07/27/201809/23/2020 Maria Ivanova 0 comments
Everyone is familiar with the expressions: “Fresh as a rose” and “Tender as a rose.” The noble flower has long been considered the standard of beauty and charm. The most beautiful female representatives are compared with him. Gardeners express different opinions about the difficulty of caring for this garden plant. One cannot but agree that the rose bush requires certain efforts from its owner to maintain it. A plant left to its own devices is unlikely to delight with lush flowering and young shoots.
Pruning roses for the winter is a necessary procedure for their successful wintering and further growth and formation of buds. Moreover, both park and garden roses require it, although in different volumes. Beginning gardeners need to understand why pruning is needed and how to do it correctly.
Why are roses pruned?

Roses grow well in warm climates. They prefer heat to frost, so for the winter the plants are carefully covered and protected from the cold.
Overgrown bushes with many shoots are difficult to hide neatly under film. In addition, their branches intertwine, interfering with air exchange. This threatens them with rotting and the subsequent appearance of diseases.
If you do not have the time or opportunity to read the entire article, watch the video on this topic:
Plants look much more attractive after trimming. Of course, you need to follow the rules for pruning branches and find out in advance what type of branch the rose will need. For some varieties, stronger shortening of the shoots is desirable, while for others, simple pinching is sufficient.
Pruning roses for the winter - is it necessary to do it?
Gardeners argue about the need to prune roses before the onset of cold weather. Many people believe that it is better to prune in the spring, when the plant can immediately produce fresh shoots. Still, the risk of rotting of non-lignified shoots is too great to leave them over the winter.
Moreover, weak shoots and unopened buds will still die before spring, and there is no point in preserving them.
How to properly prune roses for the winter in order to strengthen the bush and make it actively grow when the weather warms up?
Purpose of pruning
The procedure for removing excess shoots before winter is one of the most important for indoor roses. Its main advantages:
- Helps shape an indoor rose and give it an elegant look.
- Stimulates abundant annual flowering and development of new shoots. A pruned plant accumulates useful substances, which subsequently help it grow in the spring.
- Promotes better development of the root system.
- Helps avoid unattractive interweaving of branches.
- You can get rid of overgrown, weak, dead branches that are quickly attacked by pests, and they are also affected by diseases.
- Wintering of indoor roses after pruning takes place without infection or fungi: weak, diseased shoots are removed, leaving only healthy, strong parts.

Removing faded buds
Decide on the type of autumn pruning. It happens:
Sanitary - especially useful for young bushes
If you missed the time before winter, then it is important to carry out the procedure in the spring or any other time of the year. The purpose of sanitary pruning is to get rid of dead, damaged branches.
Regulating - forms an indoor rose, removes shoots that stand out from the contours, the weakest shoots, which are cut off slightly above the main branch.
Regular, annual or seasonal - needed to create a beautiful crown and stimulate abundant flowering.
Apical - the top is removed to stimulate the growth of indoor roses in breadth.
Rejuvenating - considered radical, carried out at intervals of 2-3 years, helps restore vitality to bushes that are too thick and tall
Sick and dry shoots are removed, long shoots are shortened.
In addition, the procedure for removing shoots is divided into three types. Choose the appropriate one based on the length of the stem and branching of the bush. So, pruning a home rose can be:
- short - relevant for small-flowered, polyanthus varieties or spring time, the branches are shortened, leaving 2-3 buds;
- medium - the most common, considered summer, but can be done before winter, applicable for all varieties except climbing, groundcover, branches are shortened to 5-7 buds, the height of an indoor rose is left to 35 cm;
- long - recommended before the onset of winter, relevant when the buds are located on the upper part of the shoots, ideal for large-flowered varieties, the branches are shortened slightly.
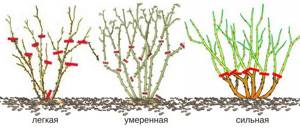
Types of rose pruning
What happens if you don't cut it?
Many gardeners feel sorry for their pets and therefore do not touch them before the onset of winter. This leads to the following consequences:
- The flower may not bloom too luxuriantly after winter or may not produce flower stalks at all.
- The plant looks sluggish, its appearance becomes sloppy, the crown is unformed. The bush begins to grow as it wants: more branches may appear on one side than on the other.
- There are fewer leaves, the branches become bare, they seem lifeless and diseased.
- The shoots are deformed.
Basic principles of pruning
Only to those who are too lazy to read the recommendations for caring for roses do they seem capricious and sickly flowers. They need care, like other garden plants, but it is not as difficult as inexperienced gardeners think.
People who planted flowers and trees on their property probably already have tools to care for them. Manuals, magazines and advice from gardeners available on the Internet will help you properly prepare for the procedure of pruning plants in the autumn season. Television often shows programs dedicated to work on a personal plot.
Circumcision tools

You can buy a set of tools for pruning roses at a hardware store in the gardening department. They are often sold in greenhouses along with rose seedlings. There you will be able to consult with specialists and choose the most suitable tools.
Typically, to care for roses you need:
- garden knife;
- scissors;
- garden hacksaw;
- pruner;
- brush cutter
All tools must be sharp to ensure effortless pruning of rose bushes. The first two are intended for processing young and thin shoots, and the last ones cut off woody branches.
The pruner can handle branches up to 2.5 cm in diameter. The hedge trimmer is a large pruner. They can be used to shorten the thickest shoots due to their long handles. They need to be held with both hands.
The main convenience of a hedge trimmer when caring for roses is the ability to avoid pricking thorns. The blades of the tool will reach the most distant branches, and at the same time you will be able to keep your hands at some distance from the bush.
All garden tools usually have brightly colored handles with a non-slip coating. This makes them easier to find in green grass and use.
Preparation for the procedure
At the end of September, rose bushes are watered less frequently so that the growth of young shoots slows down. It is also important to stop active flowering. This is achieved by pinching out new buds. Before the winter cold, plants will need phosphorus-potassium fertilizers to accumulate more nutrients in the branches.
Before you start pruning bushes, all tools that you plan to use should be disinfected in a solution of potassium permanganate. In this way, it will be possible to avoid contamination of plants by microbes.
Having carefully examined the branches and assessed the size of the rhizome, you need to try to calculate the scale of the reduction in the volume of the bush. If the top and bottom are approximately equal, the rose will survive the winter more easily and will meet the warm season with full strength.
Rules for making cuts
Before starting work, you should read the instructions several times to understand how to properly prune roses for the winter. For example, the cut must be made at an angle so that moisture does not accumulate in it. Immediately after the procedure, the place where the shoot is cut should be treated with Rannet or a special varnish-balm.
The gardener must take into account that the new shoot will go in the direction where the bud above which the branch is cut is facing. True, this is of greater importance during spring pruning, when the bush is formed.
Site selection and soil preparation
Both beginners and experienced gardeners can grow crops; the main thing is to follow all the nuances of cultivation. To plant a plant in the garden, you need to choose a sunny but protected from the winds area.
It is advisable to plant varieties with light petals in sunny areas, while roses with dark inflorescences are recommended to be placed in partial shade. If this is not done, then with high solar activity the intense color of plant buds will soon become light.
It can take up to three months to prepare high-quality soil for flowers, so for planting in the fall, the soil must be prepared in the summer or in October, if planting the crop is planned for spring.

The basic rules for soil preparation are as follows:
- We remove weeds and their rhizomes from the site.
- We dig up the soil onto the bayonet of a shovel while simultaneously transferring the soil. Next, make a ditch 40-50 centimeters deep and fill the bottom with top soil with fertilizers, and then the bottom layer mixed with fertilizers. Over several months of standing, the soil in the ditch sags and becomes saturated with useful substances. Along with this, excess moisture also leaves.
- Some gardeners immediately plant plants in pre-dug soil with dug holes, but this method is considered less effective.
If plants are planted in pre-prepared, well-drained soil, the root system will quickly develop and receive unhindered access to oxygen.
Many gardeners do things differently. They dig up the area using a spade blade without prior leveling in the fall. This will help freeze the top layer of soil and destroy pathogenic bacteria and microorganisms harmful to roses and pest larvae. Fertilizers added during this period can dissolve over the winter.
With the arrival of spring, the planting site is leveled with a metal rake and holes for planting crops begin to be dug. The depth and width of such recesses should be 25-30 centimeters higher and wider than the root system of the plant. If these parameters are observed, the pit is filled with light nutritious soil, which will give impetus to the intensive development of the root system.

When preparing the soil for a rose garden, it is necessary to take into account the influence of its predecessors. It is known that roses do not grow well in areas where there were previously cinquefoil, cherry, quince or hawthorn. In such areas, a 50-centimeter layer of soil is removed and replaced with new soil.
The acid composition of the soil can be determined by litmus paper. So red color indicates acidic soil, blue indicates neutral acidic soil. Sorrel and horsetail usually grow on acidic soil, and clover or horseradish on alkaline soil. If there is alkaline soil, superphosphate or compost or pine needles are added to its composition. Add wood ash or bone meal to acidic soil.

Timing of the procedure

Roses should be pruned when cold weather sets in, at least to -2 degrees. Otherwise, the plant will produce new buds, which will rot over the winter. As a rule, in the middle zone, gardeners carry out the procedure in late October - early November.
Recently, in the middle zone, above-zero temperatures remain until the end of December, so summer residents should adhere to the thermometer readings, and not the dates indicated in the manuals.
Optimal timing
In the Urals, preparations for winter begin in mid-August, carried out in stages.
From the moment the thermometer drops to -5 at night, you can begin to wrap roses to preserve them in winter. Approximate time: mid-October.
Important: every year the weather is slightly different from the previous one, so it will not be possible to give an exact date for covering the roses. It is necessary to focus on the average daily temperature for 3-5 days.
The climatic features are such that frost often sets in, and snow cover does not fall for a long time. During this period, the root system of the bushes may suffer, so you should not wait for snow.
But you also can’t cover it too early, otherwise the roots will begin to rot and all the prerequisites for fungal diseases will appear.
Types of rose pruning
Each variety of rose requires special pruning, and some do not need it at all. The latter include park and climbing roses. Plants that bloom once a year and produce a single shoot are only pinched without pruning.
Traditional way
Traditional pruning of bushes refers to mandatory procedures for caring for roses. This method is suitable for beginners who have recently started learning how to prune roses for the winter.
First of all, diseased, dry branches and root shoots are removed. Thin young shoots are also pruned, since they have not had time to get stronger and will only waste the strength of the bush during wintering. They are unlikely to continue growing in the spring.
After traditional pruning, the size of the bush decreases, but individual branches may continue to stand out from the total mass. Light, moderate (medium) or heavy pruning will allow you to bring the plant into an acceptable form for the winter season.
Easy pruning
With this method, the branches are shortened by about a third. It is not suitable for use for several years in a row, since the bush must be rejuvenated, otherwise it will bloom worse. It is also better not to apply light pruning to quickly growing varieties of roses.
Moderate pruning
After moderate pruning, bush roses will safely survive the winter. It is also called medium, since strong shoots are cut in half. Young shoots are shortened further, leaving up to 3-4 buds before the woody branch.
Heavy pruning
Strong pruning is used for young seedlings so that they do not weaken during cold weather, and for old bushes that require rejuvenation. With this method, strong branches up to 15 cm long are left on the bush. In spring, the bush will produce good shoots and large buds.
Heavy pruning is never used for park and ground cover roses.
Pruning climbing and ground cover bushes
Dried branches are removed from climbing roses. It is better not to leave very short shoots, 1-2 cm long, for the winter. They do not have time to ripen and will die off in the winter.
Pest and disease control
Aphid
The main pest of spray roses is aphids. These small insects settle in colonies on the inside of the leaves of the crop. Parasites suck sap from plants, which leads to wilting and curling of leaf blades. Aphids reproduce intensively, producing up to 10 generations per year.
The presence of aphids on plants can be unmistakably determined by damaged leaves or chaotically moving ants (they feed on the sap of the parasites).
To effectively combat the pest, use a soap solution with the addition of mustard powder or chemicals Karbofos, Aktelik, Rogor.

Leafhopper
Another dangerous pest of the rose garden is the leafhopper. After parasitism by this insect, the leaves of the flower become covered with white spots and lose their original appearance. With severe damage, yellow spots appear on the surface. To combat the parasite, chemicals and insecticides are used.
A pale yellow or white leafhopper with an elongated body does not pose a threat to the plant. The main damage is caused by insect larvae that feed on plant juices.

Spider mite
Spider mites cause particular harm to crops. Its oval-shaped body up to 0.5 millimeters long consists of 4 pairs of legs. The color of the body is red or orange, the larvae are greenish. Parasites damage the lower surface of rose leaves and suck out the juices, which leads to the appearance of yellow spots and loss of decorativeness of the plant.
The pest can be detected using a magnifying glass or by the thin webs connecting the leaves.
Mite settlements can be destroyed with chemicals such as Vermitek or Fitoverm.

leaf roller
Of the rose pests, you should pay special attention to the leaf roller. Caterpillars appear on the plant in early spring, begin to chew buds and young shoots, then take hold of the leaves. The caterpillars are collected by hand and destroyed; in case of severe lesions, the plant is treated with insecticides.

Powdery mildew
Of the rose diseases, powdery mildew is considered the most popular. The disease manifests itself in the form of a powdery white coating on the leaves and shoots of the crop.
The reason for its occurrence may be moderate temperature and high humidity.
Prevention of powdery mildew is spraying plants with Bordeaux mixture and applying phosphorus-potassium fertilizers. At an intensive rate of disease development, roses are sprayed with a 0.5% concentration of soda ash solution.

Black spot
This is a fungal disease that appears on the leaf blades of roses in the form of brown spots from mid-summer. Severe damage leads to complete blackening, drying out and falling off of the leaves. Fungal spores overwinter in fallen leaves and shoots, which is why organic remains must be removed from the site and burned.

Another effective solution to the problem is the spring treatment of rose leaves with Bordeaux mixture.
Even a novice gardener can handle growing spray roses. The main thing in this matter is to follow the rules of planting and caring for plants, to carry out timely treatment of flowers from diseases and pests.
What to do after cutting a flower?

Roses must be properly insulated for the winter. Most varieties do not tolerate cold well and may die in winter. The best way to preserve plants is to install a special frame around the bush, which is covered with spruce branches.
It will securely cover the roses while allowing air to circulate, which will eliminate the formation of condensation on the branches.
A popular protection option for bushes among summer residents is film or burlap. Their disadvantage is that they do not allow air to pass through, and you will have to pour sawdust inside the structure, which can absorb excess moisture. In the absence of sawdust, the branches will rot and fungus will form on them. It is difficult to get rid of, and it is destructive for roses.
Useful tips
All cut branches and dried petals of blooming roses must be removed from under the bush and burned. Leaving them on the ground can provoke the development of pathogenic microbes that will spread to the growing bush.
According to the rules of care, before covering roses for the winter, they should be sprayed with a 3% solution of iron sulfate. It destroys microorganisms remaining on the branches.
It is important to let the plant dry after treatment; do not cover it wet. In spring, roses are sprayed with a solution of copper sulfate, which is effective at above-zero temperatures.
Since the ground under the bush does not freeze thanks to the shelter, mice or rats often live in the sawdust. They feed on rose roots and, like moles, pose a serious threat to garden plants. They are repelled with pieces of burnt wool or tampons soaked in Vishnevsky ointment, placed inside a frame with film or spruce branches.
Preparing roses for winter in the Moscow region
Preparing roses for winter in the Moscow region begins in the summer. They change the qualitative composition of fertilizers, stop adding nitrogen, which promotes the growth of shoots and foliage, and increase the amount of potassium and phosphorus in fertilizing. This way the roses will strengthen the root system, and those shoots that have managed to grow will be able to ripen. Options for feeding roses in preparation for winter in the Moscow region:

- In mid-August, potassium monophosphate and superphosphate (15 g each) are added, dissolved in 10 liters of water. If it is a rainy autumn, it is better to apply fertilizers in granular form under the plants. After a month, fertilizing is repeated;
- 1 tbsp. l. calcium nitrate, diluted in 10 liters of water;
- Banana peels are a valuable nutritious fertilizer rich in potassium. Apply under the bush, embedding it in the soil, after crushing it. Or brew it as tea if dry banana skins are available;
- Wood ash - 1 tbsp. scatter dry roses around the tree trunk; if there is frequent rain, when autumn is dry, it is better to prepare an ash solution (1 tbsp. wood ash/5 liters of water).
Feeding rose bushes in the Moscow region with a predominance of phosphorus and potassium is carried out twice, with a break of a month. Roses accept foliar feeding very well, then the nutrients are fully absorbed. A solution for foliar spraying of roses is prepared by reducing the dose by 3 times.

With the onset of autumn, people in the Moscow region stop loosening the soil around roses. This is done so as not to cause the growth of new shoots from replacement buds and new fine roots. In the third ten days of September, the growing point of rose shoots is pinched, small buds are removed, and those that have bloomed are allowed to ripen.
Another important agrotechnical technique is autumn pruning of roses. It makes it possible not only to make it easier to cover roses in the Moscow region for the winter, but also to carry out sanitary treatment of the rose bush, its formation, and lay the foundation for future shoot formation, and, consequently, flowering.
Plant pruning in the Moscow region is carried out in the fall, shortly before the roses are covered for the winter. Approximately late October – early November. It is worth making allowances for the climate in the Moscow region. There are no exact dates for pruning; you should wait until a constant slight minus of -5°C is established.

In autumn, damaged leaves and shoots, broken, deformed, and with signs of disease, are pruned. Plant flowers, dried and still blooming, immature shoots are also removed. A sign of maturity of a rose shoot is a light core. You can make several test cuts to ensure the maturity of the shoot.
The issue of removing foliage is controversial; many gardeners will not remove the foliage, since this is quite a large amount of work when there are more than a dozen rose bushes. They conclude, based on many years of experience, that nothing bad happened to the roses over the winter. Another opinion is that the foliage should still be removed, as it can cause the bush to rot.
Important! The foliage is cut with pruning shears or torn off moving upwards so as not to damage the buds.

Both young, newly planted plants and bushes that have been growing for many years are subjected to pruning. Garden tools: hacksaw and pruning shears must be sharp and treated with an antiseptic. Roses are pruned in good clear weather. The type of pruning depends on the type of roses:
- Short pruning - 2-3 buds remain on the shoot;
- Average pruning – 5-7 buds;
- Long pruning – 8-10 buds.
After pruning, all plant debris must be removed from under the bush, or even better, burned, especially if there were signs of rose bush disease.
Trimmed rose bushes are treated with a solution of copper sulfate, iron sulfate, Bordeaux mixture or potassium permanganate. If the weather is warm, the plant continues to grow, even in the absence of leaves. Therefore, you should not cover roses too early; in a confined space, the plant may die or dry out.
Untimely shelter can cost the life of plants; the question of when to cover roses for the winter in the Moscow region is extremely important. Focus on the weather conditions of the region. Well, if it is possible to keep rose bushes at a temperature of -3°C, the plants will finally stop vegetative processes and go into a state of hibernation. At temperatures of -7°C-10°C, roses should be covered. Roses grafted onto rosehip roots can withstand lower temperatures in the Moscow region, while self-rooted roses are afraid of the first frost and can die at a temperature of -3°C.

To cover roses in the Moscow region, spruce branches, foliage, cardboard, burlap, agrofibre and film are used. More complex shelters are made from arcs or boards, over which some covering material is stretched. All elements of the winter shelter are securely fastened so that they do not collapse under the thick snow and are not torn off by strong gusts of wind.
Watch a video on how to prepare roses for winter:











