Grafting an apple tree is a good help for gardeners. This is an opportunity to place several different types of apple trees on a small piece of land, improve their properties, speed up fruiting, or even save an old apple tree. There are several different methods of vaccination, they differ in technique and timing.
Apple tree grafting.
What does grafting give to a tree and a gardener?
Grafting apple trees is an excellent selection method that will benefit the gardener and the apple tree. Here's what's remarkable about apple tree grafting:
- an apple tree can be rejuvenated and its lifespan extended;
- you can preserve a rare or preferred variety;
- reduce apple tree growth and crown shape;
- accelerate the onset of fruiting;
- save a dead, diseased or damaged tree;
- plant several different varieties on one rootstock.
Thus, the benefits of the grafting procedure are noticeable both for the gardener and for the fruit crop itself.
Terms you need to know
Grafting apple trees is a rather troublesome procedure. To carry it out, you need to prepare and know some basic terms.
- The rootstock is the root system, a kind of foundation on which the grafting will be carried out.
- Scion is a part of a plant that has been removed and prepared in advance, and which will be placed on the rootstock.
- Copulation - carrying out a grafting procedure using a cutting or shoot.
- Budding is the grafting of a bud or several to change the properties of the rootstock.
Typically, these few words are the most common in the terminology used by professionals.
How to understand that a tree is ready for grafting
In order for the apple tree to tolerate the procedure well, it is necessary to choose the right time for it. And this applies not only to the timing of grafting apple trees. There are a number of visual signs by which you can determine that the apple tree is ready for grafting.
These include:
- three-year-old planting with well-developed roots;
- a strong-looking trunk, free from pests and diseases;
- the process of sap flow should already be actively occurring.
Apple tree ready for grafting.
If the scion is placed on an old tree, it must first be thoroughly cleaned and the wounds covered.
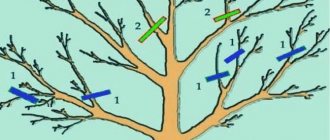
Step-by-step instructions: how to properly graft into a cleft and incision
The grafting technology is relatively simple. If the cutting is implanted on an annual tree or on a branch that is not too thick, the procedure does not cause any difficulties.
It is more difficult to graft onto a stump or thick skeletal branches.
Grafting into a cleft or incision involves the same steps as all other methods. The material must be prepared, the scion must be combined with the rootstock and the resulting connection must be protected.
Preparation: when and how
You can harvest cuttings several times throughout the year. Annual sprouts are suitable for this, preferably from the middle tiers. Cuttings are chosen from the south side, since here they have the shortest internodes.
The best scion is cut from young abundantly fruiting apple trees aged 3 to 10 years.
You need to pay attention to the cut: it should be clean, there should be no brown spots in the center.
Cut off shoots 30–40 cm long and at least 7 mm thick in diameter - a thinner scion will not take root. It is better not to take tops - branches perpendicular to the main one: they take root well, but do not set an ovary for a long time. Sprouts can also be taken from old apple trees when they want to update the garden, but do not change the variety. In this case, the branches are cut shorter - up to 15 cm.
Read about tops on an apple tree here.
The sprout should have no more than 4–5 developed buds. If there are more of them, then it is better to carefully separate the extra eyes with pruning shears.
Scion harvesting time
Gardeners still argue about the time to take cuttings. Shoots harvested in the fall do not allow the buds to swell too early, and those cut in the spring are ready for grafting at the same minute.
- In autumn, harvesting is carried out at the end of November, when sap flow stops. The cuttings are stored in a dry cellar, in the refrigerator - in the vegetable department, in the barn, or in any other place where the temperature is constantly maintained from 0 to +3 C. You can save the material even in a trench dug in the ground and sprinkled with leaves or sawdust.
A cutting that has successfully survived the winter should have even, smooth bark and tightly seated buds . When bent, the branch bends well and does not crack. If the skin on the cutting is wrinkled, but it bends, it is placed in clean water for 3 days, after making a new cut 1–2 cm higher. It is also worth checking the sprout for frostbite. To do this, make a new cut and place the shoot in water. If the cut is brown, then the cutting can be thrown away immediately. If, after standing in water, it turns yellow or brown, it means it is frozen and is also not suitable for grafting.
Cuttings in the fall should be cut with a reserve - at least 15 pieces, for engraftment onto one rootstock.
- In the spring, the shoots are cut before the sap begins to flow - in early March, and stored at a temperature of +3 C. Premature swelling of the buds on the cuttings, and especially the appearance of leaves, is not allowed. This thread will no longer survive.
Before the procedure, the cuttings are cut into a wedge, so that the length of the latter is equal to 3–4 diameters of the sprout, that is, 21–28 mm. Do not touch the cut with your hands to avoid infection.
Preparation of the rootstock
The mother plant also needs to be prepared for engraftment. If it is a wild tree or a large branch, they are cleaned of dirt and too old bark is removed. Then the tree trunk is cut at a distance of 10–15 cm from the ground. The skeletal branch chosen for the scion can either be cut down or small branches can be simply removed. The cut must be cleaned with a knife.
This link will tell you about pruning an old apple tree.
If only 1 scion is supposed to be implanted on a wild bird, then the trunk is cut down diagonally. The shoot is grafted onto a higher part.
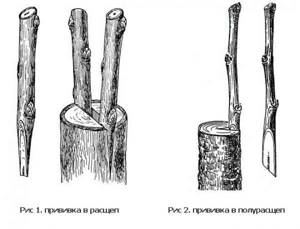
The rootstock is split with an ordinary knife: a cut is made along the diameter line with a depth of 3–4 times the diameter of the scion – 20–28 mm.

If the cutting is grafted onto a stump of large diameter - 15 cm, then it is prepared somewhat differently.
First, a cut is made on the bark along the supposed split - in this case, the bark will separate with even edges when split. Using a knife or hatchet, split the stump to a depth of 5–7 cm. To prevent the split from closing, insert a sliver or chisel into it. Then the split is expanded with a chisel or wedge.
If a cross-shaped split is performed, then the procedure is repeated so as to obtain a split perpendicular to the first.
Merging a scion with a rootstock: the right technology
The procedure depends on the nature of the scion and rootstock.
- If a cutting is implanted on a branch or young tree, then I do this: the graft is introduced into the cleft so that the cambium on the mother plant and on the sprout coincide. There is no need to immerse the scion all the way. On the contrary, it is better to leave a strip of cut above the level of the cleft, while the scion and rootstock will grow together better.
Before the procedure, wash your hands with laundry soap and try not to touch the sections of the rootstock and cuttings during work, so as not to cause an infection.
- If the grafting is carried out on a wide cut or on a stump of large diameter, then it engrafts 2 cuttings or even 4 at once. The technology is the same, but you need to make sure that it is the cambium that is combined, and not the bark of the scion and rootstock. On a stump the bark is thicker and is not an indicator.

A wedge or screwdriver is inserted into the split, and the cuttings are deepened on opposite sides of the split.
If 4 shoots are grafted, then a cross-shaped split is made on the stump and a wedge is left in one split. The first pair is inserted into this split. Then the wedge is removed, the 2nd split is expanded with it and the next pair is inserted into it.
It is even easier to plant a cutting into a side cut in the trunk. To do this, make a cut in the standard part of the apple tree and remove the bark above it. The scion is cut not with a wedge, but with a peg - with two edges at 90 degrees. One cut should be slightly longer. Using a garden hacksaw, remove the remaining layer of bark above the cut. The scion is inserted into the cut so that the longer edge is directed towards the bark of the trunk and deepened until the bark of the shorter part of the scion and the tree coincide. The vaccine is then isolated.
Isolation, feature, care
The vaccination site must be protected. To begin with, wrap it tightly with cling film, electrical tape, and rubber.
The winding ensures tight contact between the scion and the rootstock, which promotes rapid engraftment. Then the cut of the scion, the side cracks, the end of the rootstock - all open areas - are covered with garden varnish. Until the first leaves appear, it is best to keep the engraftment site closed - wrap it in a transparent plastic bag to maintain moisture. Then the film is removed.
How to cover a saw cut on an apple tree, read here.
Required tools and materials
The grafting procedure is a kind of operation for the plant. Therefore, it is necessary to prepare all the necessary tools and materials in advance so that they are at hand.
You need to prepare:
- a sharp garden knife that needs to be disinfected;
- the same sterile pruning shears;
- if necessary, a garden saw;
- durable material for strapping, adhesive tape or electrical tape, oilcloth and rope are suitable;
- garden pitch, putty or plasticine for sealing wounds.
Since the procedure is carried out quite quickly, it is better to have everything at hand so as not to waste time searching for the necessary funds.

Tools for grafting apple trees.
Apple tree copulation
Grafting an apple tree is not as easy as it might seem. It doesn’t always work out right away, but mastery comes with time. Copulation is possible when the scion and rootstock are the same size. The permissible diameter of the pagon and cuttings is 2.5-5 cm. The procedure is carried out in spring, summer and winter, when it is necessary to graft the seedling.
Important!
Most often, copulation is used for young seedlings, about 1-2 years old.
Copulation involves connecting the scion to the rootstock as if it were one branch - it should look like that from the outside. The pagon from the apple tree is cut obliquely, and the cuttings are cut in a similar way. Then you need to connect the sections to form a straight branch and tie them tightly so that they do not fall apart. But you should be diligent in moderation so as not to spoil the bark on the scion or rootstock.
Success awaits the gardener if the cambium of two branches coincides. Then the pagons will quickly grow together. But this is difficult to achieve, so you can use the improved copulation method. In this case, the cut is made in a zigzag manner on both branches. This will provide a tighter grip.
When is the best time to graft an apple tree?
There is an opinion that grafting is best done in spring or autumn. But different planting dates have positive and negative properties.
Winter
In winter, only “tabletop” grafting is carried out, in a warm room, for those seedlings that will be planted in open ground in the spring. There are several requirements that need to be taken into account:
- must be carried out at the beginning of the year, in January or February;
- You cannot vaccinate 14 days before moving to open ground;
- The scion will need to be removed from the crop before the onset of cold weather and should be stored in the cellar;
- you need to bring the materials into a warm room several days before the intended vaccination;
- After grafting, you need to store the seedling in a warm room, at above-zero temperatures.
Typically, gardeners try not to leave the graft for the winter, because the plant does not always easily tolerate it.
Autumn
In the fall, vaccinations are carried out only in rare cases, if there is an urgent need. So, if you urgently need to place a scion, a rare variety, you need to urgently multiply it, you can carry out vaccinations.
The procedure must be carried out in the warmest possible weather, at a temperature not lower than -15 degrees. This is a rather risky procedure; grafting into a split or behind the bark is acceptable, but only by budding.
Summer
Summer grafting of apple trees is considered optimal; plants tolerate it very well. The methods and technology of grafting can be almost any, at the discretion of gardeners.
Budding with a sleeping eye is a simple and convenient operation, the most suitable grafting of an apple tree in August.
Spring
There are many ways to graft an apple tree in the spring. The tree and scion tolerate manipulation well, quickly recover and begin to grow. It is in the spring that the movement of sap begins, and the plant gains strength and immunity. All wounds heal much faster.
In the spring, even a novice gardener can carry out the procedure. There are only simple requirements - the time must be chosen in the morning or evening, the weather must be calm. It is difficult to say exactly the timing, but gardeners often focus on the waxing moon.
Apple tree care after grafting
After all work is completed, the tree is left alone for 2-3 weeks. After this time, you can remove the tape and inspect the fusion site. If the branch has taken root, the grafting area is loosely tied with tape so as not to interfere with the growth of plant tissues. The bandage is finally removed only after 2 months , but if the procedure was carried out in the fall, then it is left like that until spring.
Young leaves that bloomed from the established scion in the first year are removed so that the plant does not waste energy on growing green mass. The next year in the summer, when the young shoots grown from the buds reach a length of 30-40 cm, the grafting site is bandaged again to protect it from fracture.

For a novice gardener unfamiliar with the technique of grafting fruit trees, the procedure may seem complicated, but by studying the relevant literature a little and watching a training video, you can easily fill the knowledge gap. To begin with, you can practice on other plants, for example, on a willow, try out various grafting methods, and then, with full confidence in your own abilities, begin experiments on an apple tree.
Author of the article: Kornievsky Igor Semenovich
Tags: apple trees
- Related Posts
- The best varieties and hybrids of cucumbers for growing in open ground and greenhouses
- Whitewashing trees - why it should be done, when is it better and how to do it correctly
- Ten best ornamental shrubs for your garden
« Previous entry
How to choose the right scion and rootstock
The donor and the plant to be vaccinated must meet several requirements. Among them:
- apple trees must be at least 3 years old;
- the rootstock must be a resistant variety with good characteristics;
- The scion must be taken from an apple tree that has already bear fruit at least twice;
- both plants that will be used must be whole and healthy.
If it is possible to select related varieties, the likelihood of survival will be greater. But this requirement is not mandatory, because they even vaccinate wild animals in order to domesticate them.
What else can you graft an apple tree on?
Apple trees can be grafted onto related varieties. Some are ideal rootstocks, such as Grushovka, Antonovka or Borovinka.
Cultivated varieties are often grafted onto wild animals. This is done primarily in order to give the crop the properties of resistance to cold and external influences.
Interspecific connections are also used, for example, between close relatives, apple and pear.
It is often said that grafting an apple tree onto a plum and cherry tree bears fruit. But in practice this is not always true. On plums, the crop most often does not form an ovary. Although grafting onto a cherry tree produces fruit, very often the fragile branches break even from a small number of apples. Therefore, such a procedure is impractical.
Enthusiasts try to graft an apple tree onto a birch, blackthorn, cherry plum or apricot tree. Such vaccinations have their place, but require certain care. It is necessary to choose the right scion variety so that the grafting is not in vain.

Grafting an apple tree onto a pear tree.
Timing and features of work in different seasons
Finding the right time is not difficult if you know all the nuances and follow the deadlines. It's better to prepare everything you need in advance. Be careful; debris and dust should not fall on fresh cuts.
Autumn
Not a very good time to work. All processes in plants slow down or even stop, and low temperatures can damage the connection point that has not yet been strengthened. When you are not sure that the scion will survive until spring, you can try this season.
There should be at least a month before the cold weather. Do the work immediately after leaf fall, this is the best time. Choose a warm day without bright sun and precipitation, do everything according to the chosen method.
Winter
Do everything in the house or apartment, since the temperature outside is negative. Select the time depending on the region; in the middle zone and in the south, mid or late January is suitable; if spring is late, then shift the dates to the second half of February or early March.
Cut cuttings in late autumn after the leaves have fallen. Also dig up wildflowers, place the root part in wet sawdust and place in a pantry with a temperature of 0 to 2 degrees. Plant the grafted plants in a pot of soil and keep there until transplanted into open ground.
Spring
It is well suited for grafting an apple tree onto a wild base, since all processes in the plant are activated and the cuttings take root best. Even if the cutting does not take root, there will be time to repeat the work again.
You can prepare everything you need either in late autumn or early spring, there is no difference. The best period will be the second half of April or the first ten days of May. If you graft an apple tree onto a wildflower in the spring, it is worth planting it in a permanent place in the fall.
Summer
Suitable for young trees. Select cuttings with a diameter of no more than 15 mm. During this period, the parts grow together normally, large influxes do not form, as can happen in the fall or spring.
There is no need to prepare the material in advance; cut it on the day of the work. The parts will grow together before the fall and will develop into a full-fledged tree in the spring. It is better to do the work on several plants to be on the safe side.
How to properly prepare cuttings
First of all, you need to choose an apple tree from which cuttings will be taken. The tree must be tested; it has already had to be harvested several times in order to know what the taste and quality of the fruits are like.
Preparation and storage rules:
- You need to cut shoots for cuttings in the fall at a temperature not lower than -10;
- Do not touch the cut areas with your hands; if debris gets on them, it is better to renew the cuts;
- Before cutting, the branch must be wiped dry, and if it is old, inspected for damage;
- For storage, the cut cuttings are placed vertically, the lower parts are wrapped with a wet cloth and placed in the cellar.
Often they prefer to store their tips in sawdust, so it will be easier to keep them moist.
There are a number of requirements that apply to the cuttings themselves.
- The cut should be taken from the middle of the branch.
- There should be 3-4 buds on the shoot.
- The top cut must be made obliquely, in one deft movement.
Once the rootstock has been determined, the cuttings and all the necessary materials have been prepared, you need to proceed directly to the procedure.
How to grow wild apple trees for grafting
The easiest way is to sow the seeds of an apple tree that has demonstrated its frost resistance. You can take them from your neighbors or from your own garden. The classic is the Antonovka apple tree variety, but other varieties that are not prone to frost in frosty winters are also suitable. The algorithm for growing a wild apple tree seedling is as follows.
- Seed stratification. It can be natural if they are sown on a seedling bed immediately after picking apples, and artificial - in a box with wet sand and the addition of activated carbon, which is placed in the refrigerator for 2-3 months. In this case, it is convenient to observe the stratification process and, if necessary, adjust the conditions for keeping the seeds. Stratification in the refrigerator begins in mid-January.

Before stratification, the seeds are washed to remove the germination inhibitor, a substance located on their surface. - Hatched apple tree seeds are sown on the beds, followed by mandatory picking in the cotyledon leaf phase. The central root is pinched so that the root system of the apple tree seedling is fibrous. You can plant them in separate pots with a volume of at least 0.5 liters, and then grow them to grafting in a larger pot. We will get a seedling with a closed root system. The soil for growing consists of garden soil, aged peat and sand in equal parts. Add a glass of wood ash to a bucket of the mixture and tbsp. a spoonful of superphosphate and potassium sulfate.

- During the growing season, a young apple tree will need several waterings and 2 feedings with mullein infusion or ammonium nitrate.
With good care, we will get a one-year developed apple tree seedling, which is time to graft.
Methods of grafting apple trees
Some methods are quite simple, while others require time and preparation. In any case, you will need to carry out the procedure with clean hands and sterile instruments.
Budding
Budding an apple tree in summer is grafting with an eye or a bud. The method is very simple, even a beginner can do it, provided that the scion is chosen correctly.

Apple tree budding.
This way the connection can be made in early spring or in August, when the second sap flow begins. The scion is a dormant, not yet opened bud. There is information that open buds were also vaccinated, but a number of difficulties arise with them. They need a lot of tree sap for normal development, and due to grafting, the bud does not receive enough of it until it has taken root. Thus, the scion dries out even before it grows to the rootstock.
The apple tree that will be the donor of shoots and buds must be watered in advance. To carry out budding, they also cut off not just one bud, but a whole cutting, and this must be done a couple of days before the procedure. A shoot 1.5 mm thick should be placed in a container of water, removing the leaves before doing so.
Step by step process:
- Using a sharp knife, you need to make a T-shaped cut on the rootstock, the top should be up to 1 cm, the vertical strip should be up to 2.5 cm;
- the bark that is located at the fork between the two cuts needs to be slightly lifted;
- from the cutting you need to cut the selected bud with a small layer of bark 2 mm and 20 mm long;
- The bud with the support should be placed to a bare spot on the shoot and tightly attached and wrapped.
You can check the quality of the procedure after 14 days. Grafting an apple tree with a bud is carried out quickly and is almost always successful.
Grafting into an incision
The method of grafting an apple tree into a cut is identical to the previous method, but the scion is a cutting. It is very convenient to use a grafting knife for this method, which is sharpened on the side where the chamfer is.

Grafting an apple tree into a cut.
The procedure is very simple. One precise cut is made in a pre-prepared area with a knife. The cut on the cutting is renewed and installed in the resulting hole. The joint must be covered with garden varnish to prevent infection, and the top must be covered with film.
Vaccination for bark
The process of bark grafting is complex and requires precise movements. Grafting can only be done in the spring; it is during this period that it is easier to separate the bark, but 3-4 cuttings can be placed on the rootstock at a time.
There are two important points that can ruin the whole procedure. The first is the direction of growth of the eyes, you need to place the seedling upward. Such a small thing, but careless and inattentive gardeners can ruin the whole process. The second is the speed of the procedure. Before proceeding with this operation, you need to try several times on unnecessary shoots.

Correct grafting for the bark.
The procedure is carried out as follows:
- select the cutting location in advance and update the cut of the cutting;
- make a size of 50 mm in one precise movement;
- place the tip of the cutting behind the bark;
- wrap with plastic film.
It would seem such a simple mechanism, but it requires precise and fast movements.
Copulation with tongue
Grafting an apple tree with a tongue can be done using a grafting pruner, which makes the same cut on the scion and rootstock.

Copulating an apple tree with a tongue.
In fact, the procedure is also quite simple in theory, but requires precision and training in advance. A shaped cut is made on the scion and rootstock using a knife, then the cut points are connected as tightly as possible and wrapped with film or electrical tape.
Into the cleft
This procedure is quite simple, but there is an important nuance - the branch that will serve as a rootstock must be young and healthy, no more than 5 cm in diameter.
It should go like this
- Make a split on the selected branch with a hatchet, and immediately insert a small spacer into it.
- You need to make cuts on the bottom of the scion, maybe on both sides, making a kind of peak.
- Combine the cut bottom of the cutting and the split.
- Remove the spacer, treat with garden varnish and quickly wrap.
Two or three cuttings can be placed in one split.
Implantation
The implantation procedure is identical to the cleft grafting procedure, with one important difference. The diameter of the rootstock and scion must be identical. The rest of the technology remains unchanged. They make a small gap in the rootstock, and cut off the ends of the scion, connect it as tightly as possible and cover it with garden varnish, then fix it with polyethylene and a piece of twine.

Implantation grafting for apple trees.
There are several other less popular and common methods that are used more when necessary. For example, bridge grafting on an apple tree is used when part of the trunk bark is severely damaged by rodents.
Summer vaccination
It is believed that summer periods are not very suitable for grafting - the survival rate is low, the apple tree receives more harm than good. However, young trees tolerate the procedure well in summer.
Features and methods
For summer work, they mainly use budding - they graft a bud from a shoot of a cultivated variety. The grafted eye begins to develop next year. This method is good with a minimum of grafting material - several buds can be prepared from one cutting. In the first half of August, the bark on the trees peels off well, which is favorable for budding into the butt.
If the procedure is performed during a hot period, in this case, so that the sections do not lose moisture, the grafting sites should be immediately shaded or protected with a plastic bag with damp peat moss. Vaccinations are placed on the north side. They take root well if in 2-3 weeks the average daily temperature is expected to drop below +15°C.

Summer budding
When to vaccinate
Vaccinations in the summer are recommended to be done during the period of repeated active movement of juices - the last ten days of July or the first half of August.
Favorable time is determined by the following signs:
- apples begin to gain ripeness;
- the growth of young shoots stops;
- easy separation of bark from wood.
Advantages
Summer vaccination has several advantages:
- there is no need to prepare and store the grafting material in advance;
- if the growth of spring grafting does not occur, later budding can compensate for the failure;
- correct summer graftings take root well on the rootstock, their maintenance is not so labor-intensive;
- In the fall we will see whether the vaccination has taken root or not.
Flaws
The main disadvantages of summer grafting work:
- scion growth will begin next year;
- strong dependence on weather conditions - sudden changes in temperature, especially closer to autumn, negatively affect the growth of the scion.
The video shows summer grafting by budding. Filmed by the Do It Yourself channel.
Safety precautions
Since sharp instruments are used for all types of vaccinations, you need to be careful with them. There are a number of simple tips that will help keep your fingers and hands intact.
- You need to be as attentive and collected as possible, prepare all the necessary tools and materials so that they are at hand.
- The weather should be windless and dry, the branches should be dry.
- Before starting to move with a knife or ax, it is better to visually draw a trajectory.
- It is necessary to ensure that when manipulating the knife, your fingers are not under the blade.
Taking into account all these requirements, vaccinations can be carried out simply and painlessly.
Possible mistakes of novice gardeners
There are several main reasons why vaccinations fail. Most often, mistakes are made by beginners, which is why materials get damaged.
- Loose fit of cuts. The parts grow together rather slowly, which is why they dry out.
- Infection or bacteria due to improper putty.
- Inaccurate cutting locations.
- Improper preparation of planting material.
If you look at photos and videos, read reviews and advice from specialists or experienced gardeners, then vaccination can be done very simply.
Different vaccination options using the split method
Cleft grafting is a simple and universal method. The point is that an incision is made on the rootstock, the scion is inserted into the resulting gap and secured tightly. At the same time, there are no complicated requirements in the shape and location of the cuts - when placing the scion, it is enough to use common sense and not be greedy. Although it is not recommended to use a rootstock more than 5 cm thick due to the high risk of rotting, even several shoots can be attached to it.

Features in different regions
There are several differences when carrying out the grafting procedure in different climatic regions.
- In the southern regions, vaccination can be carried out earlier than in the northern regions, approximately 14 days.
- In summer, vaccination should be carried out, on the contrary, in the northern regions earlier than in the south.
- In the north, all types of grafting are prohibited in autumn; they will not bring any benefit, they can only harm the entire rootstock.
Otherwise, there are no exact instructions on the timing of the manipulation.