History of the spread of culture
Brussels sprouts are the fruit of selection by Belgian vegetable growers; they do not grow wild. The culture, bred by breeders, traces its origins to wild kale - it once grew in abundance in the Mediterranean region, and was cultivated in ancient times.
It is believed that Brussels sprouts were developed in the 13th century. The famous scientist and naturalist Carl Linnaeus was the first to describe the new culture, calling it “Brussels”. Unusual cabbage began to be grown on a large scale in the 18th century; it appeared in Russia in the mid-19th century, but did not become widespread here. The Russian climate is not particularly suitable for this crop, so it is grown in the Russian Federation to a limited extent.
Where to buy Brussels sprouts seeds
The scientific and production association “Gardens of Russia” has been introducing the latest achievements in the selection of vegetable, fruit, berry and ornamental crops into the widespread practice of amateur gardening for 30 years. The association uses the most modern technologies and has created a unique laboratory for microclonal propagation of plants. The main tasks of the NPO "Gardens of Russia" is to provide gardeners with high-quality planting material of popular varieties of various garden plants and new world selections. Delivery of planting material (seeds, bulbs, seedlings) is carried out by Russian Post. We are waiting for you to shop: Fertilizing strawberries in spring - https://fas.st/dUzHUW" target="_blank"> NPO "Gardens of Russia"
Botanical description
Brussels sprouts (Brássica oleracea) are a vegetable crop and a type of kale that belongs to the cruciferous family. This biennial cross-pollinating plant is strikingly different from all other representatives of the cabbage family.
What Brussels sprouts look like:
- In the 1st year. On a thick stem there are small and medium-sized leaves with thin petioles. Stem height – 20-60 cm. Length of slightly lyre-shaped leaves – 15-35 cm. Leaves are green or gray-green, with a slight waxy coating on the surface. In the axils of the leaves, on the tops of short stems, small heads of cabbage grow - the size of a walnut. One plant produces 20-40 miniature heads of cabbage, each weighing about 10 g.
- In the 2nd year. Branched flowering shoots develop. The plant blooms and then produces fruits filled with seeds. The flowers are yellow, collected in inflorescences. The fruit is a polyspermous pod.
Origin and description of Brussels sprouts
Presumably, the ancestor of Brussels sprouts is wild kale. A new species was developed and domesticated in Belgium in the 19th century. Hence the name - Brussels. This heat-loving plant with a long ripening period has taken root well in countries with temperate climates. Widely distributed in Europe and the USA. It is not particularly popular in Russia due to the short summer period.
Brussels sprouts are unlike any of their cruciferous counterparts.
- This is a cabbage crop, but it has not one fruit, but many at once.
- On a rigid, tall stem about 60 cm high, small heads of cabbage are formed, similar to the usual white cabbage.
- On one stem grows from 20 to 100 light green or red fruits, depending on the variety.
- The diameter of the fruit is 2-5 cm , and the weight is 10-30 g .

Cabbage has a strong root system. She loves space, moisture and light.
Like most Cruciferous plants, this plant is biennial:
- in the first year, fruits are formed - heads of cabbage,
- in the second, flowering shoots develop - cabbage produces seeds.
The flowers are yellow, collected in a raceme, the fruit is a multi-seeded pod. The seeds in the pod are small, only 2 millimeters in diameter. They remain viable for up to 5 years.
In terms of agrotechnical nuances, Brussels sprouts are similar to regular white cabbage. In the central zone it is grown by seedlings.
Brussels sprouts contain a large amount of mineral salts (potassium, magnesium, iron). It contains three times more easily digestible proteins than white cabbage. It also contains fiber, B vitamins and carotene.
There are also contraindications: it is not recommended to include it in the diet of those who suffer from joint diseases, with kidney stones or gall bladder, as well as with exacerbation of chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.

Brussels sprouts are similar to regular white cabbage
Seed production
The agricultural technology for Brussels sprouts is the same as for white cabbage and includes three stages:
- Growing mother plants. Seeds are sown at the same time as when growing to obtain a harvest. Queen cells are harvested before frost. Take plants that are well developed and correctly formed. The heads of cabbage should be dense and large enough.
- Winter storage. Before storing, the leaves are cut off, leaving the apical bud a couple of centimeters above the heads of cabbage. Queen cells are placed in rows in piles or in cold storage, and sprinkled with sand. Storage temperature – from 0 to +1°C, humidity – 90-95%. The petioles are cut off as they dry.
- Growing seeds. In the spring, the queen cells are grown - 2-3 weeks before planting, they are dug in in the open ground. Then they are planted at intervals of 70 cm, the distance between the rows is also 70 cm. Planting is carried out as soon as the soil is ready. The seed plants are looked after - we weed, feed, destroy pests, water, hill up and tie up. When the seeds reach milky-waxy ripeness, the shoots are cut off and stored under a canopy. Or they are collected in small sheaves so that the fruits ripen.

Preparing the bed and planting seedlings
The soil should be slightly alkaline or neutral. Sour is not suitable, the crop will not grow well. Liming the soil in the fall is used to neutralize acidity.
It is recommended to prepare the bed in advance, in the autumn. For digging, manure (5-7 kg/m²), humus or compost (6-8 kilograms), mineral fertilizers (superphosphate 30-40 g and potassium salt 35-40 g per square meter of area) are added. Ash is also distributed at 150-200 g/sq.m. The ridge is loosened and left in this state until spring. In early spring, when the snow melts, the soil dries out a little, loosen the soil with a rake and leave it until planting to compact it.
Seedlings for planting in the ground should have 3-4 true leaves. Do not overgrow the seedlings, otherwise the plants will take longer to produce fruit. In the conditions of the northern regions, overgrown seedlings may poorly form a harvest; the heads of cabbage will be small and immature, since cabbage has a long growing season.

planting Brussels sprouts seedlings in open ground - pictured

Brussels sprouts seedlings under film - in the photo
In the prepared beds, make not too deep holes at a distance of 60-70 cm between the plants and in the rows. Cabbage needs a lot of light and space to produce a good harvest. The hole is thoroughly watered, a seedling is placed, and covered with dry soil. They are buried down to the cotyledon leaves, without burying the middle leaf, from which a stem with fruits will later form. You can pour a handful of ash and humus into the hole. Fresh manure cannot be used in the spring, especially when planting young cabbage sprouts.
If the seedlings were not treated with anything during cultivation, a solution of growth-stimulating preparations (Epin-Extra, HB-101, Ecoberin, etc.) can be poured into the bottom of the hole for better rooting and establishment in a new place. After planting, watering is not required; you need to mulch the Brussels sprouts with hay, straw, peat-humus crumbs, and other available materials. Depending on weather conditions, cabbage needs to be covered if there is a threat of return frosts, or shaded in a hot and sunny spring. Too hot conditions after planting plants in the garden have a negative impact on establishment.
Benefits and harms
Brussels sprouts contain a large amount of vitamins, minerals, and many other beneficial substances that have a beneficial effect on the body.
Benefits of Brussels sprouts:
- It contains a lot of carotenoids - these elements have a beneficial effect on the retina of the eyes.
- Regular consumption reduces the risk of developing asthma and increases immunity to viral infections.
- Thanks to the fiber contained in the vegetable, waste and toxins are eliminated, stomach acidity is reduced, and constipation and heartburn are prevented.
- Reduces the concentration of cholesterol in the blood, has a choleretic effect, and restores liver function.
- Strengthens the walls of blood vessels and normalizes cardiac activity.
- Contains a lot of calcium, necessary for healthy hair, bones and nails.
- Inhibits the development of breast cancer.
- Contains folic acid, necessary for women during pregnancy.
- Restores the functions of the pancreas, recommended for diabetes.
Brussels sprouts are contraindicated for people:
- with individual intolerance to the product - severe allergic reactions may occur;
- with a tendency to heartburn and flatulence - cabbage can provoke an exacerbation.
for the Urals and Siberia

Brussels sprouts are the healthiest and most delicious type of cabbage. This biennial plant belongs to the cross-pollinating family. Among other types of sprouts, Brussels sprouts stand out for their unique appearance. This type of cabbage was bred by Belgian breeders from kale.
Brussels sprouts contain valuable organic compounds - carbohydrates, fats, fiber, enzymes, carotene, as well as various vitamins. Miniature heads of cabbage are eaten fresh, stewed, fried, boiled or baked. Brussels sprouts, for winter storage, are pickled, frozen and even dried.
| ARTICLE ON THE TOPIC: Growing cabbage in open ground |
Brussels sprouts contain calcium, potassium, phosphorus, sugars, proteins, fats, fiber, 12 amino acids, vitamins (C, A, B, PP), folic acid, choline, and phytoncides. In terms of protein content, this cabbage is not inferior to milk and meat, and it contains much more vitamin C than other types of cabbage.
Such a valuable vegetable is especially useful for people suffering from cardiovascular diseases, as well as those who have undergone surgery, as it stimulates the wound healing process. Brussels sprouts juice restores pancreatic function. It is useful for people on a strict diet and for diabetes. A decoction of Brussels sprouts is not inferior in nutrition and taste to chicken broth.
CONTENT:
- Early varieties of Brussels sprouts
- Mid-season varieties of Brussels sprouts
- Cauliflower varieties
SEE ALSO:
- Varieties of white cabbage
- Broccoli varieties
- Varieties of Chinese cabbage
- Cauliflower varieties
[/td]
| Early varieties of Brussels sprouts - https://fas.st/ZCr3Q" target="_blank">
|
In the first year of cultivation, Brussels sprouts produce a tall, strong stem 30 to 75 cm high with long-petioled leaves. In the axils of the stem, heads of cabbage approximately the size of a walnut are formed. There can be from 20 to 100 such heads on one stem. It is for their sake that this cabbage is cultivated. In the second year, the mother plant can bloom and set seeds.
The yield of Brussels sprouts is quite high. During the growing season, from 1 sq.m. You can harvest up to 17 kg of crop. On average, about 5 kg of elegant fruits are collected in one harvest.
Among the special properties of Brussels sprouts, it is worth noting its resistance to cold. The plants are completely removed in late autumn. But, in the conditions of the Urals and Siberia, Brussels sprouts are grown through seedlings, which are obtained in greenhouses, greenhouses or at home.
In cold regions of Russia, the soil warms up later, so young plants are planted in the ground in early June, and harvesting occurs in early autumn. For growing Brussels sprouts, a well-lit place is allocated, since, due to lack of light, the heads of cabbage are poorly formed and gain weight.
In the Urals and Siberia, it is best to grow early varieties of Brussels sprouts - a short growing season will allow you to harvest before frost. For early ripening varieties, ripening periods range from 85 to 120 days.
Long Island | |
| A widely known American variety that appeared in the late 1890s. The ripening period is 85–100 days. Plant height is up to 80 cm, produces 30–60 green fruits weighing 10–20 g each. Tolerates frost well. They collect up to 1.2 kg per square meter. Tastes great. Resistant to fungal diseases. | |
Rosella F1 | |
| A mid-early variety from Germany, known since 1995. Bush height is 40–60 cm. Green heads weighing 12–20 g, up to 50 pieces on one bush. Productivity - 1.1–1.7 kg/m2. When the temperature drops, it does not lose its taste. Rich in vitamin C and folic acid. During freezing, it does not change its properties and structure. | |
Commander | |
| Variety of domestic selection in 2011. The growing season is 112–122 days. A medium-sized bush grows up to 60 cm. It produces 20–40 green heads, 2–4 cm in diameter and weighing 8–10 g. It is a frost-resistant crop that can withstand short-term frosts down to –10°C. Productivity - 1.8–2.3 kg/m2. | |
Dolmik F1 | |
| One of the best early varieties. Created in Holland. Grows up to 50 cm and above. The color of the heads is green-yellow, each weight is up to 20 grams. The maximum yield per meter of area is 2.5 kg. Can be planted in Siberia and the Urals. It has been grown in Russia since 1994. The hybrid is suitable for fresh consumption and quick freezing. | |
Diablo | |
| A mid-early variety of Brussels sprouts, ripen up to 55 medium-sized heads of round shape and green color. The weight of one head of cabbage is 15–18 g. The taste is characterized as excellent. Productivity is average. The variety is frost-resistant. | |
Requirements for climatic conditions and soil
Cabbage, bred in Belgium, prefers moderation in weather - it does not like heat and dampness, it needs favorable weather, moderate in all respects. The best option for growing Brussels sprouts is in climate zones characterized by long, warm autumns.
In countries with a favorable climate for Brussels sprouts, for example, in Holland, they are grown even in winter. But the largest harvests are obtained in the USA, Canada and Great Britain.
In order to grow safely, having accumulated a full set of vitamins in the required quantities, Brussels sprouts need the following conditions:
- optimal growing temperature – from +18 to +22°C;
- temperature +25°C and above is not permissible - crop growth stops, yield decreases;
- during the period of intensive growth - the predominance of sunny days over cloudy ones, and the latter should be a minimum number;
- lack of nitrogen fertilizers leading to the accumulation of nitrates in vegetables;
- The crop is extremely cold-resistant - seeds begin to grow already at +2°C, adult plants can withstand frosts down to -10°C.
The culture is cold-resistant. It tolerates frosts, which are destructive for most plants, without any significant consequences for growth and yield. Adult cabbage tolerates frosts especially well - frosts down to minus 5-7°C. After the frost has subsided, the cabbage thaws and begins to grow again. Moreover, it is believed that the frosts are good for the Brussels cabbage - the taste of its “micro-heads of cabbage” becomes even better.

Brussels sprouts, compared to white cabbage, are not so demanding on soil:
- can grow on light soils that are not highly fertile;
- prefers soils with a high calcium content;
- Recommended acidity pH is 6.0-7.0.
Care and harvesting
Care during the growing period is simply necessary. Despite the culture's cold resistance and hardiness, additional care will affect a rich and generous harvest. After planting on the ridge, 15-20 days later, when the cabbage has become stronger in place, the plants are earthed up. It is necessary to hill up in such a way that the bare root passing into the stem is not visible. During the season, 2-3 hillings are carried out.
At the same time, it is recommended to dust the grown seedlings with wood ash. But the ash needs to be distributed onto the lower leaves, without getting into the core, where the main stem will come from. Be sure to mulch to preserve and maintain air-water balance in the top layer of soil.

Harvesting Brussels sprouts - pictured

Brussels sprouts harvested - pictured
Fertilizing is done as needed, since the crop is unpretentious and can grow well without fertilizers. If you need to feed the sprouts, it is better to use organic fertilizers.
During cultivation, special attention is paid to watering, since plants of this species are very demanding of moisture. Lack of water in the soil leads to a decrease in yield. To grow large heads of cabbage, you need to water abundantly, taking into account weather conditions. Water for irrigation is taken clean and cold; the crop loves ice-cold water, but growing cucumbers requires watering with warm water. If possible, many summer residents install drip irrigation so as not to have to carry heavy buckets of water. Two weeks before harvesting, watering is reduced or eliminated altogether.
A special feature of cultivation is pinching the apical bud (core of the stem), when heads of sufficient size are formed for further ripening. Pinching too early does not allow obtaining larger-sized products. Leaves should never be broken off before harvesting, so as not to slow down the process of growth and ripening of the heads. Harvesting is carried out as it ripens, since the crop grows over a long period; harvesting begins in the second half of August. The plant is cold-resistant, so the heads are collected until November.
To keep cabbage fresh for a long time, the plant is pulled out along with the roots and put into a cellar, basement, glass greenhouse, where the air temperature will be within 0 ° ... + 5 ° C. In this case, the leaves are broken off, the cabbage remains fresh for a longer time. The heads can be frozen by first processing the heads with a knife and cutting off the stalk, which remains after being removed from the stem. It is worth noting that this cabbage ranks first among other types in terms of the composition of microelements and vitamins, for which it is so valued by many summer residents and gardeners.
Preparing for landing
In order for Brussels sprouts to produce the required number of heads of cabbage that are tasty and nutritious, the crop must be planted correctly and on time. Gardeners prepare the soil and seeds in advance - future yields depend on their quality.
Terms and conditions
The timing of planting seeds depends on several factors:
- climatic features of the region;
- current weather - this is especially important when growing seedlings;
- Brussels sprout varieties.
For central Russia, the optimal time for sowing seeds is 2-3 weeks of April. Early varieties are sown at the end of March, late varieties - after April 10. Seedlings are planted much later - in early June, but no later than the 10th.
Soil preparation
Brussels sprouts grow in any soil, even slightly acidic ones. But to get a good harvest, you need dense and at the same time breathable soils rich in organic matter. If the soil is poor and infertile, cabbage will grow, but very slowly.
When planting a crop in a new, unfertilized place, the soil is prepared by adding for each square meter:
- humus - 1 bucket;
- nitrophoska – 1/2 cup;
- lime or wood ash - 2 cups.
You can also add urea (14 g), potassium chloride (4 g), superphosphate (30 g), and during planting seedlings - 1/2 teaspoon of nitroammophosphate into each hole.
Having scattered fertilizer over the area, they dig it up, level it and water it with potassium permanganate to disinfect the soil. Add 1.5 g of potassium permanganate to 10 liters of water. Watering rate – 3 liters per 1 sq. m. Instead of potassium permanganate, you can use “Fitosporin” - it is used 1-2 weeks before planting.

Brussels sprouts consume a lot of nitrogen and potassium during the growing season. The culture is responsive to organic fertilizers. It is not recommended to use fresh manure as a fertilizer - it delays the formation and deteriorates the marketability of heads of cabbage, they become loose and are poorly stored.
When planting cabbage seedlings in an area where legumes, tomatoes or cucumbers previously grew, you can do without applying fertilizers - if organic matter has already been added before planting.
Seed preparation
If you buy only a few seeds for testing, you can take those that have already undergone industrial processing. If you have to plant a large volume of cabbage, then it is more profitable to buy unprocessed seeds - they are cheaper. But they will have to be treated in a stimulator and disinfectant yourself.
Seed treatment procedure:
- immersion in water at 50°C for 20 minutes;
- Having taken the seeds out of hot water, rinse them in running water – 1-2 minutes;
- kept for 12 hours in “Kornevin” or “Epin”;
- washed and placed in the refrigerator for 24 hours - in the bottom drawer intended for vegetables;
- dry the seeds so that they do not stick to your hands during sowing.
Hardening seeds in the refrigerator at minus 1˚C increases the frost resistance of plants and their resistance to diseases and pests.
Care: watering and fertilizing
Watering should be moderate, and the soil should not be allowed to dry out. It is advisable to settle the water so that it is not icy. When the heads form, the plant requires more moisture - watering becomes more abundant.
When the plants get a little stronger, after about 10 days, the first feeding is carried out. 2-3 grams of potassium are added per square meter of area. When forming ovaries, a mixture of ash solution and infusion of bird droppings is used for fertilizer.
During the rosette phase, seedlings are watered with the following mixture: 2 g of urea per bucket of water, 20 g of potassium chloride and superphosphate (0.5 l per specimen). At the stage of forming heads of cabbage, a different solution is used - 3 g of urea per 10 liters of water, 30 g each of potassium chloride and superphosphate. Sandy soils require the addition of magnesium compounds.
By following simple rules, you can grow wonderful Brussels sprouts on your plot.
And if you are interested in other types of exotic cabbage, we suggest you pay attention to Kohlrabi - this is a type of cabbage that looks more like a turnip. It is valued for its juicy taste and the enormous benefits that consuming this product brings to the body. And we will tell you about the features of its cultivation and storage. Author of the article: Oksana Artemenko
How to plant Brussels sprouts?
Brussels sprouts can be grown in two ways - seedlings or sowing seeds in open ground. Each method has its pros and cons; you have to choose a planting option taking into account the climatic characteristics of the region and your own preferences.
Seeds
Sowing seeds in open ground is used less often than the seedling method. It is beneficial for mass cultivation, as it allows you to avoid two stages at once - picking and transplanting into open ground. But with this method, the harvest comes later.
The seeds are sown quite early - in March-April. Focus on the soil temperature - it should warm up to +10-15°C. The order of sowing in open ground:
- Make shallow rows or holes in the prepared beds for nesting planting. Planting depth is no more than 1.2 cm. The distance between adjacent seeds is 15 cm.
- Cover the crops with film so that the seeds begin to develop faster.
- When the seeds sprout, thin them out, choosing the strongest sprout. Pull out the rest so that the cabbage has room to develop. There should be 50 cm between neighboring plants.
Early and mid-season varieties are sown in open ground, with a growing season of no more than 120 days.

Seedlings
Any type of cabbage does not tolerate transplantation well, and Brussels sprouts are no exception. Therefore, seedlings are grown in separate glasses - so that when planting in the ground, simply transfer a clod of earth with roots into the prepared hole - this reduces stress for the plant.
To grow seedlings, special cassettes or glasses are used. The volume of the container for one seedling is 200 ml. The procedure for growing seedlings:
- Fill any selected container - cassettes, glasses or seedling boxes with substrate. If using boxes, make grooves in the soil for the seeds. The depth of the rows or holes is 1 cm.
- Water the soil with warm water.
- Sow the seeds, spacing them 0.5-1 cm apart.
- Sprinkle the seeds with soil and compact it gently.
- Cover the crops with transparent material - glass or film.
- Place the containers with the crops in a warm place to get seedlings faster.
- After germination, remove the film or glass. Move the seedlings closer to the light. The optimal daytime temperature is +20°C, night temperature is not lower than +16-18°C. This temperature regime will not allow the seedlings to stretch beyond measure.
- Care for seedlings according to the following plan:
- Water as the soil dries out. Watering Brussels sprouts too frequently is contraindicated. Check the humidity at a depth of 1-1.5 cm. It is advisable to water the seedlings through a strainer so that the soil does not erode.
- To prevent blackleg, water the seedlings with “Fitosporin” or a pink solution of potassium permanganate. You can also sprinkle the soil with wood ash, with colloidal sulfur previously added to it.
- If you sowed the seeds in common containers, and not in individual glasses, there is one more step ahead - picking. Its essence is seating in separate containers. Pick up the seedlings after the first true leaves appear. You will need a small peg - use it to remove the grown seedlings - take them out along with a lump of earth and pinch the root. Bury the seedlings down to the first true leaves - if you plant the seedlings deeper, the stems may rot.
- Water the picked seedlings well and place them in the shade. The optimal air temperature is 20°C. When the seedlings begin to grow, expose them to light. But it should be cool here - no more than +16-18°C. Such conditions contribute to the formation of a strong root system.
- When the daytime temperature reaches +10°C, start hardening the seedlings for 5-10 minutes, take the seedlings out at midday. When the seedlings get used to the sun, it will be possible to take it out in the morning and keep it there until 16-17 hours.
It is impossible to overexpose seedlings - seedlings that are too large take root worse, grow more slowly and produce smaller yields. Seedlings are planted when they have 3 or 4 true leaves. Seedlings should be completely healthy and dark green in color.
After 2-3 true leaves appear, feed the seedlings with Kemira-Lux solution (1-2 g dissolved in 1 liter of water). Be careful not to get any liquid on the leaves. Feed the seedlings a second time 1.5-2 weeks before planting in open ground - add a solution of boric acid and copper sulfate (take both on the tip of a knife for 10 liters of water).
The procedure for planting seedlings in open ground:
- Stop watering the seedlings in 4-5 days.
- When the soil warms up to +10°C, the seedlings are planted in the prepared holes. Plant according to the pattern 60x40-50 cm (between rows - 60 cm, between plants - 40-50 cm).
- Transplant the seedlings into the holes using the transshipment method - remove the roots along with a lump of earth.
- Place the seedling in the holes so that the roots are comfortably located in it. The depth of the hole should be slightly greater than the length of the roots. It is better for the stems to be somewhat buried rather than for the roots to be on the surface.
- Compact the soil thoroughly so that there is no air left between the roots.
- Water the seedlings thoroughly.
We invite you to watch a video story from a gardener about how she grew Brussels sprouts using seedlings:
Growing seedlings
Brussels sprouts are best grown using seedlings, the technology of which is familiar to most summer residents.
Seed preparation
To obtain healthy and strong seedlings, the seeds are first prepared before sowing in the ground:
- The seed material is first placed in a container with hot water (50-60°C) for 15 minutes, and then in cold water for 1-2 minutes.
- The seeds are kept in growth stimulants (Kornevin, Epin) for 12 hours.
- Remove, wash and put in the refrigerator for 24 hours.
- Lightly dry, discard damaged and too small ones and begin sowing into the soil.
Nurseries purchase already prepared seeds that have undergone disinfecting and stimulating procedures under industrial conditions. Such planting material is more expensive, but is immediately suitable for sowing.
Soil selection
The best nutrient substrate for cabbage seedlings is considered to be a mixture of equal parts of turf soil, peat and sand. Before sowing, add 3-4 tbsp. l. wood ash and 0.5 tbsp. l. superphosphate (per 1 kg of mixture). Containers or boxes for seedlings are filled with this soil and additionally disinfected with a solution of potassium permanganate. Optimal pH is 6-7.
Reference. It is better not to use soil from the garden plot and humus, as they contain the rotting agent.
How to plant seeds
Cabbage seeds are sown in late March - early April. It is best to use individual containers for this, but large containers or boxes will also work. In this case, the optimal distance between the seeds of the crop will be 3-4 cm. They are planted at a shallow depth - 2 cm. Brussels sprouts seeds are characterized by early germination - the first sprouts hatch within 4-6 days.
Reference. The highest quality and strongest seedlings are obtained when grown on a closed loggia or in a heated greenhouse, since these rooms provide optimal temperature conditions.
Seedling care

Caring for young seedlings includes several important procedures:
- Temperature maintenance. Before the first shoots appear, the optimal temperature is +20°C. When the seedlings sprout, at night - +6...+8°C, during the day - about +20°C. The room is ventilated.
- Illumination. Containers with seedlings are placed in a bright place, but without direct sunlight.
- Watering. The seedlings are not watered for the first two weeks, and then regular watering is provided. The soil should not be dry.
- Fertilizing with mineral fertilizers. It is recommended to fertilize twice during seedling growth. The first fertilizing is carried out when the second true leaf appears on the plants. To do this, dissolve a mixture of 20 g of urea, 10 g of potassium fertilizers and 40 g of superphosphate in 10 liters of water. The second feeding is carried out 10 days after the first, and the dose of minerals is increased by 1.5 times. After each application of fertilizer, the cabbage is watered generously.
- Picking. It is carried out when seedlings are placed in large common containers approximately 1.5 months after sowing the seeds, when young seedlings have formed 4-5 full-fledged leaves. Together with the earthen ball, the plants are moved into separate containers.
Brussels sprouts seedlings do not tolerate thickening very well, so it should not be allowed.
This is interesting:
Proven ways to store Brussels sprouts for the winter in fresh, frozen and canned form.
The most delicious recipes for pickled Brussels sprouts for the winter.
In what form and how to properly freeze Brussels sprouts for the winter in the freezer.
Features of care
Caring for Brussels sprouts is not difficult - standard agrotechnical techniques are used. But there are still differences with white cabbage - it is recommended to hill up and pinch the Brussels sprouts.
How to water?
Soil moisture is maintained at 80%. Rules for watering Brussels sprouts:
- Water the plantings little by little, trying not to flood the growing point.
- When the planted seedlings take root and begin to grow, the plants are watered at the rate of 30 liters per 1 square meter. m.
- To water the cabbage, furrows are made between the rows - water is poured into them, and when the water is absorbed, they are covered with soil.
- During the growth period, plantings are watered several times. Moisturizing is especially important during the period of head formation. At high temperatures, the frequency of watering increases - cabbage is watered every 10 days.
- Over-watering cabbage is unacceptable - root rot may occur.
Watering rates for Brussels sprouts:
- before the heads of cabbage appear - 30-35 liters per 1 sq. m;
- after the appearance of heads of cabbage - 40-45 liters per 1 sq. m.
What and when to feed?
If the necessary fertilizers are applied before planting, then cabbage does not need to be fed during the growth and development of fruits. But if the soils are poor or sandy, it is recommended to carry out a couple of maintenance fertilizings.
Composition and timing of fertilizing:
| Fertilizing period | Composition of fertilizers |
| Half a month after planting in the ground. The plant begins to grow, a new leaf appears. | Nitroammophoska. For one plant – 1/2 tsp. |
| Heads of cabbage began to form. | Potassium sulfate and superphosphate - 25 g each, and nitroammophoska - one tablespoon are dissolved in a bucket of water. |
Fertilizing is carried out on moist soil - so as not to burn the leaves and root system. After feeding the plantings, the soil is slightly moistened.
Topping
This simple agricultural technique allows you to increase the size and weight of heads growing on the Brussels sprouts stem. It consists in shortening the shoots. Pinch off the tops when the stem reaches a height of 60-70 cm. After pinching, the flow of nutrients to the growing heads of cabbage is activated - their growth and development accelerates.
Topping is carried out no later than August. Only late-ripening varieties and hybrids are subjected to it.
Hilling and loosening the soil
When water is absorbed, the soil is loosened - this prevents the formation of a crust, which prevents the penetration of air to the root system. It is recommended to hill up the cabbage several times during the growing season - rake the soil in a thin layer, trying not to cover the heads of cabbage located below.
It is recommended to mulch planting Brussels sprouts - this agrotechnical technique prevents the growth of weeds and the evaporation of moisture from the soil. Grass, straw or black film are used as mulch.
Pre-harvest care
About a week before the harvest begins, all leaves are removed from the cabbage. If the plants ripen together, the foliage is cut off at the same time. When the leaves are torn off, try not to damage the mini-heads of cabbage. If the plants do not ripen smoothly, then the procedure is carried out 2-3 times, tearing off leaves only from those plants that are being prepared for harvest.
Planting Brussels sprouts in open ground

In order to grow a wonderful crop of Brussels sprouts, you need to choose a well-lit area with more sun. It is important to follow the principles of crop rotation to protect seedlings from cross-diseases:
- Cabbage will do well after potatoes, carrots, zucchini, legumes, grains and green manure crops, cucumbers, and onions. We recommend planting sideart mustard in front of the cabbage; read here how to do this and why it is useful;
- DO NOT plant Brussels sprouts immediately after any other types of cabbage, radishes, turnips, turnips, daikon, tomatoes, or beets. In this case, you should wait 3-4 years.
Cabbage loves fertile, well-groomed, non-acidic soil. It’s good if you can prepare the soil in the fall by digging it up with a spade and add lime for alkalization. And in early spring, when the snow melts and the soil can be loosened, add a bucket of compost per 1 m2. We recommend reading the article: How to properly prepare compost with your own hands.
If you did not add lime in the fall, this can be done two and a half weeks before planting.
When planting, pour 1 tbsp into each hole and mix with soil. l. crushed shells, onion peels, 2 tbsp. l ash and superphosphate, add 1 tsp each. urea.
How and when to plant Brussels sprouts
Seedlings, which have 4-5 true leaves, are strong and stocky, are planted from mid-May to the first half of June. This should be done on a fairly cloudy day, or after sunset. The seedlings themselves stop being watered a week before planting, and are well moistened on the day of planting. You also need to water the holes themselves before planting.
The holes are formed according to a pattern of at least 50*50 cm, 60*60 cm would be better.
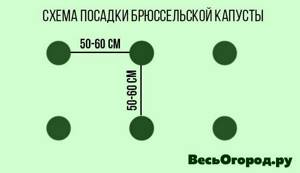
A hole is dug a little deeper than the root system of the seedlings. Carefully dump out the seedling along with the clod of earth, straighten it, sprinkle it with earth, compact it and water it.
In climatic conditions with long sunny days, early varieties of cabbage can be planted directly from seeds in well-warmed soil. Moreover, in order to get well-formed heads of cabbage, you need to plant the seeds in mid-April. Seeds are placed in moist, fertilized soil in grooves 2.5 cm deep in groups of 4-5 pieces. Sprinkle with earth and cover with cut-off 1.5 liter bottles - create such micro-greenhouses. After the first sprouts appear, they need to be thinned out slightly. After 12 days, thin out so that only one of the most vigorous seedlings remains.
Main diseases and pests of Brussels sprouts
Brussels sprouts are affected by the same diseases as other cruciferous vegetables. The most common diseases:
- rot is white and dry;
- clubroot;
- blackleg;
- black and ring spotting;
- bacteriosis mucous and vascular;
- mosaic;
- downy mildew.
Most often, “Brussels” are affected by aphids, moths, cabbage flies, as well as:
- cruciferous flea beetle;
- cabbage leaf beetle;
- flea beetle – wavy and black;
- cabbage whites;
- moth;
- rapeseed and cabbage bug;
- mole cricket
- scoop;
- wireworm;
- rapeseed flower beetle.
Read how to deal with diseases and pests of cabbage here.
The listed diseases and pests can significantly damage the yield of Brussels sprouts. If you do not take action, you may be left without a harvest altogether. To prevent damage to cabbage, it is treated with folk remedies. If there is no result, you have to use chemicals against diseases and pests, respectively.

Prevention is cheaper than dealing with the consequences, so it makes sense to take preventive measures. Brussels sprouts protection strategy:
- Maintaining crop rotation.
- Removing plant debris from beds.
- Regular weed removal.
- The use of a combination of organic and mineral fertilizers. The latter cannot be neglected by limiting ourselves to organic matter alone.
- At the first manifestations of the disease, the plant is pulled out and the soil is watered with a solution of potassium permanganate.
- Sprinkling the beds with tobacco and evil wood.
- If pest attacks are observed, spray with Decis, Karate, Corsair, Rovikurt, Ambush and others.
- If fungal diseases appear, the cabbage is sprayed with Fundazol, Quadris, Skor, Topaz and others.
Sick plants should not be put into compost - they must be burned immediately.
Landing
Semyan
How to grow a crop from seeds in the country? Procedure :
- Sow seeds to a depth of 1-1.5 cm. Separate pots filled with moistened fertile substrate are suitable for this. To prepare it, mix peat, sand, turf soil, wood ash and mineral fertilizers in equal parts.
- Before planting, treat the substrate with a solution of potassium permanganate for disinfection.
- Plant planting material maintaining a distance of 3-4 cm from each other. Cover with polyethylene and install in a room where the temperature is 18-20 degrees.
- After 4-5 days, the first shoots form.
- No watering is needed for the first 2 weeks, and then irrigate the soil as needed.
- Picking is carried out after 2-3 leaves are formed, planting the plants in separate containers.
From now on, open the covering material every day for 20 minutes.
Seedlings
To plant cabbage, choose southern or southeastern areas that are brightly illuminated by the sun. The beds on which the following crops were previously grown are suitable:

potato;- carrot;
- cucumbers;
- legumes;
- onion;
- turnip;
- tomatoes;
- beet.
7 days before planting, do not water the bed, but thoroughly moisten the soil in the pots. Fertile loamy soil with a pH of 6.7-7.4 is suitable for vegetable crops .
- Prepare the site in the fall. To do this, dig it up and add lime to the bayonet of the shovel.
- With the onset of spring, add compost or humus per 1 m2.
- Place a nutrient composition consisting of the following components into the dug hole:
- urea – 10 g;
- superphosphate – 40 g;
- wood ash – 40 g.
Planting activities should be carried out on a cloudy day or in the evening.
Procedure:
- Arrange the holes according to a 60x60 cm pattern.
- Dig them up a little larger than the roots of the seedlings. Place compost mixed with soil in them.
- Transfer the plant from the pot into the hole, cover it with soil and lightly tamp it down. Water with settled warm water.
Watch a video about planting seedlings in open ground.
When to start harvesting?
The harvest begins when the small heads of Brussels sprouts are fully ripe. Maturity is determined by the following characteristics:
- the value reaches a maximum of 1.8-2 cm in diameter;
- the heads of cabbage acquire a shine characteristic of ripe fruits;
- the leaf turns yellow at the base.
Features of harvesting early and late varieties:
- Early and early middle. Harvest in September-October. They are harvested in one go, since their heads of cabbage ripen at the same time. The stems can be cut off at the base and stored for later harvesting.
- Mid-late and late. This category of varieties is harvested in 2 or 3 passes. Before harvesting, the leaves on the plants are torn off - only from the side on which the heads of cabbage are to be collected. When harvesting in several stages, the heads of cabbage are cut off, starting from the bottom of the stem.
Sowing dates depending on the region
The growing season of Brussels sprouts ranges from 130 to 180 days (depending on the type). Therefore, they begin planting seedlings early. Seedlings are planted in open ground with 4-5 true leaves at about two months of age. By the time of planting, temperatures outside should be above zero. You can plant seedlings earlier, but then they make a shelter for them.

Based on what was written above, the approximate timing of when to plant Brussels sprouts:
- In the southern regions, seedlings are planted in the ground in early April, and seedlings are sown in the second ten days of February.
- In the regions of the Central Black Earth Region - in early March.
- In Siberia and the Urals, it is recommended to sow Brussels sprouts seeds from March 5 to March 10.
- In the Moscow region and in the North-West of the country - from March 15 to 25.
- In the Far East - from March 10 to 15.
In regions with short summers (Urals, Siberia, Far East), it is better to grow varieties of early and medium ripening. Since late varieties may simply not have time to ripen.
Storing Brussels sprouts
Brussels sprouts can be stored whole, consuming the heads as needed. The plant must be dug up before frost begins and buried in the basement and greenhouse with sand. Dig the cabbage in at a slight angle. Also, stems with fruits, folded in plastic bags, are stored in the refrigerator,
Frozen Brussels sprouts will keep for 3-4 months.
Having placed the harvested crops in boxes, place them in a cool place. If you provide them with a temperature of 0°C, they remain fresh for up to 1.5 months. And if you freeze them, they will retain their quality all winter. It is recommended to store Brussels sprouts at 0°C and 95% humidity. Under such conditions, cabbage is stored for 2-2.5 months.
Due to the characteristics of their cultivation, Brussels sprouts have not yet received proper distribution among our vegetable growers and gardeners. But with the advent of new varieties and hybrids - more productive and less demanding, the demand for this crop will grow. This vegetable has so many advantages that it is simply unforgivable to neglect it.
0
0
Copy link
Harvesting and storage
Harvesting the heads of cabbage can be done at once or gradually, removing the crop as it ripens, starting from the bottom, which will allow the upper fruits to fully gain volume and density. They are plucked en masse after the axillary leaves fall off. On average, this process takes from 3 to 4 months, counting from the date of planting the plants in open ground.
Experts recommend harvesting Brussels sprouts after the first frost (but not allowing the temperature to drop to -10°C), because In the cold, the taste of the vegetable improves significantly.
For long-term storage, the heads of cabbage are cut off along with the stalks, leaving the outer layer of leaves and a protective coating. In this form they do not deteriorate for a long time:
- in a cool place – 0.5–1 month;
- in the refrigerator – 1.5–2 months;
- in the freezer – 6–12 months.
You can also store the harvest by cutting down the entire plant with the stem. The remaining heads of cabbage will be stored in this form for about 3 months. This is not as cumbersome as it might seem at first glance: if you tear off all the leaves and stack the resulting pieces close to each other, you can place up to 30 pieces per 1 m2.
The shelf life will increase even more if the trunk is carefully dug up by the roots and placed in the ground in the basement. This will keep the heads of cabbage fresh and crispy for 4 to 6 months.
Small-headed vegetables are still rare in domestic garden plots, but given all their advantages, the widespread cultivation of Brussels sprouts in open ground is only a matter of time. Its frost resistance is ideal not only for planting in Russian climatic conditions, but also for long-term storage, which makes it possible to ensure the supply of vitamins to the body even in winter, when other sources of valuable nutrients are no longer available.
Harm and contraindications
A significant number of beneficial qualities do not exempt Brussels sprouts from contraindications. The harm of the vegetable is associated with components that can disrupt the stable functioning of the thyroid gland, which threatens hypothyroidism. Goitrogens, which are part of miniature Brussels sprouts, negatively affect hormone production. However, during heat treatment this property of the product is reduced to a minimum. Vegetables are excluded from the menu if:
- individual intolerance;
- exacerbation of pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract;
- increased stomach acidity.
If there are no contraindications, there is no established norm for consuming a healthy vegetable. Nutritionists recommend that healthy people limit their weekly intake of Brussels sprouts to three hundred grams of the product, which can be eaten fried, boiled, baked or steamed.












