What is compost and its value
To compost means to combine. If you collect all the unnecessary organic matter from the garden and put it in a pile or hole, then sooner or later the microorganisms will do their job - digest the substances. But summer residents and industry went further: they learned to speed up the process, which under natural conditions lasts two years, and also created new ways to quickly process plant residues.
The principle of ripening a compost heap is as follows: all organic matter contains bacteria that perform the primary processing of raw materials. Earthworms eat the remains of microorganisms and plants, releasing coprolites into the surrounding space. After complete processing of the components, they turn into a dark-colored substance, rich in humates and nutrients.
The value of compost is:
- in useful waste disposal;
- microorganisms living in the compost heap are able to suppress and control pathogenic bacteria, thereby protecting plants from diseases;
- fertilizer is practically free;
- improves the physical and chemical parameters of the soil - moisture capacity, aeration;
- Suitable for all plants.
When using various biodestructors, you can get up to three portions of fertilizer per season, depending on the size of the compost bin and the amount of waste.
DIY compost pile
Compost is real garden gold. It improves soil structure, regulates the flow of water and nutrients into plants, and soil acidity. High-quality compost, applied a handful per plant, doubles the yield and dramatically improves the quality of vegetables. In addition, as studies by German scientists have shown, it protects plants from diseases. And if you approach this process wisely, in a businesslike manner, then it will take not a year to ripen the compost, but only 6 - 8 weeks.
So, how to turn the contents of a garbage pit into “black gold” - how to make compost yourself? 10 simple conditions that make up the “code” of the compost heap will help with this.
Where to choose a place for a compost pit
A warm, slightly shaded and sheltered location from the wind is ideal for compost to mature. A well-drained area (where rainwater does not stagnate) with a size of at least 1 m is allocated for composting - always as far as possible from the well. A trench 1-2 m wide and 0.8-1 m deep is either laid on the site, or a container is built. In trenches, the compost dries out less, is moistened more evenly and ripens faster.
A compost heap can also be made simply on the surface of the soil, which is first dug up. For hygienic and aesthetic reasons, it is better to use some kind of container: for example, a wooden box with 3 or 4 side walls.
3-compartment silo Fresh collected compost, semi-ripe and mature compost are placed side by side. When the compost pile is used up, it can be collected and stacked again.
The “European style” compost heap is arranged in a special plastic compost barrel or in a container with a lid.
The choice of stack or silo structure depends on the available space. A stack takes up more space than a silo.
The trapezoidal stack has the following dimensions: 1.2 m wide and a maximum of 1.5 m high. The length can be any.
Silo structure : standard dimensions - 1x1x1 m. You can make it yourself from boards or bricks. Ready-made parts made of wood, plastic, wire mesh or metal are available for sale.
The material plays a subordinate role - the handling of compost during filling and unloading is important. One wall of the structure is made removable.
➢ Important: the compost bin must hold at least 1 m2 of compost. Otherwise, the rotting process will not begin. It should be open from below (so that worms and microorganisms can easily penetrate it and back). The sides of the compost material should be well ventilated and easily heated.
For those who have a plot of only 4-5 acres, composting in furrows is suitable. This method, by the way, will help eliminate unnecessary damp lowlands. In the lowest place of the plot, 2 beds are made. To make them taller, choose more soil from the furrow.
Since spring, the beds have been occupied by different crops, and the furrows are filled with available material in layers. To make the compost ripen faster, sawdust (or similar bulk material) is added and dug into the furrow.
The furrow is widened so that it is comfortable to walk on. There is no dampness or dirt in such a furrow, since all moisture goes down.
The furrow is relatively shallow and the compostable layer is small. It is airtight and therefore decomposes quickly. The next year, when the furrow is completely filled, it is dug up and loose soil is obtained, which will rise above all the beds. Thus, the lowland will be eliminated!
What can be composted...
“All waste goes into compost!” The slogan is sonorous, but not entirely correct. Almost any nitrogen-rich organic materials: peat, manure and bird droppings, grass clippings, tops and hay, sawdust and fallen leaves, kitchen waste (vegetable remains) are placed in the compost heap.
In small quantities, nitrogen-poor organic materials are added to the compost: pine needles, twigs, straw, wood waste, paper and cardboard (shredded).
Food waste is also composted: tea and coffee grounds, fruit and vegetable peelings, eggshells. Meat trimmings, leftover food and dairy products are buried deeper, as they produce strong odors and attract animals. Adding legumes will enrich the compost with nitrogen.
Green grass and tops are dried out, otherwise instead of a compost heap you will end up with a silage pit in which the process of rotting is slowed down.
…and what not
Place in the compost heap synthetics, glass, plastic, hard-to-rot organic remains (bones, lard, fat), boiled kitchen waste that can attract harmful insects and emit an unpleasant odor, diseased plants and infested weeds. And besides, citrus fruits: they oxidize the composted material, and the pile becomes unattractive to earthworms.
Important Supplements
Each individual layer of compost is sprinkled with soil, compost or a compost stimulator. Additionally, compost additives are sprinkled on it. This speeds up the decay process and saturates it with nutrients.
The following compost additives are used:
• fresh compost or clay soil (2-3 shovels per 1 m2) or compost stimulator according to the instructions;
• clay flour (betonite) and pulverized silica (approximately 500 g/m2);
• mixed organic fertilizers - such as horn, blood and bone meal (about 200 g/m2) or manure (2-3 shovels per 1 m2);
• algae lime (approximately 100 g/m2).
➢ Attention: never use with manure!
Modern technologies have given gardeners another “trick”: compost activators. They create a nutrient medium for increased proliferation of microorganisms, resulting in maturation much faster. Two types of activators are produced: only for plant waste (“Flumb-K”) and for waste of all types (“Flumb-super”).
As soon as the layers of compost raw materials are sprinkled with an activator, bacteria begin to multiply at a frantic pace (that’s why it says on the packaging: “active sex in the compost heap”), quickly “eat up” the material - and that’s it, literally in 6-8 weeks the compost is ready. Mature compost is easy to recognize: by the bright smell of fresh earth and almost homogeneous composition. It is cold and crumbles when stirred.
Why add manure?
This is done in order to enrich organic matter with the necessary microorganisms. In addition, dry layers of compost fix nitrogen, which is released in large quantities from fresh (or liquid) manure. If this is not available, a chemical catalyst can be added to stimulate bacterial growth and thereby speed up the decomposition process. The desired effect can be achieved by sprinkling the compost with extracts or extracts from vermicompost (“Gumisol”, “Vermistim”, “Effect”, “Rainbow”, “Ideal”).
If the compost contains a lot of wood shavings, straw or sawdust, nitrogen fertilizers are added to them (for example, 300 g of ammonium sulfate per 10 kg of sawdust). The quality of compost improves noticeably with the addition of phosphate fertilizers: 1-2% superphosphate or 2-4% phosphate rock by weight of composted materials.
When using compost on sandy and sandy loam soils, 0.5-1% potassium chloride is added to it. Too acidic material in the compost heap (pine needles, peat) is neutralized by adding lime or wood ash (10 kg per 1 m2 of compost). It makes sense to add ash to each layer of soil, food waste or lawn clippings.
Composting
Before laying the compost, prepare a place for it:
• loosen the soil;
• select soil from a depth of 10 cm (it will then be used for shelter);
• in normal or heavy soil, chopped branches are laid down (as drainage). For light and sandy soils, loose, easily absorbent material is placed at the bottom of the heap: for example, peat, sawdust and straw (15-30 cm thick). The height of the next layers can be from 5 to 25 cm. The total height of the heap is 1-1.5 m;
• alternative: raise the ground slightly to allow excess seeping water to drain away;
• collected and well crushed and mixed residues are laid in layers 15~20 cm thick. Alternate layers of dry brown (straw, hay, branches, bark, paper, peat, fine soil, humus, bark) and lush green material (mown grass, tops, turf, moss, weeds, food waste, manure).
➢ Important: in hot, dry summers, water the compost from time to time.
Thin layers of soil or ready-made humus (2.5-5 cm) will provide an abundance of decomposer bacteria and the absorption of water and gases that can extinguish the decay process.
• compost additives are laid between the layers;
• the topmost layer of the compost heap is covered with earth or other plant material;
• boards, straw or reeds are used to protect from light, water and rain.
Grind and moisten
This is necessary both to speed up the maturation of the compost and to make it easier to mix. In the absence of a special device, use a lawn mower, which can easily cope with grass and weeds.
It is necessary to moisten in layers using liquid household waste or slurry. This helps the compost mature faster.
Cover the compost heap with film, a tarpaulin, a lid or an old carpet - so that during rain, water does not stop the rotting process and does not wash out nutrients, and so that in winter the covering retains its heat.
The temperature in the center of the compost heap reaches 70°C, which contributes to the death of pathogens.
Mix and let stand
The rotting process can be accelerated by stirring the compost every 4 weeks. This is done so that material from outside gets inside, and the decomposition process is accelerated, and the inhabitants of the compost heap receive enough oxygen. The main process happens in the middle of the heap. Stirring is especially effective in summer. A compost heap requires a lot of space, but it is cheaper than a silo and is easy to work with.
Before the organic material turns into a homogeneous crumbly mass of dark brown color - humus will require, depending on the mixing efforts and the materials used, from 3 months to 1-2 years. It takes at least 6 months to prepare compost from mowed lawn grass that has accumulated selective herbicides.
The compost into which feces are dumped is kept for at least 2 years, since the latter contain helminth eggs and must be neutralized.
➢ Attention: when pouring the contents of a cesspool onto a compost heap, you need to remember that feces are also dangerous due to the accumulation of heavy metals, as well as toxic biologically active substances (hormones, antibiotics and their decomposition products).
What happens in a compost heap
Organic matter decomposes under the influence of oxygen, air, humidity, heat and countless microorganisms. This process takes place in several phases:
1st phase . For 2 weeks, bacteria work, their activity increases the temperature to 70°C. This kills all diseased embryos and seeds. Then mushrooms, worms, many insects and other living creatures begin to decompose the organic mass. External sign: the compost pile is settling.
Phase 2. After 2-3 months, the result is nitrogen-rich and coarse-fiber, or fresh, compost. It can already be used for targeted fertilization and mulching.
Phase 3. After another 2-3 months, earthworms make the compost dark and fragrant - ripe. It can be used anywhere in the garden. Over time, structured humus is formed from mature compost, which turns the soil into fertile soil.
Maturity test. You can find out whether the compost is ripe: sow nasturtium seeds through a sieve, lightly press them into the mass and moisten them. After 3-4 days, most of the seeds should germinate. Strong green nasturtium leaves are a sign of compost maturity.
How to use compost correctly?
• Mature: apply a 1 cm thick layer to flower beds of all types. Vegetables, shrubs, flowers and trees - if possible - should receive double the amount of compost. For plants in need of nutrients, apply a dose in spring and autumn.
• Coarse: used for fertilization (contains a lot of nitrogen) and mulching. For vegetable and fruit crops, in early spring, apply a layer of compost 1-2 cm thick along with a layer of mulch (straw, grass).
Compost can also be used as an independent organic fertilizer for digging up soil or in the form of mulch (for all garden and ornamental species).
“Two to three centimeters of compost will protect plants from disease-causing microorganisms better than a proprietary fungicide—especially disease-prone tomatoes or roses,” says prominent American compost and plant pathologist Herry Hoitink.
Additional “sources” of organic matter
Since the size of the compost heap is usually small, there is always not enough fertilizer. Therefore, if a gardener decides to fertilize an undeveloped plot, he will need 600 - 800 kg of organic matter for every hundred square meters. In this case, it is better to purchase ready-made compost or any other organic fertilizers from specialized farms with livestock yards, stables, manure storage facilities, etc.
Peat manure compost
It must be remembered that it is not advisable to use peat in its pure form as an organic fertilizer, especially on sandy and sandy loam soils (on which it decomposes very quickly: in 1-2 years).
In addition, nitrogen in this case is difficult for plants to access; peat, as a rule, is heavily watered, has weak biological activity, and contains acidified compounds harmful to plants.
The risk of buying, instead of lowland peat, low-ash and highly acidic high-moor peat, which is only suitable for acidifying the tree trunks of rhododendrons, hydrangeas and heather beds, is also too great. But the compostable material from peat mass, porous, like a sponge, with a high absorption capacity, turns out excellent.
High-moor sphagnum (moss) peat is also indispensable for the preparation of peat manure composts. In peat manure composts, organic forms of nitrogen are converted into a form accessible to plants, ammonia losses from manure are reduced, and acidity is optimized.
Such composts are often a more effective organic fertilizer than manure traditional in the Non-Black Earth Zone.
The value of manure lies in the fact that, in addition to high biological activity, it has a balanced content of macro- and microelements necessary for plants. And from this point of view, horse and sheep are recognized as the best. When manure decomposes, the soil is enriched with carbon dioxide, which is necessary for plants for air nutrition and photosynthesis processes.
However, fresh or liquid manure is not used as an independent fertilizer, since it contains a large number of weed seeds, as well as pathogens of various diseases.
The nitrogen of such manure is quickly washed out of the soil and fixed by microflora, so there is a danger of plant burns. It is used only after composting with sawdust, straw or peat, and for fertilizing it is diluted 2-3 times with water.
Bringing manure to a state of humus is also impractical, since this loses a lot of nitrogen, phosphorus, and organic substances (only 250 kg of fertilizer is obtained from 1 ton of manure). The most effective is considered to be semi-rotted manure (the straw in it is not yellow, but brittle, dark brown).
On clay soils, manure is applied in the fall, in an amount of 5-6 kg per 1 m2, to a depth of 10-15 cm, once every 5-7 years. On newly developed poor soils, this rate is doubled. On sandy lands - only in spring, to a depth of 20-25 cm, but in smaller doses and more often (once every 2-3 years).
Nutrients from bird droppings (chicken, duck, pigeon, etc.) are also well absorbed by plants, but due to the high concentration of nitrogen for liquid fertilizers, it is better to infuse it (1 matchbox of fresh droppings per 1 bucket of water).
Based on bird droppings and manure, commercially available biologically active dry fertilizers (often in the form of granules) are prepared, which, in essence, are composts of manure or droppings with peat, sawdust, straw, etc., subjected to solid-phase biofermentation.
They really have an increased level of biogenicity and nutritional value, and their efficiency is 2-4 times higher than traditional peat manure compost.
Similar articles:
Autumn and spring soil preparation for planting
How to use weeds to determine soil quality
Mulching what is it
How to feed grapes at the roots
Soil types. How to determine the type and level of soil acidity yourself
Ingredients - how to choose the right ones
Setting up a compost heap with your own hands at the dacha requires correct calculation of the components. They are divided into carbon - brown and nitrogen - green.
The first include:
- fallen leaves;
- sawdust, tree bark, wood chips;
- straw or hay;
- pine needles;
- newspaper or toilet paper;
- cut woody shoots;
- You can put natural fabrics in the compost - silk, linen or cotton, after shredding them.
Nitrogen components are:
- fresh mown grass;
- weeds;
- manure or droppings;
- fresh vegetable or fruit trimmings;
- sea plants.
For every nitrogen part there should be 2 carbon parts so that the composting process does not slow down or become disrupted.
Compost from fallen leaves
Separately, I would like to mention compost made from fallen leaves, which is also known as “leaf soil”. The basis of this species is fallen leaves, which lose minerals before falling, so that only hemicellulose and lignin remain in their tissue. These substances decompose very slowly, although they are one of the most valuable components of humus. When making a compost heap from leaves, you should know that they contain another difficult-to-decompose substance - tannin. It has astringent-disinfecting properties, which greatly inhibits the processes of compost formation. Large concentrations of tannin are found in beech and oak leaves; the tannin content is especially high in chestnut, willow and sycamore leaves. Because of this, the foliage of these tree species is of little use for compost and can only be used to cover the pile.
Composting methods – with or without oxygen
In nature, there are two types of bacteria that process waste - aerobic and anaerobic. The former breathe oxygen and die in its absence; they live in the upper layers of the soil, decomposing roots and tops into tiny particles.
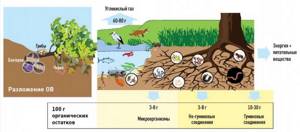
Anaerobes do not require oxygen and function in closed spaces. To cultivate them on an industrial scale, for example, for the production of preparations for septic tanks, the nutrient medium is isolated under a layer of paraffin to prevent oxygen from entering the liquid through the surface.
A compost heap can be open or closed, that is, it can be permeable or isolated from the external environment. In the first case, aerobes will multiply and work, in the second - anaerobes.
Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages. An open composter will require more effort and time to maintain so that the compost pile matures evenly.
With proper care and regular mixing of the layers, the finished fertilizer is obtained in 2 - 3 months, provided that EO preparations are used to accelerate ripening. Without additional additives, the fertilizer will be completely ready in 1.5 - 2 years.
In a closed container, you don’t need to do anything like that - just fold the ingredients correctly and close. The ripening process takes longer - approximately a year and a half without the use of biodestructors - compost accelerators.
Advantages of each method
A properly made compost heap on a site ripens faster using the aerobic method. Using EO preparations, you can get compost in 1.5 – 2 months. It is easier for gardeners to control the process, since when the components dry out, bacterial activity stops, the combustion temperature drops, and the substances stop decomposing.
It is necessary to add clean water, preferably with accelerators. The disadvantage of this method is that during the process some of the nutrients evaporate. This applies to a greater extent to nitrogen. Aerobic compost emits an odor when rotting, but it evaporates into the atmosphere and does not cause any inconvenience.

With anaerobic composting, virtually all the nutrients remain in the composter. By adding carbonaceous dry ingredients that absorb liquid, concentrated compost can be made.
It is suitable for feeding adult plants, but for young seedlings it will need to be mixed with the soil to reduce the concentration. The average time to prepare a compost heap anaerobically is 4 – 6 months. This is the fastest you can expect from bacteria, even if you add them in the form of drugs.

With a properly organized process, acidity increases and destroys helminth eggs if the composition contains manure. Weed seeds cannot withstand such an environment.
Do you need a composter at your dacha?
Every owner of a summer house or country house wants to receive harvests that are as high and generous as possible.
But, at the same time, do not use chemical fertilizers and other substances that can harm health or reduce the value of the grown gifts of nature. Such a contradiction, at least at first glance. But, if you take a closer look at the situation and understand it, there is nothing complicated. To solve this problem, you need to acquire your own source of environmentally friendly fertilizers, which can be obtained from a variety of organic waste. To obtain such fertilizers, you can either use a compost pit, which is not always convenient, or purchase a country composter. And although, in both cases, a similar product is obtained, or, more simply put, compost, using a composter is much preferable for a number of reasons. Insert for composter Fertility
4,000 rub.
Buy
pcs
Biolan compost activator 1 liter
500 rub.
Buy
pcs
Country garden composter
RUB 2,350
Buy
Out of stock
Composter Fertility
6,500 rub.
Buy
Out of stock
Piteco composter with lid 300 l black
2,200 rub.
Buy
Out of stock
Rostok composter
RUB 7,100
Buy
Out of stock
Piteco composter with lid 300 l green
2,600 rub.
Buy
Out of stock
Composter Module 800 l green
7,100 rub.
Buy
Out of stock
Biolan 220 ECO composter
RUB 39,950
Buy
Out of stock
Compogreen composter 380 l black
2,680 rub.
Buy
Out of stock
Garden composter Bulbeo 700 l
RUB 8,990
Buy
Out of stock
Composter Module 1600 l black
9,780 rub.
Buy
Out of stock
Eco-King composter 600 liters
RUR 6,890
Buy
Out of stock
Eco-King composter 400 liters
RUB 4,990
Buy
Out of stock
Garden composter BIK
6,100 rub.
Buy
Out of stock
Garden composter Bulbeo 900 l
RUB 10,990
Buy
Out of stock
Biolan 550 composter
RUB 83,750
Buy
Out of stock
Biocompo composter 900 l green
8,740 rub.
Buy
Out of stock
Meridian composter
RUB 9,900
Buy
Out of stock
Thermo-King composter 400 liters
RUR 6,490
Buy
Out of stock
Thermo-King composter 900 liters
RUB 12,990
Buy
Out of stock
Kekkila dry mix for composters 50 liters
690 rub.
Buy
Out of stock
Evogreen composter 850 l green
6,500 rub.
Buy
Out of stock
Compost activator Biolan 1.2 L
370 rub.
Buy
Out of stock
Thermo-King composter 600 liters
RUB 8,990
Buy
Out of stock
Globe garden thermocomposter
RUB 19,500.
Buy
Out of stock
Termo garden heat composter
RUB 55,000.
Buy
Out of stock
Bottom basket for garden composter
RUB 8,000
Buy
Out of stock
Garden Composter Biolan 900 Gray RUB
21,700
Buy
Out of stock
Garden composter Biolan 900 l.
Green RUB 21,700
Buy
Not available
The essence of the process in this case is quite simple. Under the influence of special microorganisms and appropriate temperature, humidity, as well as a number of other conditions, organic waste is transformed into compost, which serves as an excellent fertilizer. This is a natural and therefore harmless fertilizer that can be used both when planting various crops and in other cases.
And so, composter. Such devices are divided into two types: open composters and closed ones. An open composter is basically a seasonal type device. It comes together at the right time. And at the end of the agricultural season, it is sorted out. Both assembling and dismantling such composters is quite simple and no special skills or special physical effort are required to carry out such operations. Therefore, almost anyone can cope with such work.
As for a closed-type composter, such devices are, let’s say, permanently dislocated. But it is better to install both of them in places protected from the wind, so that there are no problems maintaining a stable temperature. You should also not place composters on asphalt, concrete, or other man-made surfaces. Place the device on the ground so that earthworms and other living organisms have easy access to your waste to be processed into fertilizer. These are the basic requirements for installing a composter.
What I would like to note separately is the fact that both types of such devices perfectly protect you from unpleasant odors and other undesirable effects. Moreover, flies and other insects, which actively spread various diseases, do not have access to rotting waste. So, composters are much safer and more convenient than conventional compost pits.
Composters also differ in volume. The entry level starts from six hundred liters. But this volume will be enough for you only if your plot is quite modest in size. Otherwise. It is better to take a more capacious composter, it is better to have a reserve. These are all the features and advantages of a composter as a category of device for producing clean and safe fertilizers. With it, your organic waste will find a new use, go to work and work for your benefit. With it, your yields will grow quite noticeably. With it, there will be no unpleasant odors or dangerous centers of various diseases and harmful organisms on your site. This is the optimization of agricultural production on a specific plot of land. And you will feel this optimization in the shortest possible time. After which, without a composter it will be very inconvenient and bad.
Of course, each specific composter model has its own pros and cons, its own operating features, and so on. But all this is either reflected in the instructions for the composter, or will become clear during operation. In any case, a composter is a useful and necessary device at every dacha in every country house where at least something is grown.
The most useful compost is with earthworms
In the middle of the last century, studies began on the activities of red earthworms, which were called Californian, since it was in California that they were first used to prepare very nutritious compost. It turned out that they reproduce faster and digest more plant residues. An adult eats as much food per day as it weighs, and reproduces hundreds of times faster, laying cocoons.

After research, it turned out that there is several times more humus after processing waste by red Californian worms than after other types. Currently, vermicompost is the most expensive organic fertilizer, which fully pays for itself. Plants require several times less substance, but it is absorbed by 98%. For comparison, mineral fertilizers are only 30%.
Organic fertilizer - you can make a compost heap with your own hands using earthworms in the warm season. To do this, they buy several individuals for breeding and put them in a container. In the warm season, they feed intensively and reproduce.
The lifespan of a red worm is 16 years under favorable conditions. It is necessary to maintain the level of moisture and temperature - this species does not tolerate frost and drying out of the habitat. The optimal temperature is 18 - 20 degrees Celsius. It is advisable not to overwater the compost heap, as eukaryotes may suffocate.
The layers are laid loosely to ensure air circulation inside. As the worms eat the food components in the compost heap, a new portion is added to the worms, and they crawl to the top layer, and the bottom is ready for use.
Worm farms with compost heaps in the garden are a good type of business. In the fall, when it gets colder, the boxes are moved to a warm place. Californian worms lack the instinct of self-preservation - with the onset of cold weather, they do not crawl into the lower layers of the soil, but huddle in a ball near the surface and freeze.

TOP 7 best garden composters
The rating of the best composters includes the following models and brands:
- Keter Eco Composter, 320L;
- Master Garden without cover 600 l;
- Master Garden with lid 800 l;
- Volnusha, 1000 l;
- Grinda 422125;
- Prosperplast Evogreen 850L;
- Prosperplast Module 800L.
Next, we will dwell in more detail on the description of each of the presented composter models. We will list their advantages and technical strengths, and talk about the disadvantages and specifics of use. We present to your attention some tips for choosing a quality composter and customer reviews. We hope you will find the article interesting and useful, and you will find a lot of the information you need in it. We wish you pleasant reading!
Keter Eco Composter, 320L

The composter is made of fairly strong and environmentally friendly plastic, painted black. The Israeli manufacturer claims high-quality and reliable assembly of the structure. The height is comfortable - 75 cm. There is a lid built into the design, it is securely fixed thanks to a special mechanism, and has 4 lower hatches. Unloading finished compost has never been as comfortable and convenient as with this design. There are horizontal holes, through which there is full air circulation. The container is light in weight (6 kg), easy to move from place to place, and resistant to deformation and external influences.
| Structure height, cm | 75 |
| Volume, in l | 320 |
| Availability of cover | Yes |
Price: from 4000 to 4299 rubles.
pros
- ease of assembly;
- full air circulation inside;
- light weight 6 kg;
- comfortable height 75 cm;
- hatches for unloading are located on all sides;
- availability for purchase in stores.
Minuses
- thin walls;
- weak fixation.
Buying a composter became our salvation. We spent a long time choosing among several models and brands and settled on this one. I liked the dimensions, ease of assembly and the presence of circulation holes. This model makes me happy; we regularly unload waste, so we never run out of compost. Previously, it was much more difficult to carry out the assigned tasks, but thanks to such devices everything becomes much easier.
garden composter Keter Eco Composter, 320L
Master Garden without cover 600 l

The composter from a Russian manufacturer is distinguished by its simplicity and functionality. From the outside it looks like an ordinary box; guests of your site will not immediately realize that fertilizer is being prepared inside. The assembly principle is as follows: several planks are connected to each other thanks to special recesses at the ends. The design turns out to be quite decent and strong. Removing the fertilizer is simple; just move aside the crossbar located at the base of the container. The height of the product is 70 cm, it is voluminous, looks neat and well-groomed. Made from sustainable high-quality plastic, it is not susceptible to external influences and is not afraid of sudden temperature changes.
| Volume, in l | 600 |
| Height, cm | 70 |
| Lid | No |
Price: from 1990 to 2390 rubles.
pros
- lightweight design, easy to transport;
- laconic appearance;
- ease of extraction of finished fertilizer;
- quick and easy assembly and disassembly;
- reliability of the design.
Minuses
- requires a perfectly flat surface;
- There are gaps in the structure.
We bought the composter last year. Before this, fertilizer was prepared in front of everyone, not the best option, dirty and ugly. But with the composter the tasks were simplified. True, the design has large gaps, but otherwise we are completely satisfied with it; the fertilizer can be easily pulled out when needed. In general, it’s a great option, I recommend it.
garden composter Master Sad without lid 600 l
Master Garden with lid 800 l

The classic format of the model: the body has a hexagonal shape, there is no bottom. It consists of four tiers; the container goes deep into the ground using several pins. The fixation is reliable, so the device fits well into the overall picture of the site. The lid tilts in two directions; the smell of the contents is practically not felt when you add new compost. The design is made of strong and durable plastic, it is not subject to sudden temperature changes, and is of high quality. The height of the structure is 120 cm, making it convenient for short people to throw waste.
| Cover included | Yes |
| Composter height, cm | 120 |
| Construction volume, in l | 800 |
Price: from 4290 to 4600 rubles.
pros
- high quality assembly;
- availability for purchase in stores;
- quick assembly;
- ergonomic shape and attractive design;
- thick walls of the structure;
- Convenient loading and laying out of compost.
Minuses
- in winter, the pins tend to expand;
- heavy weight – 18 kg.
A good and spacious composter. It copes well with the assigned tasks; we prepare fertilizer both in winter and in summer. The bookmark is convenient, the display is also carried out without problems. I like the performance of the composter, so I recommend it for purchase.
garden composter Master Sad with lid 800 l
Volnusha, 1000 l

The garden container is made of high-strength plastic material. The large volume (1000 l) provides the user with continuous unloading of compost at any time convenient for him. The material is durable, this strength is ensured by primary granules. The container survives well outdoors even in winter, since the material is not exposed to external influences, does not collapse or burst. The composter is made in the form of a cylinder tapering towards the top with wavy walls - this way the processed and decomposed organic waste below will not cause deformation of the body. In general, there are mostly positive reviews about the design - high-quality and quick assembly, reliable fixation and durability, large volume and comfortable dimensions.
| Structure height, cm | 107 |
| Volume, in l | 1000 |
| Availability of cover | Yes |
Price: from 6199 to 6350 rubles.
pros
- reliability and durability of assembly materials;
- high-quality assembly;
- assembly speed – up to half an hour, no more;
- tolerates temperature changes well;
- fastening and fixing the damper;
- attractive external characteristics;
- when disassembled, the design is compact and fits in the trunk;
- the largest volume is 1000 l.
Minuses
- heavy weight;
- The cover is light and flies away under strong gusts of wind.
The volumetric composter fits perfectly into the summer cottage. In the conditions of the Siberian winter, the material does not crack, compost is prepared quickly and without much effort on our part. We devote our time to completely different matters, but we are sure that we always have enough fertilizer.
garden composter Volnusha, 1000 l
Grinda 422125

The German manufacturer offers a budget version of the composter. It looks like a cylinder, its height is less than half a meter. The product is made of dense polyethylene material, it covers the springs. Due to this, the structure is convenient to assemble and stretch back, and this aspect is extremely important. Despite its small size, the composter copes well with its tasks. In addition, it is worth noting that it is miniature - the structure is convenient to transport from place to place, there is no need to disassemble and reassemble it every time, to ensure that all parts are present. The volume of 95 liters, although small, will definitely come in handy for important needs.
| Cover included | No |
| Composter height, cm | 47 |
| Construction volume, in l | 95 |
Price: from 419 to 424 rubles.
pros
- ease of use;
- convenient and easy to assemble, disassemble and transport;
- weight about 600 g;
- quickly cleaned and reused;
- copes with the assigned tasks 100%.
Minuses
- small size;
- weak spring;
- in winter does not tolerate low temperatures.
A small and compact composter was purchased at one time out of necessity. But it is good, and even after purchasing a large volumetric device, we continue to use Grinda. It looks great and is easy to assemble and use. There are no problems at all, so if you need a little fertilizer, then definitely consider this option.
garden composter
Prosperplast Evogreen 850L

The volume of the composter from the popular line is 850 liters. The case is comfortable and has a pyramidal shape. The design is made of durable polypropylene; it copes with the assigned tasks perfectly and is not subject to external influences, especially seasonal temperature changes. Air circulation is carried out throughout the entire area, so compost is prepared much faster and is available to summer residents in summer and winter. Assembly is easy, the kit includes detailed instructions as well as all the necessary spare parts and tools.
| Volume, in l | 850 |
| Height, cm | 134,5 |
| Lid | Yes |
Price: from 7119 to 7390 rubles.
pros
- reliability and high quality materials;
- rapid processing of deposited materials;
- Assembly takes a minimum of time - up to 15 minutes.
Minuses
- high design - 134 cm, it is inconvenient to put waste inside.
This is not the first year that a large composter has helped us out. Despite the difficulties in laying - you have to puff to get to the top, but I don’t see any other problems at all. Work at the dacha began to bear even more fruit, and all thanks to the fertilizer prepared in the composter. I think the option is voluminous and sufficient, fertilizers are available both in winter and in summer; when needed, we take some and add new waste. Fast, convenient, high quality and with care for summer residents - this is what this company is all about.
garden composter Prosperplast Evogreen 850L
Prosperplast Module 800L

According to customer reviews, this model is the best in terms of price-quality ratio. The assembly includes two large black boxes made of thick, highly durable plastic material. The modules are securely fixed to each other, with grilles installed at the bottom. It is through them that the entire air circulation cycle is carried out. Through the hinged doors, the user collects the finished compost and uses it for its own purpose in the future. The weight of both boxes is 11.6 kg, they are quite light and easy to transport from place to place if necessary.
| Structure height, cm | 135 |
| Volume, in l | 800 |
| Availability of cover | Yes |
Price: from 6100 to 6799 rubles.
pros
- strong materials;
- ease of use;
- capacity – 800 l;
- tall and easy to fill.
Minuses
- not found.
An ideal option, the cost is fully justified by functionality and reliability. I recommend this composter to everyone, you will not regret the purchase and will prepare fertilizer perfectly!
garden composter Prosperplast Module 800L
Construction of an open and closed composter
For airtight composting, it is important to know how to properly make your own compost pile. A completely sealed structure is required. A plastic container with a hatch or a concrete container dug into the ground is suitable for this purpose. In this case, the bottom must be filled with cement mortar so that nutrients are not absorbed into the soil, but are preserved for plants. There must be a cover with a hatch.
You can use a simple method - put the components in garbage bags and put them in a cool place where the sun's rays do not reach.
Making an open compost heap with your own hands is easier. It is necessary to build a box from boards, the gaps between which will promote air circulation. It is better to make 2 boxes side by side so that, if necessary, you can transfer the ripening compost from one box to another.
There are special plastic containers with holes for aerobic composting, but their price will be much higher than a homemade structure made from scrap materials - mesh, boards, slate, plastic sheets.

Rules for laying components - nitrogen and carbon ingredients
If you don’t know how to make a compost heap correctly, you can ruin the raw materials. The main thing is to follow the rule of mixing components - 1 part nitrogen - 2 parts carbon. There should be layers of soil between them.
The first - the lowest layer - is soil or peat. You can put dry straw or hay at the bottom. This is a kind of bedding that will absorb liquid and control the amount of air inside.
Next, green and brown layers alternate, which are covered with earth. Compost made from nitrogen components alone will deteriorate faster if lime is not added. If a stench appears, you urgently need to add carbonaceous substances, slaked lime, mix and add EO preparations - you can use those prepared at home. Fermented milk and yeast solutions are suitable.
If the content of carbon substances is exceeded, then the compost heap can wait a very long time for maturation. Without nitrogenous components, the decomposition process will not start. You can speed it up by adding herbs and watering with EO preparations. In the absence of both, urea or saltpeter is used as a nitrogen substance.
Video: DIY compost pile
If desired, mineral fertilizers, ash, bone meal or superphosphate are added to the finished fertilizer to improve nutritional characteristics.
What cannot be entered
Sick plants are not suitable for composting. If the temperature is insufficient, fungal spores will spread with the compost throughout the entire area. It will be difficult to remove them and the entire crop will die.
Do not add sawdust from painted boards. Chemicals cause the death of bacteria. A component such as pine litter is used carefully, as it increases the acidity of the finished fertilizer.
Plastic, metal, glossy paper, glass and synthetic fabrics are not suitable for composting as they are not digested by bacteria.
It is not recommended to place meat and fish waste - they cause a stench in the area. Such ingredients take a long time to process, so it is better to apply them directly to the garden bed and dig deeper.
How to make compost
There is a certain method for preparing compost, following which a high-quality substance is obtained in the shortest possible time. Its main instructions are:
1. Mix several components and then lay out in layers.
2. Place a 30 cm layer of soil at the bottom of the heap, then a 10 cm layer of pre-dried and chopped grass, on top of 1 layer of leaves and weeds, each 25 cm thick.
3. It is necessary to frequently add food waste to the compost heap, while keeping bones and fats away.
4. Each new layer must be moistened with water.
5. Systematically add mineral fertilizers, bone meal, and manure.
6. Constantly shift the pile, make sure that it does not dry out and that it is sufficiently, but not excessively, moistened. For work, it is better to have a separate set of shovels and forks.
At some point, the compost will be ready, this is easy to determine by color and consistency - the ripe mixture will have a loose structure, the smell of forest soil and will acquire a dark brown color.
How to care for compost during maturation
Anaerobic compost does not require any care, except that you need to choose a place for it away from sunlight. At high temperatures, microorganisms die.
The aerobic mixture needs to be watered with a new portion of bacteria every 20 days. This will speed up ripening. To make fertilizer even faster, the components are turned over with a pitchfork. Bacteria multiply better in air. A compost heap in a loose state decomposes faster.
Maintaining humidity is the second condition for the growth of the number of microorganisms. Without water, their activity stops and the maturation of the fertilizer slows down.
The best time for laying occurs when the air warms up to 18 - 20 degrees. This could be early summer or early autumn. It is advisable for the composter to be in the shade - this way it dries out more slowly and is not exposed to ultraviolet radiation, which is harmful to bacteria.