristics.
The planting hole must be prepared in advance. In November, dig a hole and add a drainage layer to the bottom . Experienced gardeners recommend using broken bricks or sand with large grains for this. Fill 2/3 of the hole with nutrient soil. To prepare it, mix garden soil, peat, compost and humus in equal proportions. If the soil is too dense (clayey or black soil), then add a little sand. It is necessary to ensure that the root system of the tree does not rot.

The planting technology is as follows:
- The holes are dug at a distance of 2 m from each other. Their optimal dimensions are 60x70 cm.
- After the preparatory processes, immerse the seedling inside.
- Cover the voids with nutritious soil. Be careful that there are no air bags.
- Water the planting material with warm water and mulch the tree trunk. To do this, it is advisable to use peat, sawdust or pine bark.
Video: Planting and caring for cypress

How does a cypress tree grow?
In total, 7 species of cypress are described in nature. In addition, there are several hundred varieties bred for decorative purposes. The largest cypress tree on a trunk in the wild can reach a height of 70 m, while dwarf cultivars are often grown as indoor flowers in pots.
The main growth indicators of some types of cypress are given in the table below:
| Type of cypress | Height of a mature tree, m |
| Pea-bearing | 30 |
| Lawson | 70 |
| Blunt | 50 |
| Tuevidny | 25 |
| Nutkan (Yellow) | 40 |
How does cypress overwinter?
Most varieties of this tree can withstand frosts down to - 20 ° C, and pea fruit - up to - 25 ° C. This makes it possible to grow them in the southern regions of Russia. Young plants are more prone to freezing and can hardly withstand temperatures dropping even to -10 °C, so in the Moscow region and central Russia, wintering cypress trees in open ground is not allowed.

In these regions, they use a different tactic, growing trees as ornamental trees in tubs or flowerpots. In the warm season they are put out in the garden, and for the winter they are put indoors.
Indoor cypress is drying out - what to do?
The growth is about 5 cm in length, up to 10 cm in width. The needles are needle-shaped, adjacent, light green when blooming, later darker and shiny. The roots are dense, thin, superficial. This cypress variety needs moist and fertile, well-drained soil, ranging from acidic to alkaline. The location is sunny or semi-shaded. Planted individually or in small groups. Recommended for growing in containers.
Fig.2 Cypress pea “Filifera Nana”
Cypress pea 'Plumosa Aurea'. A straight-trunked tree with a wide-rounded crown, up to 10 m high, up to 4 m in diameter. The shoots are arched, the branches are feather-like, dense. The growth is about 20 cm in length, up to 15 cm in width. The bark is light brown, later long-fibered. The needles are needle-shaped, bright golden. The roots are thin, but strong and densely branched, superficial. Prefers moist and fertile soils, from acidic to alkaline; does not tolerate soil compaction. The location is sunny. In park compositions, cypress trees of this variety are used very widely.
Fig.3 Cypress pea “Plumosa Aurea”
Cypress pea 'Squarrosa'. A mutant exported from Japan to Belgium by Siebold in 1843. A straight-trunked tree with a conical crown up to 8 m high, up to 4 m in diameter. The branches are protruding, very dense, mossy-curly. Growth in length and width is up to 15 cm. The needles are needle-shaped, thick, soft, silvery. The roots are strong, dense, superficial. Soils need to be moist and fertile, from acidic to alkaline. The location is sunny. Used individually or in groups in gardens and parks.
Fig.4 Cypress pea “Squarosa”
Lawson's cypress 'Columnaris'. Bred in 1914 in Boskoop by Jean Speck. A straight-trunked tree with a narrow columnar crown 5-10 m high. The branches are directed upward, tight, thin. The shoots are densely located and short. The growth is about 20 cm in length, up to 10 cm in width. The needles are scaly, evergreen, tightly pressed, brown-green. The roots are strong, branched, with many adventitious roots. It is not demanding on soils: it grows on acidic and slightly alkaline, wet and dry, but is sensitive to compaction of the upper horizon. The location is sunny or semi-shaded. An excellent plant for a hedge. However, it can be planted singly or in groups.
Lawson's cypress 'Columnaris Glauka'. Obtained in Holland at the beginning of the twentieth century. A slender tree with a narrow pyramidal crown, about 10 m high, up to 2 m in diameter. The shoots are directed upward, the branches are thin, short, more branched at the bottom. The growth is up to 20 cm in length, 10 cm in width. The needles are scaly, densely adjacent, steel or bluish in summer, gray in winter. The roots are strong, densely branched, superficial. It is not picky about soils, but does not tolerate even slight compaction. The location is sunny or semi-shaded. Planted individually, in groups, and even in hedges.
Fig.5 Lawson cypress “Calumnaris Glauka”
Lawson's cypress 'Golden Wonder'. Received in 1955 by N. Bosmann in Boskoop, and re-selected there in 1963 by Jean Speck. a tree with a slender conical crown up to 7 m high, 3 m in diameter. The shoots are densely branched. The growth is up to 15 cm in length, no more than 10 cm in width. The needles are scale-like, tightly adjacent, golden-yellow when blooming, later light yellow. The root system is highly developed and superficial. Prefers fertile, moist soils, from slightly acidic to alkaline; does not tolerate compaction well. Any location is possible, but in an area protected from the wind. This cypress tree looks best in single plantings.
How to plant a cypress tree in the country
Cypress trees are often used as landscape design elements in the design of gardens, personal plots, home areas or for decorating summer cottages. They can be planted along alleys and paths; many people use it as separate architectural elements of the garden. Cypress looks great on the site as a background for flowers, for example, when growing rose bushes. Before planting a cypress tree, you need to decide on the choice of the required variety, and also take into account all the nuances associated with the size of the future tree, its growing conditions and the possibilities for caring for it.
Selecting a landing site
Cypress does not like heat and bright sun; the best place for it is partial shade. The only exceptions are those varieties whose needles have a golden hue; such trees prefer open sunny places. You should not plant it in lowlands where cold air accumulates; frosts are harmful to it. Cypress grows well on light sandy, slightly acidic soils with sufficient moisture; calcareous and heavy clay soils are not suitable for this tree.
Soil preparation
Planting holes for cypress should be prepared in advance, in the fall. Usually their depth is 0.7-1 m, diameter - 0.6-0.8 m. A layer of drainage made of broken brick or coarse crushed stone with a layer thickness of 0.2 m must be laid on the bottom.

The free space between the stones can be filled with sand. To fill the cypress roots, a special soil mixture is prepared, consisting of soil, sand, peat and humus, taken in a ratio of 1: 1: 0.5: 1.5.
Preparation of planting material
Cypress seedlings are usually purchased from specialized stores or nurseries. In this case, their root system must be closed, that is, the seedling must have a lump of earth on the roots or be sold in a special container. The plant itself should have a healthy appearance, the needles of the tree should be green without brown spots.
Cypress planting rules
Unlike fruit trees, which are planted primarily in the fall, cypress trees are usually planted in April or May, sometimes even in early summer. At this time, the soil warms up sufficiently. Before planting, a peg is driven into the bottom near the center of the hole, which will initially serve as a support for the future tree. The soil in the planting hole, as well as the lump of earth that is located on the roots of the cypress seedling, must be impregnated with Kornevin’s solution (root formation stimulator). After this, the seedling is placed in the planting hole next to the garter peg and covered with nutrient soil, holding it strictly vertically. From time to time, the soil around the tree trunk is slightly compacted to prevent voids from forming. The root collar should be 10-12 cm above ground level.
The planted plant needs to be watered abundantly. After the soil has settled, it is necessary to add soil so that the root collar of the tree is flush with the ground. The seedling needs to be tied to a stake to protect it from possible damage by the wind. The soil around the tree trunk must be mulched with peat, pine needles or small tree bark; this will significantly reduce moisture loss. Once firmly rooted, the tree can be untied from the support and the peg itself can be pulled out.
Care
Caring for plants is not difficult. In the first few weeks after planting, Red Star cypress needs abundant watering. Also, do not forget about loosening the soil and removing weeds. If you do not do this, the plants may be affected by diseases and pests more than usual.
Watering and fertilizing
For the first 2 weeks after planting, young seedlings are watered every day . At least 15 liters of water must be poured under one tree. Before irrigating the soil, it is better to loosen the top layer of soil so that moisture can better penetrate to the root system.
Did you know? It is recommended to keep several cypress branches in the house, as the plant fills the house with phytoncides. These substances are useful for the respiratory system and air disinfection.
From the third week, watering is carried out every week, using 10 liters of water. Adult cypress trees also need abundant watering . The irrigation interval is increased to 2 weeks. Use at least 12 liters of water per plant.
Fertilizers are applied 3 times during the growing season:
- in the spring , before buds form, water with a solution of potassium nitrate (30 g per 5 liters of water). For one tree use 10 liters of liquid;
- in summer , in mid-July, you need to add a solution of nitroammophoska (40 g per 10 liters of water), and pour the entire volume under each bush;
- at the end of October, cypress trees are fed with a solution of superphosphate (50 g per 10 liters of water). 12 liters of water are poured under one plant.

Loosening and mulching
Particular attention should be paid to loosening the soil before watering and fertilizing. This will ensure a better flow of nutrients and moisture to the roots, which provokes better plant development. You need to loosen the top layer of soil at intervals of 1 week . Thanks to such actions, a crust will not form on the surface, which can lead to rotting of the root system.
Important! Try to propagate the crop vegetatively to preserve varietal characteristics. If you propagate plants with seeds, the daughter trees will differ significantly from the mother trees (in height, shade, etc.).
Mulching the soil is carried out in October or November (depending on when the first frosts begin in your region). First you need to loosen the top layer of soil, water it and lay out a 20-centimeter layer of mulch. The best materials for this are humus or sawdust.

Trimming
The Red Star cypress variety does not need crown formation. And without regular trimming, the crown will be neat and symmetrical. Sanitary pruning is carried out in the spring, before sap flows in the trunk . It is necessary to remove branches damaged by frost or pests, and also trim dry shoots.
Video: Red Star cypress
Possible diseases and pests
Among the most common diseases that affect the red star cypress variety are gray rot and bacteriosis . Symptoms of the first disease include the appearance of plaque on the root system, and after a while the shoots and needles dry out. Treatment is carried out by spraying with copper sulfate (10 g per 8 liters of water) at intervals of 2 weeks. Against bacteriosis, which manifests itself in the form of brown spots on the surface of the needles and trunk, use a solution of Bordeaux mixture (30 ml per 5 liters of water). Plants need to be sprayed every 3 weeks.
Find out how to distinguish thuja from cypress.
Pests of this variety include:
- pine cutworm. It is necessary to fight it with “Fitoverm” (50 g per 10 liters of water);

- coniferous spider mite. It is recommended to use “Akarin” (20 g per 10 l of water) or “Kemifos” (50 g per 6 l of water);

- thuja bark beetle. For treatment use “Tiovit Jet” (20 g per 5 liters of water);

- aphid. To combat this parasite, use “Tanrek” (70 g per 10 liters of water).

All spraying against pests is carried out once a month. You can first irrigate the crown with strong water pressure to wash away not only dust, but also adult parasites.
Caring for cypress in the garden
In order for the cypress tree to maintain its beautiful appearance, it needs some care. The following activities must be carried out:
- watering;
- feeding;
- loosening the soil;
- mulching the tree trunk circle;
- pruning;
- preventive spraying against pests and diseases.
Watering and fertilizing
Cypress loves moisture, but cannot tolerate too much of it. Mature trees need to be watered at least 1-2 times a week at the rate of 1 bucket of water for each. In dry, hot weather, this figure should be doubled. Cypress responds well to high air humidity, so trees must be sprayed, especially during drought. Young trees are also sprayed with water at this time, since the heat significantly slows down their growth and development. After watering, it is advisable to mulch the soil around the trunk with peat, tree bark or wood chips to reduce moisture evaporation.

To feed cypress trees, complex mineral fertilizers are most often used, applying them in the form of an aqueous solution by the root method into the tree trunk. Typically, fertilizing is done once every 2 weeks from spring to mid-summer. From August, fertilization stops so as not to stimulate the plant to grow in the pre-winter period.
Important! For young trees, the concentration of fertilizers should be reduced by half.
Trimming
Cypress easily tolerates pruning. It is pruned for the first time no earlier than a year after planting or transplanting. In the spring, after removing the winter shelter, sanitary cleaning is carried out, cutting off frozen tips and broken branches. At the same time, formative pruning of the tree is carried out, giving its crown an appropriate pyramidal or conical shape.
Important! You cannot trim more than 1/3 of the green mass of the crown at a time.

In the fall, after the end of the period of active growth, sanitary pruning is carried out again, removing dried or damaged branches. At the same time, the current year’s growth is trimmed by 1/3, while maintaining the selected shape of the tree crown.
Cypress transplant
Due to the extensive system of horizontal roots, replanting cypress trees is associated with certain difficulties. To carry out the procedure painlessly, at least six months before the proposed transplant (or earlier), the tree is dug up onto the bayonet of a shovel, gradually cutting its roots. The procedure itself is carried out in mid-spring. The tree is replanted along with a lump of earth on the roots, and the sequence of actions is similar to planting a seedling. After transplanting the plant, it is necessary to water it abundantly.
Winter shelter for cypress
The root system of the cypress tree is located close to the surface, and in case of severe freezing of the soil it can be damaged. To protect it, the root zone around the tree trunk is covered with a thick layer of mulch made from sawdust, fine tree bark or other porous materials. To cover the above-ground part of the plant when preparing a cypress tree for winter, spruce branches are used or a special shelter is built around the tree. Most often they are a wooden frame covered with non-woven covering material.

Important! When covering trees for the winter, you cannot use plastic film, which does not allow air to pass through.
Cypress care
Temperature:
Moderate, cool in winter - at least 5°C, optimal wintering at 8-10°C.
From the end of May to the end of August, cypress
in the fresh air, in the shade and protected from drafts.
Hot air from central heating radiators is destructive for cypress. Lighting: Cypress needs bright diffused light, shading from direct sunlight, especially in summer. In winter, cypress needs a bright room. If in summer it is not permissible to keep cypress on an open windowsill (except for northern windows), then in winter you will have to move the cypress as close to the light as possible, even to the southern window, but only until the hot spring sun. With a lack of light, the cypress stretches out and loses its shape; on the contrary, with too much light, the leaves turn yellow and crumble. Watering:
Abundant from spring to autumn.
Moderate in winter. Cypress does not tolerate excess water and does not tolerate drying out of the soil. More precisely, drying out the earthen coma is simply destructive for the conifer. Watering in winter depends on the room temperature, for example, when kept at a temperature of 8 ° C, watering will be approximately once every 10 days, and at a temperature of 12-14 ° C once every 5-7 days. Air humidity: Regular spraying in spring and summer. If in winter it is not possible to provide the cypress with a cool room, then it should also be sprayed with warm water in the morning and evening. Fertilizer feeding:
From May to August, cypress is fed with liquid mineral fertilizer for indoor plants, the fertilizer is taken at half the recommended dose.
Feeding is carried out once a month. Transplantation:
Annually in spring, in April - May.
Cypress does not tolerate injury to the root system very well, so complete replanting with replacement of soil is only necessary, but usually transshipment is used, with partial replacement of the top layer of soil. Simply put, they replace only that soil that is easily separated from the roots itself if the conifer is removed from the pot. Soil for cypress - 1 part turf soil, 2 parts leaf soil, 1 part peat soil, 1 part sand. Cypress loves loose soil; when replanting, make sure that the root collar is not buried in the ground, otherwise the plant may die. Good drainage is a must. Reproduction:
By lignified cuttings in spring and summer. Seeds in spring.
Cypress propagation
You can propagate cypress trees yourself. To do this, you can use one of the following methods:
- seed;
- cuttings;
- layering from the mother tree.
It must be remembered that the seed method will retain only the species characteristics of the tree; all varietal components will be lost. To propagate varietal cypress species, vegetative propagation methods, for example, cuttings, should be used.
Cypress propagation by cuttings
To prepare cypress cuttings, use the lateral branches of adult trees, the apical shoots from 5 to 15 cm long are cut from them. The lower part of the cutting is freed from needles, after which it is planted in a container filled with a mixture of perlite and sand (in a ratio of 1:1) with the addition of a small amount of coniferous bark. The nutrient substrate is moistened, then the container is covered on top with plastic film, simulating greenhouse conditions. After about 4-8 weeks, the cuttings will take root if you maintain constant humidity close to 100%.

It is also possible to plant cuttings in open ground. At the same time, they are covered with plastic bottles with the neck cut off. If rooting goes well, the cuttings can be left in open ground for the winter, having previously covered them. If root formation is weak, the plants are taken to a warm room for the winter.
By layering
To obtain layering, you need to carefully bend one of the lower branches of the cypress tree to the ground. At its lowest point, an incision is made, which will later become the center of root formation. To prevent the walls of the cut from closing, a small pebble is placed between them. The shoot is carefully placed in a dug trench, secured with a wire clamp and covered with earth. Along with watering the mother tree, you should also water the site of the future cutting.
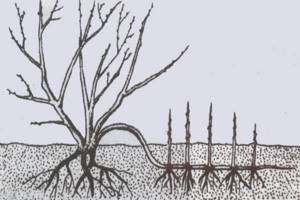
By autumn, the cuttings will have formed their own root system, but you should not rush, you need to leave it to overwinter along with the mother tree. It will be possible to cut it off from the donor branch next spring, in April, and then transplant it to a permanent place in the usual way.
Seeds
Properly collected and dried cypress seeds remain viable for 15 years. Before planting, they are subjected to stratification. To do this, the seeds are placed in a container with a light soil substrate and buried in the snow. You can also use a regular refrigerator. In spring, the container is opened and placed in a warm place (+ 20-23 ° C), well lit, but without direct sunlight. If everything is done correctly, shoots will appear in a few weeks.

When plantings are dense, seedlings need to be pruned. As soon as the air temperature rises above 0 °C, the container with planting material must be taken outside daily, gradually hardening the plants. After the seedlings have grown stronger, they are planted in open ground, in a slightly shaded place. The first winter the seedlings should overwinter under cover.
Thuja cypress (Cypress thuja)
The species is native to the western United States and is distributed along the entire Atlantic coast. Often found in the Appalachians, where it grows at an altitude of 460 m above sea level.

IN THE PHOTO: Cypress trees in nature. Photo by Donald Cameron.
This variety of Cypress resembles Thuja in appearance, which is why it got its name.
Description of the plant:
Plant size and type:
An evergreen tree 20–28 m high, less often up to 35 m in its natural environment. When grown in gardens, it usually grows up to 2–3 m; in a container it reaches a height of 1–1.5 m.

IN THE PHOTO: Compact container specimens of Thuja cypress. Photo by rainbowgeorgescu.
Root system:
The root system is highly branched, with fairly small hairs. The degree of growth of the underground part of the plant greatly depends on the composition and moisture of the soil.
Trunk and shoots:
The trunk is straight, up to 0.8 m in diameter. Shoots cover ¾ of the trunk. The branches are thin, gradually expanding, slightly flattened. The color of the bark of the trunk and branches varies from ash-gray to brownish-reddish.

IN THE PHOTO: The bark of a plant trunk. Photo by keara.giannotti.
The bark of young specimens is smooth, but as they grow, it cracks and becomes irregularly furrowed.
Crown:
The crown is lush, narrow, mostly cone-shaped.
Leaves:
Seedlings up to one year old have needle-like leaves. Later they become scaly, 2–4 mm. length. The arrangement of leaves on the shoots is in pairs and opposite.
The foliage of Cypress arborvitae emits a light and pleasant “cedar” aroma.

IN THE PHOTO: Needles of a young Thuja cypress.
The color of the needles of the species specimen at a young age is blue-green. In the second year of life, the leaves acquire a brownish color and subsequently retain this color throughout the entire life cycle of the plant.
Peduncles:
Peduncles are solitary, in the form of short petioles.
Flowers:
The flowers are small and undecorative. Female flowers develop on short branches, male pollinators grow at the tips of the shoots. The color of female flowers is green, male flowers are yellow or reddish.
Bloom:
In the middle zone it blooms in April.
Fruits and seeds:
The cones are spherical, with a diameter from 4 to 9 mm. The cone of Cypress arborvitae is covered with 6–12 scales, each of which protects one or two seeds. The color of immature buds is green or purple. By the time they ripen, the fruits become brown in color.

IN THE PHOTO: Cypress cones a year after ripening. Photo by Valery Kudeli.
The cones open in the second half of autumn, releasing an average of 5–15 mature seeds. The seeds are round, 1 mm in diameter, red-brown in color. The older the tree, the more seeds it produces each year.
Popular varieties:
Popular tall varieties of Thuja cypress are 'Aurea' and 'Andelyensis'.

IN THE PHOTO: Cultivar 'Andelyensis'. Photo by American Conifer Society.
These cultivars grow up to 3–5 m, ideal for creating hedges, landscaping parks and gardens, and single ornamental plantings. The crown of 'Andelyensis' is pyramidal, while that of 'Aurea' is conical.
Both varieties are distinguished by highly decorative foliage color, which changes depending on the season. The needles of 'Aurea', yellow in the warm season, take on a bronze hue in winter. The green foliage of 'Andelyensis' becomes purplish with the onset of cold weather.
Visually similar to 'Andelyensis', the 'Little Jamie' variety differs from it in its conical crown shape and more compact size, up to 130 cm in height. Therefore, 'Little Jamie' is better suited for an alpine slide or container.

IN THE PHOTO: Compact variety 'Little Jamie'. Photo by DensiFlora.
Juvenile forms of the cultivar 'Ericoides', whose height does not exceed 180 cm, are also often grown.

IN THE PHOTO: Thuja cypress 'Ericoides' in winter colors. Photo by sam-pratt.
Common varieties of Thuja cypress with blue needles: 'Glauca', 'Hopkinton', 'Blue Sport'. With their help, they create interesting color accents in the landscape of a garden, front garden or flower bed.
The 'Variegata' cultivar is suitable for planting in a bright place with light shade. It is notable for its decorative spotted foliage in various tones of golden color.

IN THE PHOTO: Variegated variety 'Variegata'. Photo: Wollemia.ch.
Agricultural technology:
Temperature:
It belongs to the winter-hardy varieties of Cypress, but during severe, prolonged frosts it needs shelter. Room contents are moderately warm, at +18–23°C.
You can learn about the nuances of keeping and caring for Thuja cypress in a container from the publication: “Coniferous plants in the house - mission possible.”
Lighting:
Light-loving crop, grows well in the sun. At the same time, to avoid burns, the needles should not be placed in direct sunlight for more than a few hours a day.

IN THE PHOTO: A south-east or south-west window is suitable for indoor Cypress arborvitae. Photo by gabortakacs92.
Requires protection from the scorching spring sun after winter dormancy, especially when young.
Watering and spraying:
Water as the earthen ball with roots dries. Overwatering is dangerous because it provokes rot of the plant roots. Thuja cypress growing in open ground is watered only in the dry months.
When the air is dry, the needles of indoor and outdoor specimens are moistened by spraying. Otherwise, it loses its decorative effect.
Substrate:
Peat-sandy nutrient soil with drainage is preferable. Grows best in acidic, slightly acidic and neutral soils.
Transfer:
When kept in a container, the young plant is replanted annually in the spring. For a mature specimen, replanting once every two to three years is sufficient.
Feeding:
Excess nutrients, especially organic ones, are unsafe for tree roots. Therefore, the plant is fed only at a young age or when growing in very poor soil. You can use any complex fertilizers for coniferous crops.
Trimming:
Rarely requires pruning due to slow growth rate. If necessary, it is done in the spring.

IN THE PHOTO: Bonsai from Thuja cypress. Photo by bonseiart.
Diseases and pests:
Like many coniferous plants, it is very vulnerable to pathogens of fungal diseases. Therefore, preventive treatment with fungicides is desirable: Fitosporin-M, Bordeaux mixture, Abiga-Pik and other preparations based on copper oxychloride.
It is important to protect Cypress from scale insects, spider mites, spruce aphids, and mealybugs. For this purpose, Karbofos, Actellik or Aktara are used. To avoid the destruction of roots by nematodes, you can treat the soil and root system before planting with Vidatom-L.
Reproduction:
It is usually propagated by seed or grown from cuttings taken in the spring.
The title photo of the article is by Michael Pascoe.
Editorial team LePlants.ru
Why does cypress dry out?
The main reason for drying out of cypress trees is lack of moisture. Often, a plant's needles evaporate more water than its roots can absorb. Therefore, it is so important to regularly spray the tree crown, especially in hot weather.
If the yellow color that appears on the needles is not related to the peculiarity of the cypress variety, this may indicate a lack of magnesium or excess calcium in the soil. Alkalinization of the soil, which is indicated by an increased calcium content, can be removed by adding high-moor peat to the soil, which gives an acidic reaction. The mineral composition of the soil and acidity level can be accurately determined using chemical analysis.
In addition to insufficient watering and unbalanced nutrition due to poor-quality soil, the cause of yellowing and wilting of cypress trees can be damage by diseases and pests.
Indoor cypress is drying out - what to do?
The growth is about 5 cm in length, up to 10 cm in width. The needles are needle-shaped, adjacent, light green when blooming, later darker and shiny. The roots are dense, thin, superficial. This cypress variety needs moist and fertile, well-drained soil, ranging from acidic to alkaline. The location is sunny or semi-shaded. Planted individually or in small groups. Recommended for growing in containers.
Fig.2 Cypress pea “Filifera Nana”
Cypress pea 'Plumosa Aurea'. A straight-trunked tree with a wide-rounded crown, up to 10 m high, up to 4 m in diameter. The shoots are arched, the branches are feather-like, dense. The growth is about 20 cm in length, up to 15 cm in width. The bark is light brown, later long-fibered. The needles are needle-shaped, bright golden. The roots are thin, but strong and densely branched, superficial. Prefers moist and fertile soils, from acidic to alkaline; does not tolerate soil compaction. The location is sunny. In park compositions, cypress trees of this variety are used very widely.
Fig.3 Cypress pea “Plumosa Aurea”
Diseases and pests
Cypress trees get sick relatively infrequently. Among the diseases, the greatest danger is late blight root rot, which appears due to stagnation of water in the roots of the plant. At the same time, no traces of disease are observed on the root collar of the tree. Wilting begins with individual branches, gradually the entire tree turns gray and dies. Root rot can only be combated at an early stage of its appearance. To do this, the cypress tree is dug up, the roots are washed, and the rot is cut off to a healthy root. At a later stage, such a measure will not help; the tree must be destroyed.

Among the pests that most often attack cypress trees, the following insects pose a danger:
- Aphid.
- Spider mite.
- Shield.
- False shield.
- Thuja leaf miner.
To combat these insects, trees are repeatedly sprayed with various preparations: acaricides, insecticides, and complex preparations with a wide spectrum of action. However, it is not always possible to achieve complete destruction of pests. Sometimes a heavily infested plant must be dug up and burned to prevent the insects from spreading to neighboring trees.
Pests of outdoor and indoor cypress
In order for your plants to be protected from pests, you need to know what kind of parasites can live on your plant.
The main pests of indoor cypress
Cypress needs to be constantly “inspected” for the appearance of pests and damage by them. Most often these are aphids, scale insects and spider mites.
You will notice the presence of spider mites on your plant if white cobwebs appear on the branches. Insecticides are used to combat it. For example, “Vermitek”, “Aktofit”, “Fitoverm”. You may have to reuse these medications. Folk remedies such as soap solution will be effective in the fight.
Important! Separate medications have not yet been invented to treat scale insects, so any remedy for indoor insects can be used to combat this insect.
The scale insect sucks the juices out of the plant, and the tree dries out. Brown spots on the trunk are the first sign of scale insects. The fight against this insect consists of treating with soapy water and any of the insecticides. You can collect insects by hand, but be sure to do this with gloves.
Aphids are white insects that live on the inside of leaves. It can only be destroyed with special preparations, the treatment of which will have to be repeated.
Outdoor cypress pests
Juniper scale insects and seaside mealybugs are very common. If you notice caterpillars on your bush, this is a sign of damage to the bush by gypsy moth butterflies and juniper cutworm. These insects damage buds and cones. Insects can also damage the trunk and bark - this is done by pine beetles and bark beetles. If you notice pine beetles on your cypress tree, then the branch damaged by this insect must be cut down and the cut treated with oil paint. In order to destroy bark beetles at an early stage, you should inject the bark with the drug "Aktelik". In May-June, plants are treated with drugs such as Fufanon and Profi.
In order for your cypress to exude health and evoke only positive emotions in you, it is necessary to properly care for it and protect it from all kinds of pests and diseases.











