admin 09/22/2017 1,632 Views
Winter-hardy perennial herbaceous plants valued for their bright blue flowers. Among them there are small rosette or carpet-forming evergreens that are planted in rock gardens, and tall, impressively sized herbaceous plants for mixborders and natural-style parks.
Gentian
Although gentians are famous for their blue flowers, some species and varieties can have white, yellow, purple, and even pink flowers. The flowers are solitary or collected in inflorescences, funnel-shaped, tubular or bell-shaped, 4-7 petals (usually five petals). Leaves are opposite or whorled.
Plants are quite picky about soil, so take care of this before planting.
Most spring and summer gentians are sun-loving and grow well in neutral or calcareous soil. They grow luxuriantly if they are provided with good drainage, which is usually the case in alpine hills or in containers raised above the soil surface in flower beds or in potted plants. However, Gentiana asclepiadea prefers wetter conditions found in tree-covered areas and grows well among shrubs in partial shade. The magnificent G. lutea (G. yellow) is a vigorous border plant for sunny locations.
Most species that bloom in autumn need acidic, moisture-retaining soil rich in leaf humus, and prefer places on alpine hills where the rays of the afternoon sun do not reach. G. sino-ornata is an excellent container plant and is also suitable for growing in the front of borders. Just keep in mind that in the middle zone, wintering in a container is unfavorable for plants. In warmer, drier areas of the country, fall-blooming gentians benefit from indirect light, but in cooler northern regions they thrive in open areas. All of the plants listed below are winter-hardy and tolerate frosts of at least -20°C. Most gentians contain bitter substances, hence their Russian name.
They have medicinal properties, but self-medication can be dangerous.
Description of the plant
Gentian is a perennial or annual (depending on the species) plant, distributed on all continents in tropical and subtropical climate zones. There are more than 500 species in the family. However, most plants grow in alpine and subalpine meadows. Their flowers are usually blue, sometimes yellow or white, and their stems are short and straight. One species that is most familiar to us all, blue gentian, is colloquially known as blue St. John's wort. We all know that St. John's wort, like other types of gentian, is widely used as a medicinal raw material.
Types and varieties
In ornamental gardening, annual gentians are rarely used, while perennial representatives of this genus are very popular. We offer you an introduction to the most popular species, varieties and hybrids of this plant.
Stemless gentian (Gentiana acaulis)
Or Koch's gentian (Ciminalis acaulis = Gentiana excisa = Gentiana kochiana) - in nature, this winter-hardy herbaceous perennial is found in the mountains of Western Europe. It has stems up to 10 cm high, oval-elongated green leaves with which the plant meets winter, and large upward-facing blue or blue flowers up to 5 cm long, blooming in May-June. This species has an alba variety with white flowers.

In the photo: Stemless gentian (Gentiana acaulis)
Gentian (Gentiana asclepiadea)
Or cottonweed - a perennial up to 80 cm high with pointed oblong-oval leaves up to 10 cm long and straight peduncles up to 5 cm high, on which 1-3 blue or dark blue, and sometimes white flowers are formed.

In the photo: Gentiana asclepiadea
Dahurian gentian (Gentiana dahurica)
The species is native to the Sayan Mountains, Mongolia, Dauria and Tibet. Its stems are up to 40 cm high, straight or erect. The basal leaves, narrowed at both ends, have a linear-lanceolate shape. The stem leaves have a short vagina, and the upper ones have almost none. This is a blue gentian: large flowers located in the axils of the upper leaves are painted in an intense dark blue hue. Dahurian gentian has been in cultivation since 1815. It is grown both for cutting and as a container plant.

In the photo: Dahurian gentian (Gentiana dahurica)
Yellow gentian (Gentiana lutea)
It grows wild in Asia Minor and Central Europe, being one of the tallest crop species: the plant can reach one and a half meters in height. It has a tap root, the lower leaves are large, petiolate, oval-elliptic, and the stem leaves are much smaller. Numerous yellow flowers up to 2.5 cm long are formed in the axils of the upper leaves and on the tops of the stems. Flowering begins in mid-summer and lasts one and a half to two months. This cold-resistant species, which overwinters without shelter, has been in cultivation since 1597.

In the photo: Yellow gentian (Gentiana lutea)
Large-leaved gentian (Gentiana macrophylla = Dasystephana macrophylla = Gentiana fetisowii = Tretorhiza macrophylla)
It has a wide growing area: China, Mongolia, the Far East, Central Asia, Eastern and Western Siberia. It has ascending or straight stems up to 70 cm high and 3-6 mm in diameter. The bases of the stems are shrouded for 2-8 cm in fibrous remains of old leaves.

In the photo: Large-leaved gentian (Gentiana macrophylla)
Gentiana pneumonanthe
Growing in Europe and Asia, it has erect, unbranched, densely leafy stems up to 65 cm high, lanceolate-linear leaves up to 6 cm long and up to 6 mm wide and forms dark blue flowers with a bell-shaped calyx and tubular-club-shaped at the top of the stems and in the axils of the leaves. whisk

In the photo: Gentiana pneumonanthe
Gentiana septemfida
It grows wild in Asia Minor, Iran, Crimea, the European part of Russia and the Caucasus. The plant reaches a height of 30 cm, it has numerous erect or ascending stems covered with lanceolate leaves, and dark blue flowers up to 4 cm long, collected in heads. Gentian seven-parted has been in cultivation since 1804.
- Climbing roses: planting, care, cultivation

In the photo: Gentiana septemfida
In addition to the described species, in cultivation you can also find spring gentian, Delecluse (or Cloucy), Dinaric, Kolakovsky, Chinese decorated, grandiflora, ciliated, jelly, dotted, triflorous, narrow-leaved and rough.
Recently, thanks to the work of breeders, many hybrid forms of gentian have appeared, which are highly decorative. Of these, the most interesting are:
- Gentian Nikita is a plant with many medium-sized azure-blue flowers;
- Bernardi is an August-blooming plant with partially tubular dark azure flowers;
- Dark Blue is an autumn variety with bright ultramarine flowers, decorated with dark stripes along the inside of the petals;
- Blue Emperor is a dwarf variety with ultramarine flowers;
- Farorna is a hybrid variety with pale blue flowers with a creamy white corolla;
- Gloriosa is a Swiss variety with wide-open blue flowers with a snow-white throat;
- Elizabeth Brand is a hybrid with elongated azure-colored flowers and short brownish stems.
Diseases and pests
Diseases and their treatment
In open ground, gentians can suffer from gray or basal rot, leaf spot, rust and some viral diseases. Of all fungal diseases, gray mold is the least controllable, and viral diseases are in principle incurable.
Gray rot - this disease can be recognized by rapidly growing gray-brown spots that appear during periods of high air humidity. As the disease progresses, gray mold forms on the spots. Affected areas of plants should be immediately removed with a sharp sterile instrument, capturing healthy tissue, after which the wounds should be treated with Fundazol solution. To prevent the development of gray mold, dusting or spraying plants with fungicides is used.
Most often, gray rot develops in plantings that are too dense and have poor air circulation.

In the photo: Growing gentian in the garden
Spotting is also fungal in nature and appears on the leaves of the plant as small yellowish-brown spots with a purple rim. Spot pathogens are destroyed with copper-containing preparations, for example, Bordeaux mixture, copper sulfate or more modern fungicidal agents.
Rust is caused by fungi that are highly resistant to chemicals. You can find out that this particular disease has affected the gentian by the dark brown pustules that form on the leaves of the plant, in which fungal spores ripen. Affected areas of plants should be removed and burned immediately, but under no circumstances should they be put into compost. At the first sign of rust, treat the area with a fungicidal solution.
Basal rot most often affects Asian species of gentians that bloom in autumn: as a result of the development of infection in conditions of high humidity during the seedling period, the base of the plant's stem rots. To protect seedlings from condensation drops and prevent the development of the disease, place plastic film or glass at a slight angle. As an effective preventive measure, dusting the basal part of gentians with Zineb is used.
- The most beautiful shrubs for a summer cottage
Pests and their control
Of the pests, gentians can be bothered by thrips, slugs, snails, ants, caterpillars and nematodes.
Slugs and snails eat the leaves and buds of gentian, greatly reducing its decorative value. It’s good if their natural antagonists – toads and hedgehogs – live on your site. But if these animals are not in your garden, you will have to set traps for mollusks: lay potatoes cut in half around the area or dig jars filled to the very neck with a third of the volume filled with beer or fermented compote.
Ants in an area with gentian are not so much harmful as they are annoying, and as soon as your patience comes to an end, use an insecticidal preparation against them, which can be purchased at a specialty store.

In the photo: How to grow gentian in open ground
Thrips are small sucking insects that reproduce more actively in the warm season. They feed on plant cell sap, leaving small discolored dots where they bite. Thrips are destroyed with insecticidal preparations.
Caterpillars are dangerous for young seedlings and germinating seeds. They are combated with the help of insecticides, which are used to treat the area with gentian several times with an interval of 10 days.
Nematodes can be detected only by the result of their destructive activity: slight deformation of the apical leaves, retarded growth and development of the plant, and curvature of its stems. You can get rid of pests by treating gentian three times with a special preparation against nematodes, which can be purchased at a garden pavilion or store.
What you need to know about plant care
Here are some rules that must be followed for better growth of gentian:
- plantings must be watered frequently;
- It is advisable to fertilize the soil (best with rotted manure);
- Weed the plantings in a timely manner;
- protect the plant from the scorching sun, but provide it with light (do not plant next to deciduous trees);
- Some species love high air humidity, so it is better to plant them on the banks of reservoirs.
Gentian can reproduce in three ways: from its seeds, by cuttings or division. Some plant species can reproduce in one way.
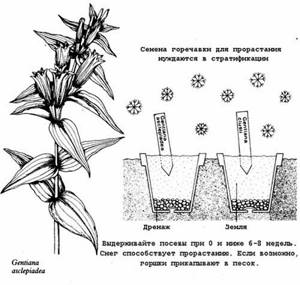
Things to remember:
- It is best to separate the shoots in the spring (you can also do it in the fall);
- seeds are stored for a maximum of one year in a dry place at room temperature;
- It is also better to separate cuttings in the spring-autumn period.
You may also be interested in the article in which we talk about interesting options for making decorative fences for flower beds.
Useful properties of gentian
Both the root of the plant and the flowers and leaves are very useful, as they contain biologically active substances that have a positive effect on the body in various diseases. In general, gentian is deservedly considered an excellent general tonic. Most often, yellow gentian is used as a medicinal plant.

The root of the plant is useful because:
- lowers temperature;
- increases the level of hemoglobin in the blood (important for people suffering from anemia);
- increases blood pressure in hypotensive patients to normal;
- stimulates the gastrointestinal tract.
The herb is also used for:
- stimulation of appetite;
- improving bile formation;
- improving the functioning of the liver and gallbladder;
- treatment of flatulence and constipation;
- treatment of rheumatoid arthritis;
- eliminating seizures;
- treatment of tuberculosis;
- deworming;
- expectorant effect;
- eliminate heartburn;
- allergy relief;
- increased heart contractions;
- scarring of difficult-to-heal wounds;
- treatment of certain eye diseases.
It should be noted that it is the yellow gentian that is now under strict protection due to excessive extermination.

Use in landscape design
In landscape design, gentian is used in different ways. If you want, plant it along a stone path, in a border planting. The rocky hill will also accept the culture well. This plant also goes well with stone. You will also be pleased with the gentian planted in a continuous carpet - you will not be able to take your eyes off the blue cover, and the yellow variety will delight the eye with its sunny color.

We also suggest you learn how to make a living border from plants.
How to grow gentian in your summer cottage
Gentian (Gentiana) was famous for its beneficial properties back in the second century BC. At that distant time, King Illyrius Gentius used the roots of this plant to cure such a terrible disease as the plague. Currently, many varieties of gentian can grow excellently in open soil, and delight many summer residents with beautiful flowering both in spring and with the onset of autumn. In this article we tried to collect information about the proper planting and cultivation of gentian.
Gentian is a beautiful plant. But proper planting and proper care in the open ground are important here. Look at the photo of this plant and you will definitely like it. Small plants will delight you for a long time with their lush and bright flowers in a rock garden or rock garden. Growing gentian yourself can present you with some difficulties. But this plant is so beautiful that it needs to be planted in your garden.

Gentian: varieties and varieties
There are about 400 varieties and species of shrubs, perennial herbs and shrubs in the Gentian family. It is less common to see annual species of this plant. Gentian can reach a height of 10-15 cm to one and a half meters. The stems of the plant are straight with whole leaves. Gentian flower stalks are funnel-shaped or bell-shaped. Various varieties have lilac, blue, white and light blue shades. It is very rare to find gentian varieties that have yellow flowers.
The classic color of gentian is bright blue. The plant begins to bloom in early spring, summer or autumn. This will depend on the species. Even in ancient times, people noticed the beneficial properties of gentian. They began to use this plant in medicine with great success. Under natural conditions, gentian grows in the mountains of the Caucasus, the Far East, Siberia, Western Europe, Altai and Transbaikalia. Miniature gentian is a fairly popular plant among landscape designers for creating flower arrangements. Gentians, miniature in height, are very popular for growing them on rocky hills, in rock gardens and rock gardens.

Planting gentian
Gentian can very rarely be observed in the garden plots of amateur gardeners, since its cultivation requires appropriate conditions. Gentian has different varieties. Taking into account the different growing conditions of various varieties of gentian, it is necessary to choose the right area in the garden: it should be either darkened or sunny. In practice, these plants are grown in partial shade or in western areas.
Plant care
Gentian flowers are a capricious plant and require special planting and proper care. In this article you will find not only a photo of this plant, but also growing rules.
So, some varieties of gentian do not like too dry soil or hot air. Based on this, these plants must be provided with an area with high humidity. It would be best to place gentian near ponds, fountains or pools.
Gentian requires special care when grown in open soil. Only then can the gardener’s work be justified when bright blue flowers appear on the plant.
Recommendation! The soil for these plants should contain pebbles or gravel for better drainage.
The gentian root system does not like stagnant water. In addition, most plants do not do well in soil that contains a high lime content.
Caring for gentian consists of regular watering during the period of its growth and development, loosening the soil, applying fertilizer and removing weeds. Many species of this plant need to be irrigated with acidified water.

Fertilizer and top dressing for gentian
Gentian perfectly accepts the addition of organic fertilizers to the soil. Especially things like rotted manure. At the time of planting, you can add ash or bone meal under the roots of the plant. When growing gentian, it is allowed to use complex mineral fertilizers.
Gentian propagation
You understand that gentian requires special care. But now it’s worth talking about such a moment as the reproduction of this type of plant. Gentian is propagated vegetatively: by dividing the bush, cuttings, seeds or individual layering. Considering the fact that this plant is quite difficult to tolerate transplantation, vegetative propagation must be done carefully. Be sure to pay special attention to the roots when dividing the bush. Gentian negatively tolerates damage to tap roots.
On a note! One of the safest methods of propagating gentian is cuttings.
Gentian is propagated by seeds by sowing in the ground. Before you start planting seeds, the beds must be dug well and the soil sifted. Sowing should be done in late autumn. The seeds need to be lightly covered with soil.

Diseases and pests
Pests quite rarely settle on gentian bushes. Sometimes the plant is harmed by naked slugs. You can remove them yourself from the leaves and stems of the plant. Ants and thrips, which can harm gentians in open soil, are easily removed with special preparations. Very often, various fungal diseases can develop on gentian: gentian rust, gray mold, root collar rot. To prevent these diseases, it is imperative to follow agrotechnical methods of caring for plants. Treatment consists of treating the plant with fungicides.

Gentian: combination with other plant species
Now you understand what the gentian flower is. You know that proper planting and care are important here. It is worth saying that this type of plant goes very well with other flowers. Cushion-shaped gentian will create an excellent combination with low plants for rockeries: iberis, perennial edelweiss, small-bulbous plants, primrose.
High varieties of gentian in combination with heather and rhodonedron can create beautiful flower arrangements. Many landscape designers use gentian to decorate ponds, fountains, pools and waterfalls. For this reason, the beautiful and bright flowers of this plant will fit perfectly into a composition with low-growing ferns, grasses, and variegated hostas.

Gentian in landscape design
All varieties of gentians are used in landscape design: tall bushes, stemless forms that bloom from spring to autumn. The beautiful bright blue hue of gentian flowers stands out so much that the plant is used to highlight yellow and white companion flowers in compositions. Quite often, gentian is used to frame paths, for planting in borders and flower beds, and in solitary plantings.
Video on the topic: gentian planting and care
Also read:
- How to grow perennial plants for your garden
- What annual flowers bloom all summer. Catalog…
- How to plant ranunculus correctly. All the secrets of growing
- Interesting DIY garden crafts. Ideas and photos
- Catalog of unpretentious and small perennials.…
- What perennial unpretentious flowers exist for...
- Planting low-growing perennial flowers yourself
- How to grow armeria correctly
Options for combinations with other plants
Gentian goes well with sage, sedge, and bells. Plants that bloom either earlier or later than others grow in nature next to cereal crops. Some species make an excellent composition with ferns.
Alpine plants should be chosen as partners for this culture:
- wolfberry;
- saxifrage;
- arabises;
- dwarf irises;
- levisii.
As you understand, gentian is not only a beautiful plant that brings a lot of aesthetic pleasure to humans, but also a crop that brings great benefits to the human body. Planting does not take much time, growing it is not as difficult as it might seem at first. And the benefits and pleasures are countless!











