What is hydrogel
The powder or beads are translucent or almost white in color - this is a converted polymer. A specific feature is the ability to absorb moisture in large volumes. Polymer granules, powder or rounded particles absorb about 200 g of water per 1 g.
Important characteristics and properties:
- Once absorbed, the liquid may evaporate or penetrate into the soil. Just a couple of tablespoons of hydrogel accumulates about 3 liters of water.
- After placing polymer particles into the soil, the process of gradual release of liquid into the environment - the soil - begins. This property allows you to nourish flowers with life-giving moisture if the owners do not have the opportunity to water indoor flowers daily.
- The same effect is obtained when adding a granular product to open ground, under trees in the garden and on beds with vegetable crops.
- It is no coincidence that the name of the product contains the base “hydro”, which means water. Hydrogel is a “lifesaver” in all situations when adding moisture to the soil is required, but the owner cannot participate in the process himself.
Types of hydrogel soils
There are two forms of hydrogel: agricultural or colorless, and colored or aquasoil. The names of these ball-shaped granules are changed to dense and soft. Accordingly, the types differ not only in consistency, but also in quality and technique of application in practice.
Dense
Hydrogel aquasoil is distinguished by its strength of form and the presence of different colors. Such large granules are not suitable for gardening. If only a small flower garden. In any case, it is not recommended to use it in open ground.
In addition to multi-colored balls, there is an assortment of granules with glitter, rhinestones and stones, which are not very noticeable if the granules are dried.
Soft
Colored hydrogel is easy to use, but the cost and benefits are less. The method of using aqua soil differs from the soft type, since it is quite suitable for maintaining a plant without soil. Soft hydrogel is elastic, pliable and smaller in size. Benefit:
- moisture preservation, availability of use and acquisition;
- can be applied directly to the roots;
- can be used in different ways: pressed into the soil, placed on top, placed only roots or seeds;
- improves the composition of the soil, absorbs liquid only when necessary (in the presence of excess water);
- makes the soil loose. If the soil is sandy, it provides strengthening.
In what cases is it used
Hydrogel is used in the following situations:
- for “dry” watering of plants;
- the owners are going to leave home, and there is no one to look after the plants; timely watering is impossible;
- you need to quickly and efficiently feed indoor flowers or garden crops when applying fertilizers;
- the soil is too wet, the owners are looking for a way to quickly remove excess liquid from the soil;
- colored hydrogel (also known as aquasoil) is used to create original floral compositions;
- the housewife grows indoor flowers from cuttings;
- the process of seed germination (not all gardeners approve of the use of hydrogel in this case).

Types of safe polymer
There are two categories sold in agricultural stores and florist centers:
- hydrogel,
- aqua soil.
The material differs not only in cost, but also in appearance. Each type of moisture-absorbing polymer mass has advantages and disadvantages.
The use of bright beads and translucent granular mixture is somewhat different. Before purchasing a safe polymer for indoor flowers, gardening and vegetable gardens for the first time, you need to find out which variety is suitable for a specific purpose, and find out the pros and cons of each category.
Soft
Main characteristics:
- The hydrogel base is a polymer, safe and non-toxic;
- granules are small in size, color is translucent, with a slight cloudy white tint;
- particles actively accumulate moisture;
- hydrogel is often mixed with soil, added to a flowerpot, under fruit trees or in the ground in garden beds;
- the main property is the ability to both absorb excess liquid in the substrate and gradually release water into the soil when the substrate dries out;
- The cost of the hydrogel is reasonable: a 20 g sachet costs about 40 rubles, a large weight (approximately 1 kg – about 800 rubles). The consumption is small: 2 tbsp. l. polymer granules absorb up to 3 liters of liquid;
- the soft structure allows the elements of the root system to easily pass between adjacent particles, absorbing life-giving moisture as necessary;
- certain types of indoor flowers and ornamental plants, such as bamboo, can be temporarily grown without adding a substrate if, for some reason, the gardener did not buy suitable soil in time;
- The polymer environment is an unsuitable place for the development of bacteria and fungi; there is no basis for the nutrition of microorganisms. For this reason, rot and bacterial infections never develop in the hydrogel;
- the soil becomes looser after adding polymer soft granules;
- in the garden and on the beds, using a modern moisture-absorbing agent, it is easy to remove melt water, which accumulates in excess during sudden warming;
- hydrogel is an additional component for delivering nutrients to plant roots, but when using a transparent polymer material, traditional fertilizers cannot be abandoned.
Dense
Helpful information:
- A more expensive type of hydrogel is called aquasoil.
- The granules are large, of various shapes: cube, ball, various shades, including bright ones.
- The cost is much higher than that of traditional moisture-absorbing material, and the product is not suitable for constant use in the garden.
- The hydrogel is suitable for growing plants for some time; aqua soil is used to create original floral compositions and interior design.
- Aqua soil is used by decorators and designers; flower growers rarely use aqua soil constantly: the plants dry out, grow poorly, and do not receive enough nutrients that are not contained in the synthetic material. For a very short period, you can place flowers in aqua soil to effectively decorate a green corner or after cutting flowers for a bouquet, but you will have to feed the specimen and follow other rules of use so that the plant does not die.
Hydrogel - what kind of beast?
Among the many substrates for hydroponics (coconut, vermiculite, expanded clay, mineral wool, sphagnum and others), there is a very special substrate that is used in both hydroponic and soil methods of plant cultivation - hydrogel. What is it and what is it used for?
In the soil method of growing plants, hydrogel is used as an additive to the substrate - soil, peat, sand. It has a remarkable ability to fill with moisture and retain it for a long time, so it is indispensable if plants are left for a long time without the care of the owner.
In addition, hydrogel is used when transporting plants. If you need to transport a cutting of a plant to a new place, then it is very convenient to place its roots in hydrogel - it will not allow the root system to dry out, and the cutting will arrive at the new place in a completely healthy condition.
As a substrate in hydroponics, hydrogel is used in almost the same way. Despite the fact that experienced hydroponists use a variety of devices to control the humidity of the substrate, many of them “play it safe” by adding a hydrogel to the main substrate that can hold the nutrient solution and then gradually release it to the roots so that they do not experience a deficiency of moisture and nutrients.
In addition, the hydrogel also performs a completely opposite function: if for some reason the substrate turns out to be waterlogged, the hydrogel will absorb excess moisture and prevent the root system from rotting.
The hydrogel can be added to the substrate immediately or when the plant is developing. In the first case, the dry hydrogel is poured with clean water (1 gram per 1 liter of water) and wait several hours until the granules swell to the maximum. Then the finished hydrogel is thoroughly mixed with the substrate so that no lumps form. You can mix it with hydroponic substrates such as vermiculite, perlite, expanded clay, and add it to sphagnum. Coconut substrate and mineral wool with hydrogel are usually not mixed due to the elasticity of these substrates.
If the plant is already planted in the substrate, then the hydrogel can still be added. To do this, vertical holes are made in the substrate, trying not to damage the root system, and the hydrogel is poured into them in dry form. Then the plant is watered abundantly. The hydrogel swells. During the process, the substrate may rise. In this case, you need to carefully mix the top layer of the substrate. The roots of the plant will “find” the hydrogel in about two weeks. And from now on it will be possible to make watering more rare. This is a significant saving.
Hydrogel as a substrate in hydroponics can be used for rooting cuttings. Many people like this method, since moisture is very important for the formation of new roots, and the hydrogel allows the plant to receive it in full. The cuttings will not dry out and the roots will grow very quickly.
When choosing a hydrogel as a substrate for hydroponic installations, preference should be given to a French or domestic product - they are of higher quality. Chinese hydrogel looks very beautiful, can be multi-colored, but does not quite meet the requirements. It absorbs and releases an insufficient amount of moisture.
When growing vegetable crops, hydrogel is used as an additive. However, hydroponic gardeners also use this interesting substrate as the main one. However, before using hydrogel, you need to carefully study the plant's moisture requirements and find out whether similar methods are suitable for it.
Advantages and disadvantages
Positive points:
- maintains water balance in the soil;
- increases the level of soil aeration;
- prevents drying out of the soil, the formation of a dense crust and cracks on the surface;
- a small amount of granules is required to retain moisture in the substrate;
- suitable not only for filling the soil with moisture, but also for removing excess liquid when the substrate becomes waterlogged in a flower pot or garden;
- accelerates the delivery of nutrient mixtures to the roots;
- eliminates the need to water indoor flowers every day;
- prevents the death of plants from moisture deficiency if the owners go on vacation or a business trip for a long time;
- safe, odorless, the risk of allergies is minimal;
- low cost;
- the consumption is low, which significantly reduces the cost of maintaining optimal soil moisture;
- when the hydrogel decomposes, harmless components remain: water, ammonium and carbon dioxide;
- does not evaporate, does not emit toxic substances under the influence of heat indoors, in the garden or in the garden, however, direct sunlight can cause the softened product to bloom;
- fungi and bacteria do not multiply in a synthetic environment, the substance is sterile and safe to add to the soil;
- used not only in its pure form, but also combined with a substrate;
- colored aqua soil is an affordable means for creating spectacular floral arrangements and room decoration.

Flaws:
- You cannot reuse colorless granules for one plant and then for another plant;
- when planting other varieties and varieties, the sterility of the base is lost;
- not suitable as a main component for growing plants;
- the cost of aqua soil is quite high;
- hydrogel does not replace organic matter and mineral fertilizers.
Application area
Soil hydrogel can be used immediately after purchase - scattered in a flower pot or in the garden. Application in home gardening is more like planting a plant directly in a colored hydrogel. At the same time, the plant feels great and receives the necessary micro and macroelements.
Since, in addition to liquid, the granules will absorb all introduced fertilizers, vitamins and fertilizing. The material significantly reduces stressful situations that a flower can get into in a country house or in an apartment:
- transfer;
- pruning;
- preparation for winter;
- treatment of diseases and extermination of parasitic creatures.
Adding water with the necessary additives to the mixture with the hydrogel (which looks like small beads) turns the granules into large peas. But the original appearance is gradually returning.
This happens after the liquid enters the soil. Hydrogel beads are reusable, which does not require constant intervention in the growth process.
The substance is recommended not only in closed ground, but is also suitable for open ground (garden, vegetable garden), where shrubs, trees, and flower beds are planted. Use the same as at home.
A good solution for summer residents who cannot water daily. In 15% of cases, hydrogel is used as a decorative primer, as they make a common mistake - they are confused with aqua soil.
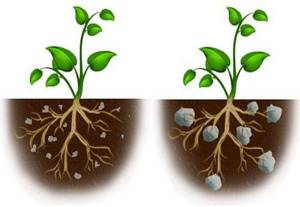
Application in indoor floriculture
The use of hydrogel for growing decorative foliage plants and species with spectacular buds in “pure” hydrogel is not carried out. Be sure to mix the polymer granular mass with the substrate. Proportions: no more than 2 g of hydrogel per 1 liter of soil mixture. The best option is to add a little granular product during the plant replanting period.
Before leaving, pour hydrogel onto the bottom and near the walls of the flowerpot, and mix a small amount of granules into the top layer of soil.
Before filling the flowerpot, you need to ensure that the material absorbs the required amount of moisture. It is important to observe the norm of the moisture-absorbing composition, taking into account the volume of the flowerpot. First, take out a flower with a lump of earth. On a note! In rare cases, you can keep certain species, such as bamboo, for some time in containers with transparent granules, but you will have to additionally feed the flower and make sure that the polymer does not bloom from unsettled water. Often, a lack of air in the area where the underground part of the plants is located leads to poor growth, and the flower has to be replanted. Growing roots in a glass container give the substance an unattractive appearance.
Application in gardening and horticulture
Granular polymer is not used for all vegetable crops. Often, the use of hydrogel negatively affects the condition of plants: the gardener hopes that the soil is moist from the inside, and does not always water the beds on time. The result is slow growth and wilting of vegetable crops.
In vegetable growing, hydrogel is used for a limited list of types:
- potato;
- radish;
- tomatoes;
- cucumbers;
- cabbage.
The granular composition is buried approximately 5 cm and mixed with soil. For heavy, loamy soils per 1 sq. m, 20–30 g of polymer are added; for light soil, 10 to 20 g of hydrogel is sufficient for the same area.
Application in gardening:
- moistening the soil, creating a looser substrate when planting young trees, propagating shrubs by layering and cuttings. For 1 part of hydrogel take 5 parts of soil. The procedure is useful in areas where the soil quality is not as good as required for certain types of fruit trees and shrubs. For young shrubs and seedlings, a swollen hydrogel is useful so that the roots gradually extract moisture from the polymer granules;
- removal of stagnant melt water after sudden warming amid heavy snowfalls in winter. Dry hydrogel is scattered over the area and mixed with soil;
- moistening the soil near apple trees, cherries, pears, plums and other fruit trees. The older the plant, the more granules are needed to improve the quality of the soil and gently moisten the soil over a long period. Average consumption: 20–40 g of polymer granules per tree. First, punctures are made in the near-trunk zone to a depth of about half a meter; not only the optimal amount of polymer is poured into the holes, but also fertilizing (mineral fertilizers). Next, add the substrate, fill the holes with hydrogel, and water the soil well. As the granules swell, the substrate around the trees often rises slightly. For shrubs, consumption is less: from 3 to 10 g, granule depth: 25–30 cm.

Hydrogel in plant life
Then I had no idea why cucumbers sometimes start to taste bitter. Later I learned that bitterness in fruits appears when the soil dries out (even for a short time), and then there is no way to get rid of it.
How to protect growing fruits from bitterness? To ruin the entire harvest just because you failed to water the plant in time - what could be more terrible?
Probably, many gardeners have encountered the problem of insufficient watering of plants (especially those who cannot water the garden every day). In hot, dry times, watering plants only occasionally is clearly not enough.
Not only cucumbers do not tolerate a lack of moisture well: many plants, although the soil dries out, survive, but lose their decorative appearance, weaken and are at risk of attack by pests and the appearance of diseases. In plants suffering from a lack of water in the soil, leaves and shoots begin to droop, turn yellow, dry out, buds and ovaries fall off...
Results of using hydrogel
Not long ago, unusual crystals appeared on sale that can solve the problem of soil drying out - these are hydrogel crystals or, as they are sometimes called, “water crystals.” I used hydrogel for the first time several years ago (when growing indoor plants) and was pleasantly surprised by the results. If previously plants that required regular watering sometimes turned out to be too dry (especially if I had to leave home for several days), then with the use of hydrogel a new life began for them - I could not water them for a week, or even two. At the same time, the plants developed beautifully and showed with all their appearance that the hydrogel was helping them.
Unfortunately, plant lovers still rarely use hydrogel when growing vegetables, flowers, trees and indoor green pets. Perhaps the active use of hydrogel is hampered by a lack of information about this reliable assistant for plant growers.
Hydrogel will save your time (which was previously spent on frequent watering), money (on buying new plants to replace those that died from lack of water) and will improve your mood from contemplating pets happy with their lives. You will almost forget what a wilted plant is!
I would like to share my experience of growing plants using hydrogel. First, I'll tell you a little about the crystals themselves and how they work. Hydrogel crystals are similar in appearance and size to sugar and are irregularly shaped and irregular in size. When it gets into water, the hydrogel crystal absorbs it, increasing in size by about 300 times. So the crystal becomes a kind of reservoir of water, which, if there is a lack of moisture in the soil, will give up its reserves to the roots of the plants, and if there is an excess of moisture, will absorb it. Thus, the hydrogel saves plants not only when the soil is dry, but also when it is waterlogged!
Due to their structure, hydrogel crystals improve the characteristics of a wide variety of soils: clay soils become more loose, and loose soils become lumpy.
Plants grown using hydrogel, even in the most extreme heat, need to be watered once a week or less.
The crystals will work in the soil for a very, very long time; they do not need to be changed. It is worth adding hydrogel crystals to the soil in a garden bed, in a greenhouse, on a lawn, in a pot or in a balcony box - and they will begin their many years of work in providing plants with water in a timely manner.
When using hydrogel, mineral fertilizers for plants should be used at approximately half the concentration, so the hydrogel also saves fertilizer!
And most importantly, the hydrogel is an environmentally friendly product with a neutral reaction: it only improves the properties of the soil and does not harm it in any way.
Application of hydrogel crystals
The hydrogel is sold in garden departments of stores; there are a variety of packaging options. The packaging volume of hydrogel crystals ranges from 10 g or more (for use in indoor and balcony floriculture) to 5 kg for use in the garden.
When using hydrogel in open ground, it is added to the soil in dry form at the rate of 25-100 g of crystals per square meter of surface (the specific amount depends on the composition of the soil). For clay soils, less hydrogel is taken, for sandy soils - more. For ordinary garden soil, it is enough to add 30-40 g of crystals per square meter.
Typically, this method of adding dry gel crystals is used in the garden when laying lawns and flower beds, and when preparing beds.
After adding hydrogel crystals, the soil must be watered abundantly. Please note that since the crystals, absorbing moisture, greatly increase in size, the soil may rise after watering.
For plants with a shallow root system, hydrogel crystals are mixed with the top (10 cm) layer of soil. For plants with a relatively deep root system, the gel is mixed with a thicker top (20-25 cm) layer of soil.
You can add hydrogel to the holes directly when planting plants.
In this case, before adding it to the well, the hydrogel is pre-soaked in water - at the rate of 300 g of crystals per bucket of water (10 liters). After about 30-40 minutes, the crystals will swell and fill the entire container. In this form, the hydrogel is mixed with soil, poured into the holes during planting (at the rate of 1 part of the swollen hydrogel to 5 parts of soil).
The hydrogel can be mixed into the top layer of soil of already planted plants. Pre-soak the gel and mix it with the soil located around the plant - to the depth that the plant roots will allow. It is better to do this with your hands so as not to damage the roots.
The same method of using hydrogel, as when planting in a hole, is used when planting plants in containers or flower pots - in indoor and balcony floriculture.
Never add dry hydrogel crystals to the soil of containers, because when the hydrogel swells after watering, it will greatly increase in size and squeeze the plant out of the pot. Be sure to pre-soak the crystals in water and add them to the soil of the container in the form of a ready-made gel.
I’m not advocating covering the entire garden with hydrogel at once—try first using the crystals on the most problematic plants, which suffer the most from dry soil. Having seen the result, you yourself will want to grow as many plants as possible using hydrogel.
And then your cucumbers will never again experience bitterness from the soil drying out. When growing indoor crops, do not use hydrogel for all plants in a row - use it only for plants that consume large amounts of water and require frequent watering.
Hydrogel, for example, is not suitable for epiphytes and some plants with dense, leathery leaves, since when using hydrogel such plants may not require watering for months. As a result, the soil in the pot will remain wet for a long time, and fungi and algae will begin to grow on the surface of the soil, blocking the access of air to the roots of the plants.
But plants with soft leaves and herbaceous plants respond very well to the addition of hydrogel to the soil. They stop withering and lose leaves less often and grow better.
Using hydrogel, I grow passionflowers, thunbergias, dwarf pomegranate, myrtle, calliandra, oleander, acalypha, abutilon, acanthus, hypoestes, aphelandra, brovallia, datura and other nightshades (pepper, nightshade), irezine, coleus, mimosa, fuchsias...
This list can be continued by your observations of other plants grown using hydrogel!
Galka Okhapkina
Based on materials from Gardenia.ru
Should I use hydrogel: pros and cons
Most flower growers, gardeners and gardeners speak positively about hydrogel:
- The best option when growing ornamental, fruit and vegetable crops is to use a “soft” category product to moisten the soil and activate the supply of nutrients to all parts of the plants.
- The complex effect (hydrogel balls optimize the level of soil moisture: if there is a deficiency, it fills the soil with water, if there is an excess, it absorbs excess liquid) helps to grow a good harvest and luxurious flowers.
- When comparing lists of advantages and disadvantages of hydrogel, it is easy to notice: there are many more advantages. Soft granules made from a safe polymer literally save flowers when the owners leave for a long time, and help gardeners and gardeners replenish the soil in arid regions and in “heavy” soil.
Opinions about aquasoil (solid hydrogel) are not so clear-cut. Synthetic material is suitable for decoration, creating interesting, bright floral compositions, but growing indoor flowers in such “soil” is not worth it due to the sterility of the composition and lack of nutrients. It is important to remember: hydrogel and aqua soil do not replace a substrate with organic substances.
Subject to the rules of use and norms for each type of plant, it is useful to add hydrogel to the soil. Another variety, aqua soil, is suitable for creating spectacular compositions when decorating rooms. It is useful to follow the advice of experienced flower growers, gardeners and gardeners, and take into account the information from the article.
What is hydrogel and how to use bright colorful balls to grow plants? More useful information in the following video:











