When to plant hawthorn
Hawthorn can be planted before winter or in spring. A bush planted in autumn begins to bear fruit at the age of six.
Advantages of autumn planting:
- favorable prices for seedlings;
- wide range of varieties;
- seedlings are sometimes sold with fruits - there is an opportunity to immediately evaluate the taste;
- the plants do not require post-planting care, since autumn is the ideal conditions for rooting.
Hawthorn is planted simultaneously with other garden crops. The estimated date is October. Before the onset of frost, the bush must have time to take root, that is, form young overgrowing roots.
Plants that have taken root in the fall will better withstand the current winter. Bushes planted in the fall will undergo hardening and will be stronger than plants planted in spring. Next year they will quickly begin to grow.
Start of planting
In the middle zone, the time for planting hawthorn is mid-September and lasts until early November. In the Urals and Siberia, winter begins earlier. In these regions, autumn planting of hawthorn begins in September and ends in mid-October.
The first autumn seedlings arrive at the retail chain with leaves still on. If you received leafy planting material, immediately after planting, carefully remove all the leaves - the plant will no longer need them and will interfere with rooting.
Rules for planting hawthorn in open ground, care and propagation at home
Everyone has probably heard the word “hawthorn”.
What is it? This is a tree that can be found in the forest, and is also grown in the country as a medicinal plant. Let's find out more about this plant. And what beneficial properties it has. And also about what can be prepared from its fruits and leaves. Enjoy reading.
Hawthorn is divided into two types: a multi-stemmed tree and a semi-evergreen plant. The height of this tree can reach five meters, and sometimes even twelve meters. The crown of the tree is spherical in shape, the bark is brown and ribbed. The branches can be straight or drooping with many spines. Leaves can also have different shapes and sizes. They are round, ovoid, and the length of the leaf can reach twelve centimeters.
The plant blooms in spring. The color of the flowers depends on the variety. They can be red, white and pink. Hawthorn fruits ripen in September and can be red, black, orange, or yellow.
Let's take a closer look at the following questions: how to properly care for such a plant, what are its benefits, when should it be planted, how to deal with pests and diseases, whether it can be replanted, how to prune it correctly, and much more.
Some gardeners grow this tree to obtain medicinal and beneficial fruits, and some make it into a hedge.
What time of year is best to plant it? You can plant a seedling both in spring and autumn. The place for planting the tree must be carefully selected. It should be on the sunny side and have heavy soil and good drainage.
Let's start by preparing the seat. First you need to dig a hole. Its width and depth should be about seventy centimeters. Place broken bricks or crushed stone at the bottom of the hole. After this, take the seedling, straighten its roots and place it in the hole. You need to fill the seedling with the prepared mixture. To do this, mix sand, peat, soil, humus and lime. Fill the seedling with this soil mixture so that its root collar is five centimeters above the ground. After planting, a small tree must be watered well. After this, you need to mulch with peat or humus. The shoots of the seedling must be shortened by ten centimeters.
If you plant trees for the purpose of producing fruit, then the distance between them should be at least two meters.
To create a hedge, planting occurs differently. First you need to dig a trench. Its depth and width must be at least fifty centimeters. After this, the seedlings are planted at a distance of fifty centimeters from each other.
- It is necessary to water the bush at least once a month. One bucket of water per plant. If the weather is too hot, watering increases to twice a month.
- After watering, the soil must be loosened to a depth of fifteen centimeters, and the weeds around the tree must be removed.
- During the flowering period, the plant needs to be fed. Cow dung mixed with water (one to ten) is suitable for this procedure.
- Sick and dry branches must be pruned in a timely manner. Pruning should be done with the onset of spring.
- The branches of the hedge are cut in half in the first two years after planting. After this, their height is left no more than seventy centimeters.
- If you decide to transplant a seedling, then this should be done in the fall.
Sowing
Seeds are sown in late autumn, at the end of November. Hawthorn seeds are covered with a durable shell and do not germinate without long-term stratification, so they are sown only in the fall. Over the winter, under the snow, they will undergo natural ripening and germinate in the spring. True, some will sprout only after a year, and many will not appear on the surface at all, since most of the hawthorn seeds are sterile.
Preparation for sowing:
- Remove the seeds from unripe berries.
- Soak in water for three days.
- Mix with a small amount of sand and grind until the surface of the seeds is slightly scratched.
- Make a 1% solution of potassium nitrate – 1 g. per liter of water.
- Soak the seeds in fertilizer for two days.
- Sow in a well-loosened bed.
Source

Hawthorn is a shrub that can often be found not only in summer cottages, but also just on the street. This plant is very unpretentious, able to survive in almost any soil, and also withstands harsh weather conditions and unfavorable ecology. Gardeners often use it as a hedge. The crown of the hawthorn can be trimmed and shaped to give it a neat appearance, and the strong and sharp thorns will fulfill their intended purpose, preventing uninvited guests from entering your area.
Hawthorn propagation
Hawthorn can be propagated in several ways, which is very convenient for summer residents, who can choose the most suitable one for themselves.
Propagation of hawthorn by seeds
It is not easy to propagate hawthorn by seeds, since there is a fairly long period of stratification (mandatory, about 1 year), as well as long germination, sometimes up to two years. Moreover, you can’t expect all the hawthorn seeds to sprout.
The seeds are selected in a slightly unripe form, left for three days in clean water at room temperature, rubbed with sand and rinsed. Next, you need to infuse the seeds in a solution of potassium nitrate (1%) for two days and plant them in open ground, but strictly in late autumn.
After the seedling germinates and reaches a height of 55-65 cm, it is cut to 3 buds from ground level, and the side shoots are removed, leaving only 2 shoots for subsequent growth.
Learning to propagate hawthorn in a variety of ways
Propagation of hawthorn by root cuttings
Hawthorn rhizomes are dug up, shaken off the ground and carefully cut. For this purpose, roots about 20 cm thick are taken, cut into pieces 9-10 cm long and buried at an angle. Place the root in the hole with the thick side up and dig it in with 2 cm of soil. Planting takes place in a greenhouse or a special school, and hawthorn is planted in open ground in early spring or mid-autumn.
Hawthorn propagation by layering
One of the most popular methods of propagating this plant, since layering can be grown in several ways.
Horizontal layerings take root well by buds if you dig in the lower side branches completely, placing them under the ground along their entire length and lightly pressing them into the soil.
Propagation can also be carried out by arc layering, that is, in the standard way, when the lower side branches are only partially buried, pressed to the ground and covered with soil.
We propagate hawthorn at the dacha by seeds, cuttings, layering, budding
But you can grow additional hawthorn seedlings by vertical layering, filling the lower part of the bush with soil to the level of distribution of branches. Thus, after a certain time, each branch that is under the soil will give roots, it can be separated and planted independently.
Reproduction of hawthorn is possible both by grafting and cuttings. Using the first method, you will get fairly high-quality planting material, but green hawthorn cuttings take root and take root very poorly.
Planting hawthorn
So, what points should be taken into account when planting this plant:
In principle, hawthorn can grow in both sun and shade, but shade may result in slightly fewer flowers and a poorer fruit harvest. Therefore, if possible, it is better to give preference to the sunny side.
As mentioned earlier, the shrub is unpretentious, but for better rooting of a young plant it is better to create a certain energy reserve. To do this, dig holes of at least half a meter and place organic fertilizer at the bottom, for example, mullein, humus, manure, peat or lime. Sprinkle the fertilizer on top with a layer of sand, and then plant the hawthorn, compacting it with soil.
Leave a distance of about one and a half to two meters between neighboring plants.
When to plant hawthorn.
The most popular periods for planting are spring and autumn. Some gardeners carry out this procedure in the summer, and often the plants planted at this time take root very well.
Hawthorn care
Despite its unpretentiousness, the shrub requires simple care:
Depends on the variety. There are species of hawthorn that were originally bred to be drought-resistant. Natural precipitation is sufficient for them. If your shrub is water-loving, do not forget to water it, and in dry, hot summers do this in double volume.
Periodically, the soil around the base needs to be fluffed up. This is done to saturate the soil with oxygen and facilitate the flow of nutrients and water to the roots.
Do not let weeds take hold in the hawthorn area; remove them in a timely manner.
It is enough to apply fertilizer twice a year: in early spring and during the formation of buds.
If you are the proud owner of a decorative hawthorn variety, take care of its proper insulation and shelter in the autumn-winter period.
How to propagate hawthorn
There are two possible scenarios here:
- Propagation by seeds.
- Daughter root shoots.
To preserve their species qualities, young seedlings are grafted.
Source
Growing hawthorn
It is not at all difficult to grow a beautiful, fragrant and useful plant in the countryside, because hawthorn is unpretentious and does not require special care or time. How to grow hawthorn correctly?
How to grow hawthorn in the country with your own hands?
Place for hawthorn in the country
Try to choose a warm and sunny place for the plant. Avoid shading and even partial shading, because in such conditions the flowering and fruiting of the tree tends to zero. Hawthorn feels great in open areas, where it can even be planted to help decorate the area, if the bush is shaped in an original way.
Soil for hawthorn
Our beneficial plant prefers heavy, but well-drained and fertile soils. Before planting, it is advisable to prepare the mixture yourself, and not just plant the hawthorn in the soil. To do this, you will need to mix peat, sand, humus and leaf flour, and also add a little lime, but very carefully so that the root system does not come into direct contact with it. When planting, be sure to provide high-quality drainage, which can be lined with a 12-15 cm layer of broken brick or gravel.
Determining a place for planting and preparing the soil for hawthorn are important factors in the growth of a healthy plant.
Hawthorn transplant
Hawthorn is planted in a permanent place at the age of approximately two years. To do this, you can choose spring or autumn, whichever is more convenient. The hawthorn planting scheme is as follows - 2x2 m between planting holes, and each hole is 60-70 cm deep.
When planting, make sure that the root collar of the plant remains at ground level. After planting, be sure to water and mulch with peat, about 4-5 cm.
Transplanting hawthorn after 5 years is no longer recommended, since the plant has time to acquire a very serious and long root system. Hawthorn will show maximum fruiting by the age of 10 years.
How to properly replant hawthorn on a site?
Hawthorn care
As mentioned earlier, due to the unpretentiousness of the plant, special care is not required, but it is still necessary.
First of all, you need to carefully monitor the general condition of the bush and promptly remove diseased, dry and interfering branches and shoots from it. It is also necessary to trim the bush if you want to shape the plant for landscape design. Hawthorn is trimmed in the spring, but diseased shoots can be removed at any time.
The basis of care is also the removal of weeds in the tree trunk circles, constant renewal of mulch, and sometimes loosening the soil by 10-15 cm. In the fall, you can dig up the bush as deep as a spade.
Hawthorn is an unpretentious plant that requires only minimal care
Fertilizers and watering for hawthorn
Hawthorn is fertilized very simply - with one spill of slurry just before flowering. This supply of nutrients should be enough for the bush until the next feeding.
Hawthorn - planting and propagation
The hawthorn is elegant with rich malachite foliage, large inflorescences, autumn foliage, and colorful fruits against the backdrop of the emerging snow. In Rus', hawthorn was noticed in the 19th century and at first it was used only to decorate gardens and parks. Michurin looked anew at hawthorn as a fruit plant and developed its variety Ryazan.
At the moment, certain varieties of hawthorn are grown with triumph in Spain and Italy, Korea and Algeria, and in some provinces of China its fruits are valued no less than apples. In the Russian Federation, the plant is grown mainly in amateur gardens.
Hawthorn fruits are rich in sugars (up to 14%), organic acids, tannic and coloring elements. They also contain quite a lot of pectin (1.1%). The value of the fruit is added by the significant content of biologically functional compounds - up to 100 mg% vitamin C, more than 6 mg% vitamin E, over 12 mg% carotene (almost like in rose hips and carrots). The seeds and flowers of this plant are rich in essential oils.
The medicinal properties of hawthorn have been known for a very long time. Back in the 1st century BC, its fruits were used as a remedy to treat heart disease, dizziness, shortness of breath and even insomnia. Currently, it is successfully used in many countries around the world for cardiac disorders and
functional changes in the nervous system. For hypertension, an extract of the fruit or a tincture of its flowers is used. Eating fruits helps lower blood cholesterol levels, reduce the excitability of the nervous system, and partially or completely eliminate tachycardia and arrhythmia. Flower tincture helps with vascular spasms.
But you shouldn’t overuse hawthorn. You cannot eat more than a glass of berries at one time, otherwise a sharp drop in blood pressure and heart rhythm disturbances may occur.
Hawthorn is famous as an excellent honey plant. You can also use it as an impenetrable green hedge. A decoction is obtained from hawthorn bark, which is used to dye fabrics red.
Hawthorn is a plant from the vast Rosaceae family, which includes more than 25 species, common in the European part of Russia, Central Asia, Crimea and the Caucasus. Of such a variety of species, blood-red, soft and pontine hawthorns deserve the most attention.
Hawthorn in garden design
Since almost all types of hawthorn are undemanding to soil conditions, tolerate shade, are winter-hardy, and respond well to the presence of lime in the soil, they are often used in group plantings to create undergrowth under an openwork canopy, and also as a single tree (tapeworm).

Some species of American origin have a dense crown and thorns, and therefore are ideal for impenetrable and decorative hedges.

Blood-red hawthorn looks especially impressive when planted in rows. This type of landscape composition goes well with horse chestnut, maple, oak and other ornamental trees. He also looks amazing in his autumn outfit:

As you can see, you can choose the types and varieties of hawthorn depending on your growing purposes, and planting and caring for it is not at all complicated. We hope that now you can easily decide where and how to plant hawthorn in your country house.
What types of hawthorn are there?
The advantage of hawthorn is that it is a native plant in Russia. Problems with acclimatization do not arise either in the subtropics or on the border with the Arctic Circle.
A wide variety of hawthorn species allows you to decide on the most suitable one, or collect a whole collection of these plants on your estate.
Common hawthorn or prickly hawthorn
The most common species in Russian gardens. The plant can be shaped as a tree or as a bush. The tree grows up to 5-7 meters, which is not very convenient for harvesting. On a personal plot, its growth must be controlled, especially since prickly hawthorn tolerates pruning well. Huge sharp thorns are its peculiarity and the only drawback that complicates harvesting.
It blooms with white simple flowers very profusely. Common hawthorn berries are miniature apples with bright red skin, fleshy yellow flesh and a core of several small seeds. They ripen in late August – early September. They have a sweet and sour taste and are considered a remedy for many diseases.
This variety is resistant to frost, tolerates even snowless, cold winters, and is unpretentious to the soil. Common hawthorn is decorative both during flowering and during ripening.

Siberian hawthorn or blood red
Also very hardy to frost and temperature changes. Tall, in cultivated form it needs pruning and crown formation.
The main methods of propagation of hawthorn. Detailed description

Hawthorn is a member of the Rosaceae family. Among the large number of varieties and species of this plant, there are huge ten-meter trees and small shrubs. The external attractiveness allows the use of hawthorn in landscape design. Of particular value are the fruits, which are actively used for medicinal purposes. Representatives of agricultural enterprises and ordinary amateur gardeners are actively propagating hawthorn both for sale and for growing on their own plot.
Selection of seedlings
- Only plants between two and five years old and no more than half a meter tall are suitable for replanting. Young plants are best grown independently or purchased from reliable stores.
- The tree must have a living, well-developed root system - moist, with a lump of earth.
- The trunk should be smooth, with a glossy bark, without visible damage.
- Before purchasing, the roots and trunk are carefully examined for the presence of putrefactive formations and mycelium of fungal diseases.
- Any type of hawthorn for the temperate climate zone is suitable, the main thing is to follow the recommendations.
An ordinary wild hawthorn can become a good rootstock both for its cultivated varieties and for other fruit trees.

Selecting a location
In the wild, hawthorn often grows in deciduous forests, along river banks, choosing rocky slopes of ravines or shaded edges. But in order to quickly wait for fruiting, it is better to plant it on the estate in a well-lit place.
It does not tolerate stagnant moisture; it is necessary to ensure drainage and good soil drainage.
Hawthorn prefers heavy soils, which in itself reduces the circle of its neighbors and makes it possible to plant this bush in a place unsuitable for other crops. But for good yield, the soil under bushes of all varieties must be fertilized.
In order to finally decide on the location for planting the hawthorn, you need to put your site in perspective: to what height and in what diameter the future bush is planned to grow, what plants it will displace and how it will subsequently fit into the layout of the territory.
Site preparation
Preliminary work before planting hawthorn does not take much time. This useful plant is planted in a deep hole, which should be prepared in advance:
- the planting hole is dug about a meter deep;
- you can spill it with boiling water or treat it with chemical disinfectants;
- the bottom is covered with a twenty-centimeter drainage layer - expanded clay, gravel or crushed stone;
- the lower layers of the planting pit are limed so that in the first years of the plant’s life the roots do not come into contact with the layer of lime - a small amount of drainage on top is enough;
- The planting mixture with which the roots of the plant will be sprinkled should consist of equal parts of sand, peat, humus and other plant mulch.

Reproduction methods
Having learned how to propagate hawthorn using different methods, you can choose the most suitable option for yourself. You can get a young specimen of an unpretentious and useful plant in the following ways:
Cuttings
Shoots are harvested in the fall after the leaves fall or in early spring before the sap begins to flow. They use parts that are located closer to the center of the branch, because the apical and lower ones take root much worse. The ideal material of good quality for propagation is a young one-year-old cuttings without damage, not woody (green), up to 1 cm thick. The trimming is carefully cut under the bud diagonally with a sharp tool and placed in the rooter for about an hour.

The blanks are planted at a distance of 20 cm from each other, the width between the rows is approximately 40 cm. Plants can be placed in a permanent growing area no earlier than after a year. Typically, young bushes are placed in a room with intensive care for growing for about another 3 years.
Graft
Propagating hawthorn in this way is the most reliable way. Red rowan is considered the best rootstock. The vaccination is done in early spring after warm weather has settled. Young shoots with a diameter of about 1 cm are selected for the scion. The procedure can be performed in three ways: Reproduction work is carried out carefully, without touching the cuts with your hands to avoid infection. In about a month it will become clear whether the graft has taken root - new young shoots should appear.
Root growth
Similarly, you can get a new hawthorn in three vegetative ways.
Separate young plants that grow near the mother bush. Reproduction by such offspring is mainly carried out with bush forms; shoots appear in trees much less frequently. At the end of summer or beginning of autumn, the lateral shoots are carefully separated from the mother plant without damaging its largest root. Young shoots are left in the same place until spring. After the start of spring growth, it will be clear whether the young bush has survived. It is carefully transferred, transplanted to a permanent place.

Propagation by root cuttings. Separate a part of the rhizome at least 2 cm thick from an adult bush, make blanks about 10 cm long from it. Dig them in at a slight angle, the thicker end should be at a distance of about 2 cm from the surface of the ground.

Growing cuttings. Strong annual growths located near the roots of the plant are placed in grooves. They are fixed in the ground, leaving only the top outside. The base is tied with soft wire, watered regularly and fertilized with ammonium nitrate a couple of times a season. It is better to plant the next year, having first checked whether the cuttings have grown good roots. The harvested shoots are planted in a greenhouse for further cultivation.
Seeds
Growing hawthorn from seed is a rather labor-intensive method. It is not recommended to propagate valuable varieties using this method, because a young seedling grown from a seed does not always inherit all the characteristics of the parent plant.

Select fruits that are not fully ripe. They are inspected and those that are rotten or damaged are rejected. The hawthorn seed is very hard, so the sorted seeds are soaked and placed in warm water for several days. In this case, it is necessary to ensure a constant temperature in the container with the material, for example, by placing it on a switched-on radiator. This method of preparing for sowing is called stratification. Its use helps to partially destroy the thick shell of the fruit. As a result, seedlings appear earlier than without stratification.

After this procedure, the fruits are kept in light soil in a warm place for several months. Later they are placed for the winter in a room with a temperature slightly above zero degrees.
“Immediately before sowing, the seeds should be further processed.”
Scarification is used - a method that allows you to partially artificially destroy the hard shell of the fruit. For hawthorn, two methods of such processing can be used: Chemical. The seeds are poured into a three percent acid solution (hydrochloric or sulfuric) for 2-3 hours. You can place them in one percent sodium nitric acid for 24 hours, then rinse thoroughly with cold water.

Thermal. The fruits are alternately immersed in boiling water and ice water, every 30 seconds.
“Scarification was successful if the seed increased in size and swelled.”
In the fall, the fruits prepared last year are sown in fertile soil. They need to be well watered, covered with peat and straw and left for the winter. Young shoots are very weak, often get sick, and can only germinate after one and a half to two years. At first, they grow by about 10 cm annually. When small hawthorns reach a height of 55-65 cm, they are shortened, leaving three buds above the ground. Keep two shoots on each bush, the remaining lateral shoots are removed.
Hawthorn is a light-loving and drought-resistant plant. This is an unpretentious representative of the rose family, but young bushes require special attention.
To plant young shoots, prepare loose soil based on peat and sand in equal parts. Acidic soil is undesirable; a small amount of chalk is added to prevent this problem. Add lime to the prepared hole, making sure it does not come into contact with the roots. It is useful to make drainage from broken stone or gravel. Distribute the roots in the hole, trying not to touch them with your hands. If some roots remain on the surface, this will slow down the development of the hawthorn in the future. Neighboring plants are placed at a sufficient distance from each other so that over time their roots do not touch. Soft soil is needed, so the soil is mulched.

In the spring, in the second year after propagation, nitrogen fertilizers and urea are applied to young seedlings, and in the fall - a solution of nitrophoska. Young hawthorns need a greenhouse with high air humidity. They will appreciate systematic watering; the soil under the seedlings should be constantly moist. In summer, gardeners prevent plants from overheating, shade them from direct sunlight and spray them generously. Plantings are loosened in time and weeds are removed between rows.

Young seedlings can grow in partial shade or in the sun. It is better to choose a well-lit and warm area as a permanent habitat. This will allow you to get a lot of fruit in the future, because the lack of light impairs fruiting.
“It is not recommended to replant a plant older than five years.”
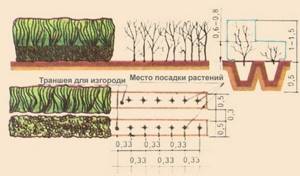
Planting schemes
Close proximity to this plant is not shown. A well-developed root system requires that the bush be planted at a considerable distance from its closest neighbors - 5-7 meters from tall and medium-sized trees, 3-5 meters from shrubs and at least two meters from vegetable plantings.
With other bushes of this type, for example, for growing hedges, an acceptable distance will be one and a half to two meters. It is better to orient such plantings from north to south.
You need to understand that the formation of a green fence does not promote active fruiting. With thickening of plantings and constant pruning, fruit ripening will decrease.
Hawthorn care
This is a non-capricious plant and does not need constant attention. Basic measures for caring for hawthorn include:
- watering;
- infrequent feeding, in case of obvious developmental delay;
- sanitary pruning - removal of dead and diseased parts;
- bush formation;
- harvesting to avoid rotting of the berries.
Hawthorn is a long-growing plant; for better fruiting at any age, the soil around it must be updated. At the border with the root system, dig holes up to a meter deep and fill them with rotted manure.
Plant nutrition
It is much worse to overfeed a hawthorn than to underfeed it. If the growth of the bush slows down and its appearance deteriorates, then it is necessary to pay attention to the nutrients that the plant is not receiving enough.
The amount of fertilizing depends on the purpose for which the tree is grown.
For fruit varieties, up to three feedings are carried out:
- the first - at the very beginning of the growing season;
- the second - during the flowering period to promote the ovary;
- the third is carried out when the fruits ripen.
For decorative hawthorns, it is enough to apply two fertilizers.

It is better to give preference to organic compounds - slurry, humates, weed infusion.
If the plant drops its fruits ahead of schedule, it means it lacks moisture. Proper watering is the key to good fruiting. This should be done once a month. In dry summers, two or three. The main condition for watering is its abundance. 10-20 liters of warm water are poured into the planting hole. You can combine watering with fertilizing for greater efficiency.
Growing hawthorn
It is not at all difficult to grow a beautiful, fragrant and useful plant in the countryside, because hawthorn is unpretentious and does not require special care or time. How to grow hawthorn correctly?
How to grow hawthorn in the country with your own hands?
Place for hawthorn in the country
Try to choose a warm and sunny place for the plant. Avoid shading and even partial shading, because in such conditions the flowering and fruiting of the tree tends to zero. Hawthorn feels great in open areas, where it can even be planted to help decorate the area, if the bush is shaped in an original way.
Soil for hawthorn
Our beneficial plant prefers heavy, but well-drained and fertile soils. Before planting, it is advisable to prepare the mixture yourself, and not just plant the hawthorn in the soil. To do this, you will need to mix peat, sand, humus and leaf flour, and also add a little lime, but very carefully so that the root system does not come into direct contact with it. When planting, be sure to provide high-quality drainage, which can be lined with a 12-15 cm layer of broken brick or gravel.
Determining a place for planting and preparing the soil for hawthorn are important factors in the growth of a healthy plant.
Hawthorn transplant
Hawthorn is planted in a permanent place at the age of approximately two years. To do this, you can choose spring or autumn, whichever is more convenient. The hawthorn planting scheme is as follows - 2x2 m between planting holes, and each hole is 60-70 cm deep.
When planting, make sure that the root collar of the plant remains at ground level. After planting, be sure to water and mulch with peat, about 4-5 cm.
Transplanting hawthorn after 5 years is no longer recommended, since the plant has time to acquire a very serious and long root system. Hawthorn will show maximum fruiting by the age of 10 years.
How to properly replant hawthorn on a site?
Hawthorn care
As mentioned earlier, due to the unpretentiousness of the plant, special care is not required, but it is still necessary.
First of all, you need to carefully monitor the general condition of the bush and promptly remove diseased, dry and interfering branches and shoots from it. It is also necessary to trim the bush if you want to shape the plant for landscape design. Hawthorn is trimmed in the spring, but diseased shoots can be removed at any time.
How to propagate hawthorn
Hawthorn grows slowly. It begins to bear fruit 5-10 years from the date of planting, depending on the variety. But it is easy to propagate vegetatively. The easiest way is propagation by shoots. young shoots themselves sprout around the trunk; they can simply be transplanted to a new place.
Propagation by cuttings
For cuttings of hawthorn in the spring, young shoots are selected when pruning. Branches 30-40 centimeters long are cut obliquely and placed in water to germinate. It's good to add a growth stimulator. Germination may take two months.
Sprouted cuttings are rooted in a nursery at a temperature not lower than 25 C. They are planted at a distance of 25-30 centimeters from each other. They are transferred to a permanent place after 2 years.
Reproduction by layering
The most win-win option is propagation by layering. To do this, in the spring, the lower shoots are bent to the ground and strengthened with a wire bracket. The soil is pre-loosened. The place where the cuttings are fixed is watered abundantly. When the young shoot begins to grow vertically, it is earthed up. Layers are separated from the trunk in the fall, on the eve of frost, and replanted. Such seedlings can be immediately transferred to a permanent place. The advantage of propagation by layering is that the rooting of the young shoot is noticeable already in the current season.

Copulation
Copulation is grafting with a bud or bud on a die. It is carried out according to general rules:
- the trunk of the rootstock above the bud selected for grafting is cut off;
- a bud is cut from a scion plant along with a section of green bark;
- a cut is made on the rootstock, similar in size to the grafted bud;
- The scion is applied joint to joint to the cut on the rootstock;
- wrapped with cloth and treated with garden varnish.
It must be said that hawthorn takes root well in a new place as a scion. And it itself serves as a rootstock for a number of fruit plants. Especially if you need to adapt the plant to more severe climatic conditions.
Reproduction by seeds (seeds)
This method of hawthorn germination is suitable only for the most patient. The germination rate of hawthorn seeds is very low. Depending on the variety, 30 to 50 percent of the collected seeds germinate. It is better to choose unripe fruits for sowing and extract the seeds from them by mechanical processing, grinding them with sand or other large particles. They require long-term preliminary stratification. The seeds are mixed with peat soil mixture, moistened and left for a couple of months indoors at a temperature of 4-5 C. The seeds are regularly moistened. After this time, the box with sprouted seedlings is transferred to the light and cultivation begins.
Sow the germinated seeds under a greenhouse. When the seedlings become stronger, they are transplanted into a nursery for two to three years.
This propagation method is used mainly for breeding new varieties. Such a bush will begin to bear fruit in 7-10 years.
The nursery for young hawthorn seedlings should be covered with a thick layer of foliage or spruce branches for the winter.

Hawthorn propagation
Hawthorn can be propagated in several ways, which is very convenient for summer residents, who can choose the most suitable one for themselves.
Propagation of hawthorn by seeds
It is not easy to propagate hawthorn by seeds, since there is a fairly long period of stratification (mandatory, about 1 year), as well as long germination, sometimes up to two years. Moreover, you can’t expect all the hawthorn seeds to sprout.
The seeds are selected in a slightly unripe form, left for three days in clean water at room temperature, rubbed with sand and rinsed. Next, you need to infuse the seeds in a solution of potassium nitrate (1%) for two days and plant them in open ground, but strictly in late autumn.
After the seedling germinates and reaches a height of 55-65 cm, it is cut to 3 buds from ground level, and the side shoots are removed, leaving only 2 shoots for subsequent growth.
Learning to propagate hawthorn in a variety of ways
Propagation of hawthorn by root cuttings
Hawthorn rhizomes are dug up, shaken off the ground and carefully cut. For this purpose, roots about 20 cm thick are taken, cut into pieces 9-10 cm long and buried at an angle. Place the root in the hole with the thick side up and dig it in with 2 cm of soil. Planting takes place in a greenhouse or a special school, and hawthorn is planted in open ground in early spring or mid-autumn.
Hawthorn propagation by layering
One of the most popular methods of propagating this plant, since layering can be grown in several ways.
Horizontal layerings take root well by buds if you dig in the lower side branches completely, placing them under the ground along their entire length and lightly pressing them into the soil.
Propagation can also be carried out by arc layering, that is, in the standard way, when the lower side branches are only partially buried, pressed to the ground and covered with soil.
We propagate hawthorn at the dacha by seeds, cuttings, layering, budding
But you can grow additional hawthorn seedlings by vertical layering, filling the lower part of the bush with soil to the level of distribution of branches. Thus, after a certain time, each branch that is under the soil will give roots, it can be separated and planted independently.
Reproduction of hawthorn is possible both by grafting and cuttings. Using the first method, you will get fairly high-quality planting material, but green hawthorn cuttings take root and take root very poorly.
Hawthorn diseases
Cultivated hawthorn is vulnerable to fungal diseases. It is affected by tinder fungi, septoria, various types of rust, powdery mildew, brown, ocher, white, gray spots and leaf rot. These diseases are expressed in the appearance of spots on fruits and leaves, curling and withering of foliage, shedding of berries, dwarfism of the plant, and developmental delays.
These diseases also affect other garden plants - apple, rowan, and pear. Having appeared on one bush, they begin to take over the entire garden.
Often the cause of the development of diseases is weather conditions and carelessness of the owners. The following factors contribute to fungal diseases:
- poor pruning, leading to thickening of the bush, dampness and stagnation of air inside the crown;
- wet weather, excess precipitation or accumulation of moisture in the roots of the tree;
- thickening of plantings, proximity of hawthorn to infected trees;
- neglect of crop rotation rules and poor quality cleaning of the site.
Controlling fungal diseases in perennial plants is more difficult. It is better to pay more attention to prevention - mandatory spring treatment with a solution of copper sulfate or preparations containing sulfur.
If signs of fungal diseases are detected on the leaves and fruits of hawthorn, the infected parts are removed and burned. The tree is treated with a fungicide in two stages with a break of ten days.

Disease Prevention
Common diseases of hawthorn are rust, hole spot and powdery mildew. In case of disease, treat with fungicides. For planting, choose well-ventilated areas and follow the care technology. It is not recommended to place coniferous trees nearby, which are carriers of rust.
As a preventive measure, plants are sprayed with one percent colloidal sulfur, which improves the appearance and increases the immunity of young shoots. Hawthorn propagation is difficult but interesting work. With a serious and thoughtful approach to the process, you can get wonderful young plants that will delight you with their aesthetic appearance and healthy fruits.











