Disease Prevention
Creating beauty in a personal plot, this plant, like its fellows, is susceptible to disease and invasion of harmful insects. To avoid the latter from destroying the living fence, the following principles of care must be adhered to.
- Pests that traditionally attack plant leaves, such as aphids and insect larvae, do not like it when potassium and phosphorus are found in the liquid media of the plant. Irrigation of honeysuckle bushes with a mixture of lime and superphosphate will help provide these substances. You can also include a little ash in the composition.
- Harmful insects will not settle on the plant in winter if a composition containing urea is sprayed around before dropping the leaves.
- In summer, regularly treat honeysuckle bushes with insecticides.
Drying of honeysuckle branches
This plant retains its excellent appearance if you carefully monitor its health, destroy harmful insects in a timely manner, prevent other diseases, and also take care of the formation of a beautiful crown.

Blooming honeysuckle honeysuckle
Honeysuckle honeysuckle is a wonderful way to decorate the landscape of a garden plot. Thanks to it, you can control light and shadow, zone space and create recreation areas and living fences from lashes.
Description of Honeysuckle Honeysuckle
Honeysuckle Honeysuckle has a pleasant aroma and unique flowers, creating comfort and shade in the garden or in the gazebo. In the wild, the plant is found in southern Europe, in the Caucasus mountains, and lives up to 50 years.
The original name of honeysuckle Honeysuckle is Lonicera caprifolium, which means “folium” - leaf, “carpa” - goat
These curly bushes up to 6 m long have different shades of colors and always attract the attention of passers-by
Appearance
The shrub has bright green ellipsoidal leaves, vertically growing branches 4-5 m long (depending on the age of the honeysuckle). Gray-green shoots turn red in the sun and tightly wrap around any support. The leaves gradually grow together into a disc, in the middle of which first a flower is formed, then a bunch of ripe berries.
Honeysuckle flowers have a subtle pleasant aroma and decorative appearance. They become a source of inspiration and a symbol of beauty, but they are not edible and do not contain medicinal properties. This is a characteristic difference between Honeysuckle and other varieties of honeysuckle. The plant smells intensely in summer, and the aroma intensifies in the evening.
Honeysuckle has red, blue, purple, white and yellow flowers. When ripe in late July or early August, they turn deep orange or bright red. Each flower individually lives no more than 3 days, after which it fades. The flowering period of the entire shrub lasts no longer than 3 weeks.
Growth
If there is support, honeysuckle grows up to 6 m in length. Thanks to this property, the shrub becomes a vertical gardening for summer cottages and garden plots. For proper growth, form the bush during the planting period, find reliable support for it. Otherwise, honeysuckle loses its decorative appearance.
In the wild, Honeysuckle is found on sunny edges and in forests, and grows up to 1 meter in length in a year. Due to its beauty and vertical tortuosity, it has been planted in Russian gardens since the 19th century.
Varieties of honeysuckle
Honeysuckle is considered the most beautiful representative of honeysuckle among 10 varieties. Gardeners are attracted by the variety of colors and shades, the preservation of the decorative appearance even after the bush has flowered. The most popular honeysuckle varieties Honeysuckle with a brief description:
- Few-flowered. The bush is pale red in color with a small number of flowers.
- Alba. Early flowering bush, blue or white flowers.
Other decorative varieties of honeysuckle are also used to create landscape design:
- Inga. Flowers are white, pink, red and yellow with an intense scent, collected in capitate inflorescences.
- Telman. The flowers are hot yellow in color with a moderate aroma and look like lights on the bushes.
- Belgica Select. The flowers are purple or pink, the fruits are red. The plant blooms 2 times a year - in May, then in August-September.
- Harlequin. The flowers are pale pink in color with a moderate aroma, decorating many gazebos in the garden.
- Graham Thomas. The flowers are long, white-yellow in color with a pleasant aroma. They bloom from the second half of July to September.
Some useful properties
Few people know that honeysuckle flowers contain essential oils that are aphrodisiacs. An alcoholic extract is prepared from the flowers for use in perfumery and homeopathy. It is able to heal wounds, has anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effects.
It is not without reason that this beautiful plant is loved by gardeners. With very little effort, you can grow it in your garden and admire honeysuckle for a long time
- Author: Maria Sukhorukikh
Rate this article:
- 5
- 4
- 3
- 2
- 1
(0 votes, average: 0 out of 5)
Share with your friends!
Types and popular varieties
The genus Honeysuckle includes up to 200 species of shrubs and vines, including crops with edible fruits. In gardening, preference is given to decorative climbing species. Their densely leafy stems rise high, the flowers are unusually beautiful and often fragrant. The fruits are painted in bright colors. In climbing vines they are often poisonous.
The most ancient and famous cultivated species of honeysuckle is honeysuckle. Honeysuckle (or fragrant). This vine blooms earlier than others, in June. Cream or pink-yellow lush flowers bloom in the late afternoon and fill the entire garden with their aroma, attracting butterflies. From mid-summer the flowers darken, even to brown shades. In autumn, honeysuckle is strewn with brightly colored fruits, turning red in a ring of large fused leaves. This species is winter-hardy.

Honeysuckle Honeysuckle
Much more thermophilic. Curly (German, Lithuanian). Its white, pink or purple flowers are excellent honey plants, and its purple fruits are poisonous. The most striking variety of this species is “Serotina”. The vines of this variety are decorated with crimson flowers.
North American species Brown in the middle zone requires shelter for the winter. It has very decorative foliage, dove-blue below and bright green above. Large tubular flowers are carrot-colored. The variety "Dropmore Scarlet" is interesting because of its orange-colored flowers.

Brown's honeysuckle
The hardiest species is the w. Tatar. In May, the entire bush is covered with small white or pink flowers. Varieties "Amold Red" and "Morgen Orange" - with red, "Elegant" - with striped bright red flowers.

Honeysuckle Tatarian
It is famous for its abundant flowering. Korolkova. Its soft pink flowers cover the bush so tightly that neither branches nor foliage are visible.

Honeysuckle Korolkova
Unlike other species, g. Geralda does not shed its leaves for the winter. In the spring, when young shoots begin to grow, last year's foliage falls off. The yellow flowers are very fragrant.

Gerald's Honeysuckle
Autumn feeding of honeysuckle after fruiting
The shrub really loves fertilizing with organic matter, and you can simply give it by sprinkling it under the bush (for example, as mulch) once every 3-4 years (it is believed that the most suitable fertilizer for honeysuckle is rotted horse manure = humus ).
In general, the feeding scheme for honeysuckle during the growing season is as follows:
- after fruiting (in autumn) - phosphorus and potassium fertilizers (Superphosphate + Potassium Sulfate, Diammofoska, Potassium Monophosphate or any ready-made complex fertilizer marked “Autumn”).
And if you are a supporter of organic farming, then your choice for autumn is bone meal (phosphorus) + wood ash (potassium).
- in early spring - nitrogen fertilizers (ammonium nitrate or similar, optimally - humus or compost).
- during the period of flowering and the beginning of fruiting (including for climbing inedible honeysuckle) - complex fertilizers that contain all the main macroelements.
Features of growing different types of ornamental honeysuckle in the regions
Among the types of decorative honeysuckle there are climbing and erect ones. It is the climbing honeysuckle that is grown much more often than others.
erect honeysuckle
Of the erect species, Tatarian honeysuckle (a dense shrub up to 4 meters in height) and Korolkov's honeysuckle (well-cut, used for highly decorative hedges) are more or less known. Both species are quite drought- and frost-resistant and are grown in various regions; they often do not require shelter for the winter, especially for Tatarian honeysuckle.

Many erect types of honeysuckle are also very decorative during the flowering period.
Alpine honeysuckle (a shrub no more than a meter high) is shade-tolerant and winter-hardy, grows for many years and can also be planted in almost any climate. Honeysuckle (a shrub up to 3 meters high with beautiful flowers) lives up to 100 years, is not afraid of severe frosts, but requires high soil moisture.
climbing honeysuckle
Of the vines (climbing species), honeysuckle is the most widely known. In addition to it, a honeysuckle called “German honeysuckle” is planted for decorative purposes, blooming with large flowers that attract bees, but it is much more thermophilic and feels good only in warm regions. A very picky vine called Brown's honeysuckle: it can only grow on highly fertile soils and does not tolerate dry weather. Gecrotte's honeysuckle makes similar demands.

Brown's honeysuckle has very original flowers, but it is more difficult to grow than honeysuckle.
Thus, we can say that among the types of decorative climbing honeysuckle, only honeysuckle is relatively unpretentious, which, thanks to its properties, is planted in almost all regions of our country, except the very north. In the northern regions, for growing honeysuckle it is necessary to create special conditions, especially carefully covering it for the winter.
The agricultural technology of decorative honeysuckle is radically different from the agricultural technology of edible honeysuckle. For the latter, the conditions of cold regions are preferable to those of the south: in heat and drought, edible honeysuckle grows poorly and bears little fruit. Edible honeysuckle is rarely cultivated south of Tambov or Samara, and in Crimea and Ukraine its cultivation is of no practical importance.
Decorative honeysuckle, on the contrary, is much easier to grow in the south: there the vine does not even need to be removed from its supports for the winter, but in cold regions it is necessary to protect the honeysuckle from frost. In the wild, honeysuckle grows in the Crimea, the Caucasus and European countries; it is even called Italian honeysuckle. Just as it grows for many decades in the Crimean forests, not knowing what winter is, so in gardens and near houses it also feels calm in winter.
Where the temperature in winter drops below 20 degrees below zero (this is a guideline), honeysuckle must be protected from frost. It grows successfully both in the Moscow region and even in the Leningrad region. Some lovers, at their own risk, do not cover honeysuckle for the winter. Some varieties actually tolerate frost well, but many freeze slightly from the tops. They are subsequently restored, but this takes time and effort. Therefore, at the end of October in problem regions, vines are lowered from their supports and covered, for example, with coniferous spruce branches or spunbond. This is especially required for young plants, in the first 2–4 years of life.

It is not easy to cover vines, but in harsh climates it is necessary
In Crimea, as in other southern regions of our country and Ukraine, honeysuckle grows well and blooms profusely. It is usually planted in the spring, choosing a place according to the principle “head in the sun and feet in the shade,” that is, where the flowering will be in the sun, and the roots are covered from the heat so that the soil moisture does not evaporate. The Crimean climate, not to mention the coast, is famous for its heat and dry air, so you have to water the vine often. When feeding, try not to overdo it with nitrogen, so that the foliage does not fill the entire vine to the detriment of flowering. Otherwise, honeysuckle care in the region follows general rules.
Video: honeysuckle in Siberia
There are many types of decorative honeysuckle, but climbing ones are especially valued, among which honeysuckle stands out. It is used to decorate the walls of houses, gazebos, and fences: the vine looks great both during flowering and with red fruits. Caring for decorative honeysuckle is simple; it is grown in almost all regions.
First meeting
A beautiful liana has settled in the gardens for a long time. “Captivating dreams” - in the language of flowers, it is mentioned even in ancient Greek literature as a symbol of devoted love. At one time, it was customary to give bouquets of honeysuckle honeysuckle to a loved one as a sign of fidelity.
This ornamental plant can be found in all regions of Europe except the northern ones; it also feels good in the Caucasus. The liana grows up to four, and sometimes up to six meters. In sunny places, its foliage becomes dark green, and young shoots have a purple-red hue. In the shade the shoots are light green. Elegant foliage remains until late autumn.

The long, graceful flowers last on the stem for 3-4 days, and the total flowering period is only about three weeks. But then orange or red berries appear on the leaves in the very core. The fragrant liana blooms only in the fourth year after planting, but its lifespan is 50 years. Gardeners distinguish two varieties of honeysuckle: few-flowered, whose flowers are painted in pink and red shades, and white - its flowering lasts two weeks less.
Advantages and disadvantages of honeysuckle honeysuckle
It is worth listing some of the advantages of honeysuckle honeysuckle, as well as some of its disadvantages. Of course, the plant has a sufficient number of advantages, and honeysuckle has been included in the category of a designer plant by many designers.
We list a few positive features that make honeysuckle stand out from many other plantings:
Honeysuckle is very easy to care for; it gives excellent flowering, which makes it very decorative; there are a huge number of colors and shades that honeysuckle gives when flowering; Honeysuckle very quickly adapts to weather conditions, no matter where it grows or ends up; Honeysuckle gives off a very pleasant aroma; it can produce active growth even if it is located in conditions that are not the most favorable for itself; Honeysuckle can grow to such shapes and sizes that it becomes a magnificent hedge in areas; thanks to the honeysuckle honeysuckle, you can create shade in your garden plot, and all this will be in the fresh air - as you need after a long working day to relax; Honeysuckle is characterized by high immunity and stress resistance, as this is very important for any plant that grows in personal plots.
Of course, when a gardener chooses certain varieties, he should also pay attention to the fact that honeysuckle has its drawbacks. Because of them, the impression of the plant can deteriorate too much, and sometimes honeysuckle can cause some trouble in caring for
- Honeysuckle fruits are not edible at all; they can also be simply decorative and slightly poisonous.
- Flowering goes by very quickly, some complain that sometimes they don’t even have time to enjoy it - the flowers fade in literally three days.
- The branches need to be trimmed periodically, as this is a very tall and climbing plant. And in order for it to look neat and not thickened, you need to carefully care for it. The support must be formed in advance, because its presence will determine how the plant will look and how it will feel.
- When transplanting honeysuckle, the external characteristics may noticeably suffer, so initially the plant should be planted in such a way that it feels comfortable in a given area.
- The bush should be shaped and should also be watered regularly - these are also the conditions that should be followed when caring for honeysuckle.
Design solutions
The climbing vine serves as an excellent backdrop for highlighting many other plants in the landscape. This is an ideal option for decorating gazebos or disguising outbuildings.
It is vertical gardening that will help hide many of the imperfections of the site!
You can find many photos with examples of successful solutions in landscape design using honeysuckle honeysuckle.

It can serve for:
- masking walls;
- creating a hedge;
- demarcation of garden zones;
- creating shadows, etc.
Selecting a site, preparing holes
Every gardener can grow a plant, regardless of his skill level; the main thing is to choose the proper place for growing, prepare planting holes and provide all conditions for care.
For planting, it is preferable to choose the side from the south. Light partial shade will not affect flowering and fruiting. If you plant the plant in a heavily shaded place, the growth will not slow down, the shoots will continue to spread, but the flowers will not appear as intensely. Climbing species grow in both light shade and sunny areas. Lianas climb well if the stems receive sunlight.

Since the flowers of decorative honeysuckle attract bees and other insects, the plant should be planted away from the gazebo where people sit to relax. Support structures for climbing varieties are best built and installed immediately before planting, so as not to damage the roots when the plant begins to grow. Obelisk supports look very attractive and impressive. They can be made from different materials: metal (the strongest and most reliable support), willow rods and wooden slats.
Did you know? You can grow a home bonsai from Japanese honeysuckle by properly forming and twisting the shoots.
Honeysuckle grows well in a variety of soil types, but like many other plants, it prefers well-drained, loose, humus-rich soil. Decorative honeysuckle does not like soils with predominantly sand and clay, as well as wetlands. Soils with a neutral alkaline reaction (pH from 5.5 to 8) are well suited.
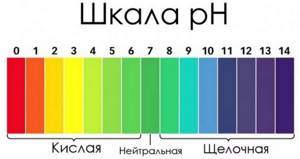
Planting holes must be prepared in advance (2-3 weeks before planting), digging them to a depth of 30 cm. The diameter of each hole should be 30–40 cm, depending on the size of the root system. Broken tiles, bricks or pebbles are used as drainage. The holes are filled with organic substances: compost, peat, a small amount of coniferous tree bark and minerals - 20 g of nitrophoska per plant.

Selection and preparation of planting material
Saplings with an open root system can be 2-3 years old. They should have 2-3 shoots 40–50 cm long
You should pay attention to the appearance of the growths. There should be no dryness or cracked bark
They should bend freely. Peeling on the bark is possible - this is normal.
The roots of the plant should be free of signs of rot. The presence of several kidneys is mandatory. It is advisable to buy seedlings from trusted suppliers, nurseries or at garden exhibitions.
You need to get complete information about the plant from them:
- exact name of the variety;
- features of planting and care.
Find out how to properly plant honeysuckle seedlings in the ground in the spring.
Planting scheme
Honeysuckle is an unpretentious crop, but when planting it is necessary to follow all stages, without ignoring any of them. It should also be taken into account that the chosen location will be permanent, since honeysuckle is not replanted. It grows in one place for at least 20–25 years or more.
- Drainage material is placed in the prepared hole, enriching it with fertile soil and minerals.
- Pour water into the planting hole -5 liters.
- The seedling is installed so that the root collar is not level with the soil surface.
- Water the plant in stages so that water slowly fills the soil.
- Mulch the soil with compost, dry leaves or humus. The layer should be 4-5 cm.

General rules for preparing for winter
Honeysuckle is a climbing or erect bush, the blue berries of which are widely used in folk medicine. Thanks to many beneficial substances, berries have a beneficial effect on the cardiovascular system. They are used to strengthen the walls of blood vessels, lower blood pressure and prevent the risk of developing arteriosclerosis. According to encyclopedic data, there are more than 800 species of this culture in nature. Some shrubs perform an exclusively decorative function, others are used in medicine and cooking.
So, preparing honeysuckle for winter begins at the very beginning of autumn. During this period, feeding plants in the garden with nitrogen-containing preparations stops. Only potassium-phosphorus additives are added to the soil. The soil is moistened to a depth of about 80 cm. Please note that if autumn is damp and rainy, water-recharging irrigation is not necessary.
Autumn is considered the ideal time to transplant a honeysuckle bush. During the time of rest and rest, the plant will have time to adapt to new growing conditions, strengthen and relax. With the arrival of the first spring warmth, the bush actively grows. Preparing honeysuckle for frost involves anti-aging pruning of the crown. All old branches, damaged by precipitation and damaged by insects, need to be trimmed from the bush.
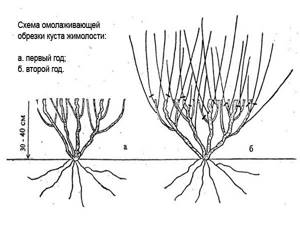
By its nature, honeysuckle is highly frost-resistant. The plant can withstand even severe Siberian frosts, but is afraid of sudden changes in temperature conditions. For this reason, it is recommended to carefully prepare the shrub for wintering.
Decorative honeysuckle: types and varieties
Decorative honeysuckle most often includes species with a climbing bush shape. They bloom profusely at the turn of spring-summer, so these species are successfully used in landscaping.
climbing honeysuckle
Here we can distinguish two main types that are most popular - honeysuckle and Brown's honeysuckle. The first one spreads its branches to 6 meters, but can only climb up to 2.5 meters up the support. Honeysuckle entwines everything in its path. Decorative honeysuckle is suitable for decorating a romantic corner, such as a gazebo. It makes a wonderful hedge.
Important! Honeysuckle is a heat-loving plant, and it may not survive on the north side.
In regions where there are cold winters, Brown's honeysuckle does not bear fruit. "Fuchsioides" "Dropmore Scarlet".
Bush honeysuckle
The most popular variety of shrub species is Tatarian honeysuckle.
This plant is perfectly adapted to harsh winters. The shrub reaches a height of up to 2.5 m, and begins to bloom at the age of three. Towards the end of spring, honeysuckle turns pink, which later becomes red berries. The color of the flowers varies among varieties.
Important! If the soil in your garden is not fertile enough, it is recommended to plant several bushes of Zabelli honeysuckle in a sunny place. It is unpretentious to natural conditions, grows up to one and a half meters, and beautiful crimson flowers grow on it.
Alpine honeysuckle.
Reproduction methods
There are three ways to propagate honeysuckle: seeds, layering and cuttings. With proper care of the sprout, each of these methods allows you to get a new plant.
By layering
A simple method of propagation that gives 100% results. At the beginning of summer, the lower branch (over 1 year old) of the bush is pressed to the soil and sprinkled with earth. The top is left outside. By autumn, the shoot will take root, however, it will be possible to separate it from the mother plant and transplant it to a new place only next spring.

Seeds
When propagating honeysuckle by seeds, you will have to wait several years for a full-fledged plant. Seeds are collected in the fall and immediately sown in open ground or in cups with peat substrate. In the case of artificial cultivation, the sprout must be monitored, watered regularly, and planted in open ground in the warm season. Honeysuckle seeds sprout without stratification.
Cuttings
In summer, you can cut lignified cuttings 10 cm long from the top of the bush, tear off the leaves and put them in water. In order for the branches to take root, they are stimulated to form roots. The shoots are placed in water with a plant that already has roots.
After the roots appear, the cuttings are planted in cups with substrate. Throughout the year, the sprouts are kept indoors, cared for, watered, and in the spring they are transplanted into open ground.
Planting and care
One of the advantages of this culture is its unpretentiousness to soil and care, but even here there are aspects that cannot be ignored.
Honeysuckle Honeysuckle should be planted in a place where there is support: a fence or the wall of a building; you can also install trellises, because it is a climbing crop.
Honeysuckle fragrant prefers sandy or loamy, fertile, loose, moist soils and well-lit areas. The pH level of the soil should be 7.5-8.5; if the values are more acidic, you can add lime.
The landing site should be away from swamps and groundwater, and also protected from the wind.
Plant the shrub as follows:
- Two weeks before planting, the soil is dug up and rotted manure is added.
- Dig a hole 50 cm deep and the same width.
- Drainage made of crushed stone, broken brick, expanded clay or pebbles is laid at the bottom of the pit.
- Then add a soil mixture of turf soil, sand, peat, humus in a ratio of 3:1:1:1.
- The seedling is lowered into the prepared hole with the roots straightened.
- Sprinkle with soil, and the root collar should rise above the surface by about 5 cm.
- Water generously.
- After the water is absorbed, the tree trunk area is mulched with peat or sawdust or wood ash.
Bushes should be located at a distance of at least 1.5 m from one another if plants are planted in holes. And at least 1 m if planted in a trench. Planting in a trench is carried out in the case of the formation of a hedge.
Honeysuckle will take root well if planted between August and October. They also practice spring planting, but here it is necessary to take into account that in May-June the fragrant vine is actively growing and there may not be enough strength for high-quality rooting.
- Water generously with warm, settled water in the amount of one or two buckets per plant, as needed, the soil under the bushes should not dry out.
- Loosen the soil in the tree trunk circle.
- Be sure to pull out weeds.
- Mulching the area under the bushes will keep the soil moist longer and slow down the development of weeds, and mulching with humus and wood ash will allow the honeysuckle to receive additional nutrients.
- Feed in the spring with complex fertilizers or rotted manure, compost, humus, vermicompost.
- When carrying out formative and sanitary pruning, it is important not to overdo it, otherwise you may not be able to wait for flowering next summer.
Reproduction of honeysuckle honeysuckle
Honeysuckle is propagated in several ways. Each option has its own characteristics, advantages and disadvantages.

Seeds
Propagating vines by seed is the most difficult method. This technology allows you to get a large number of healthy plants, but it requires a lot of time and effort.
To grow honeysuckle from seeds, first prepare planting material. Seeds are collected in July from ripe, soft berries. They are peeled from the pulp and dried.
The collected seeds are immersed for half an hour in a light pink solution of potassium permanganate. This will reduce the likelihood of disease in adult plants.
To increase germination, the seeds are mixed with wet sand, poured into a container and placed on the bottom shelf of the refrigerator. Every two weeks the substrate is moistened with a spray bottle. The seeds remain in this form from autumn to spring.
In spring, seedlings are planted:
- The boxes are filled with a substrate prepared from 1 part sand, 2 parts garden soil and 3 parts humus. If the acidity is high, ash is added to the soil. The soil and boxes are first treated with a solution of copper sulfate.
- A mixture of sand and seeds is poured onto the soil. Cover the top with a 1 cm layer of soil.
- The soil is moistened from a spray bottle with warm, settled water. The boxes are covered with film.
- After the shoots emerge, the film is removed and the boxes are put away in a bright place at room temperature.
- Until autumn, the plants are in boxes. When it gets warmer, they are taken outside. The soil is moistened as it dries.
Seedlings are transplanted into open ground in the fall.
Cuttings
This method allows you to quickly obtain planting material that easily takes root when planted.
Cuttings are prepared in the spring, before flowering ends.
It is important to choose the right whip: it must break when bent and have a diameter of at least 5 mm
The cutting is taken from the central part of the lash. It should have 2-3 internodes. The upper cut is made at a distance of 1.5 cm from the kidney at a right angle. Step back 10 cm from the top and make a cut at an angle of 45°.
At the bottom of the cutting, all leaves are removed. They are cut in half at the top.
Planting material is planted in a greenhouse in a substrate prepared from 2 parts humus, 2 parts sand and 1 part garden soil. A distance of 20 cm is maintained between seedlings.
For a month, the workpieces are sprayed with warm water from a spray bottle 3 times a day, then the shelter is removed.
In autumn, seedlings are mulched to protect them from winter cold and increase frost resistance. In the spring they are transplanted to a permanent place.
By layering
The easiest way to propagate vines. In this case, proceed according to the following scheme:
- In autumn, suitable shoots are selected. They should have a thickness of no more than 5 mm.
- They retreat 5-7 cm from the cuttings and dig a hole 20 cm deep. The hole is half filled with a mixture of nutrient soil with lime or ash.
- The layer is placed in a recess, leaving its upper part at the top, fixed with a bracket and covered with earth. The cuttings are watered and mulched.
- In the spring, the cuttings are dug up, separated from the main shoot and planted in a new place.
Dividing the bush
Dividing the bush allows you to immediately transplant the plant to a new location. This is the fastest option for propagating honeysuckle:
- The plant is dug up along with a lump of earth. After this, the root is divided into parts using a shovel.
- The cut areas are treated with ash. The shoots are shortened by a third of their length.
- Each part is rooted in a permanent place. The crown is formed in a year.
It is not necessary to dig up the entire vine. It is enough to dig it out on one side at the base and separate a part.
Where is the best place to grow honeysuckle?
The planting location is very important to obtain good plant growth. Blooming honeysuckle loves the sun, in such conditions it blooms better
Protection from the wind is important. These could be trees or any buildings.
Lighting for better growth
Honeysuckle, like other species, needs a lot of sun; it is with its help that decorative honeysuckle will grow well and bloom for a long time. It is better when the plant is planted on the eastern side of the site, as the early sun will allow it to be saturated with strength to open the flowers in the evening and give the surroundings a pleasant aroma.
Did you know? According to some doctors, the smell of these flowers helps overcome stress and nervousness.
Soil for growing honeysuckle honeysuckle
It is not demanding of the soil in which the plant will grow in the future. The acidity range is quite large - from 3.9 to 7.7. Climbing honeysuckle grows best on slightly acidic and neutral soils with a pH of 5.5-6.5.
Together with honeysuckle, the following ornamental shrubs will look great: viburnum, spirea, hydrangea, mock orange, elderberry, clematis, magnolia, hibiscus, deutzia, felt cherry, rose hip, snowberry, juniper, heather.
How to care for honeysuckle to grow a beautiful shrub
To decorate your garden and get a harvest of delicious fruits for the table, you need to learn a few secrets of growing honeysuckle. In fact, these are not even secrets, but basic rules for plant care, which also apply to other decorative specimens.
Of course, we are talking about such procedures as regular watering, thorough weeding, careful loosening of the soil, nutritious feeding, haircuts and protection from all sorts of misfortunes in the form of diseases and insects
You will be surprised, but after planting for three whole years, you will have practically nothing to worry about, except that you will need to water the bush and fight weeds. By the way, if you were not lazy and carried out the mulching procedure, then these actions will be reduced to a minimum.
But you should learn how to care for honeysuckle in the future from the very beginning.
First of all, you should take care of watering the plant. Despite the fact that it is practically not demanding in this matter, during the period of high temperatures - May-July - the shrub needs abundant watering. Remember that if the temperature is quite bearable and there is sufficient rainfall, you can carry out this procedure no more than 4 times per season
The volume of required moisture is 10 liters for one bush at a time. As for such an important condition for growing honeysuckle as loosening the soil. It is necessary to loosen the soil around the plant, firstly, after watering, and, secondly, be sure to immediately remove all weeds
You just need to do everything very carefully, since the roots of the bush are close to the surface: do not go deeper into the soil than 8 cm. To know how to grow healthy and fruit-bearing honeysuckle, you need not to ignore another piece of advice from experienced gardeners - feeding the plant. It is carried out after planting only two years later. Keep in mind that it is best to add organic elements to the soil. For example, in late autumn you can feed the bush with about 5 kg of compost, not forgetting to add 40 g of superphosphate and 100 g of ash. This “portion” is calculated per m2. But in the spring you can play around with saltpeter: apply 15 g of this substance under the bush with the addition of a large spoon of urea. Again, this is volume per m2. There is also such a thing as “summer feeding”. It is carried out after the harvest, around the very beginning of July. During this period, for example, a mixture of slurry is added to the soil, which is diluted in 10 liters of clean water. Growing honeysuckle at the dacha also means that the gardener will be engaged in harvesting that same crop. In order not to ruin the fruits, you need to know when it’s time to serve them. And this moment comes when they turn a rich blue color. Remember that berries can be damaged very easily, so try to place them in any container in one layer. Unfortunately, the harvest will not last long in your refrigerator if you do not freeze the berries. Or, of course, you won’t make very healthy jam, wine or liqueur.
Look at the photo: decorative honeysuckle is a beneficial addition to the landscape design of any site.
But such beauty is sometimes destroyed by certain types of diseases and pests. These, for example, are spotting, powdery mildew, and drying out of branches that develop due to fungal infections. If you encounter them, you will witness your plant drying out, turning black, turning yellow, or losing its leaves prematurely. Gardeners fight these scourges with the help of products called fungicides. The most commonly used are colloidal sulfur, copper chlorides or Bordeaux mixture. But instead of treating the manifestations of possible diseases, it is better to prevent them - simply spray the bush with the same fungicides at the beginning of spring and at the end of autumn.
But sometimes you have to fight not only fungal infections. Sometimes honeysuckle is attacked by pests such as various types of aphids, miners, false scale insects, sawflies, leaf rollers, moths and spider mites. In such situations, gardening experts take out a variety of preparations: Confidor, Rogor - for sucking pests, and Decis and Elexar - for leaf-eating pests.
Diseases and pests that affect honeysuckle Honeysuckle
To prevent the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms and pests to this plant, preventive measures should be taken:
- phosphorus and potassium, which are added as part of mineral supplements, give the vine juice an unpleasant taste, so aphids and other “harmful” insects that feed on the foliage stop “attacking” Honeysuckle. Usually superphosphate, wood ash or lime are scattered into the tree trunk circle;
- those pests (or their larvae) that remain overwintering in the soil can be destroyed if, before the onset of leaf fall, the foliage is treated with a urea solution (with a concentration of 5%);
- You can also use such effective biological preparations as Bitoxibacillin and other similar ones to treat honeysuckle Caprifol.
Disease Control
The appearance of gray-brown spots on young leaves means that the honeysuckle is suffering from ramularia. The middle of the spots turns brown, and later the disease spreads to the stems and petioles. The plant loses nutrients and weakens. Treatment consists of spraying with Fundazol or copper sulfate.
If the leaves are covered with dots with a red-brown border, this is cercospora. For treatment, the same drugs are used as for ramulariasis.

Red bumps on the branches mean that the bark is affected by the fungal disease tuberculosis. This disease causes young shoots and leaves to wither. To defeat the disease, it is necessary to cut out the affected areas and spray the vine with copper sulfate or Bordeaux mixture.
Aphids, which infect most garden plants, are also dangerous for honeysuckle. To destroy the pest, special preparations are used, such as Elexar or Confidor.
In a humid summer, a thickened bush can be affected by mites. At the same time, the leaves curl and fall off. The drugs Actellik, which is also effective in combating aphids, and Omite help to destroy it.











