Description of Cossack juniper
Juniperus sabina is an evergreen creeping shrub that is a member of the Juniper genus. Sometimes the plant is a medium-sized tree, the height of which does not exceed 4 m. The trunk of such a plant has an arched shape and is covered with reddish-brown bark, which tends to peel off.
The bush is dioecious, reaches a height of 1–1.5 m. The natural habitat of this species is the Caucasus Mountains, Kabardian District, rocky slopes of the Urals and Siberia, as well as forests of steppe zones. The shoots of the plant are very poisonous and contain essential oil (3–5%).
Types of needles:
- Young specimens have needle-shaped needles with pointed tips. Blue-green and soft on top. The length of the needles is 4–6 mm;
- mature plants have scaly soft needles, the thick aroma of which is a characteristic feature of the variety.
Did you know? Within 24 hours, 1 hectare of juniper spreads about 30 kg of phytoncides.
The needles remain unchanged for three years. The crown diameter is 2.5 m. Cossack juniper bears fruit in small round cones (volume 5–7 mm). The cones-berries are brownish-black, with a slight bluish tint, two-seeded. The growth rate of the shrub is slow, the annual growth is only 5 cm in height and 15 cm in width. Life expectancy is 50 years.

Seed ripening occurs twice a year: in autumn and spring.
Description of the plant
Junipers (Juniperus) are evergreen coniferous shrubs and trees of the Cypress family. The shrub usually grows from 2 to 6 m in height. Some varieties are tall trees and form entire forests. Their leaves are small, prickly needles and look similar to pine or spruce.
Juniper is a distant relative of pines and spruces. The plant has a unique ability to heal just by growing nearby. When you inhale the resinous aroma, your soul becomes calm and joyful.
The peculiarity of juniper is that its flowers are unisexual, female, in the form of round greenish cones, and male flowers - in the form of earrings with 3 or 4 stamens. The plant blooms in June and bears fruit from August to September. Juniper fruits - cone berries - contain loose brownish pulp, which is widely used for medicinal purposes.

Appearance of the plant
Juniper is a forest inhabitant of the northern regions. But it is also successfully grown in suburban areas. Indeed, in addition to its medicinal properties and incomparable smell, it is surprisingly effective and can decorate any place.
Varieties
Descriptions of the varieties of Cossack juniper will help you choose the optimal option for landscape design. The type of shrub has about 25 varieties.
Important! It is not recommended to plant Cossack juniper near playgrounds, as the cones and needles of the plant are poisonous.
The most popular varieties:
- Tamaris (in Latin the variety is called Juniperus Sabina Tamariscifolia
). The height of the bush is up to 1 m, the diameter of the crown is 2 m. The branches are short and grow vertically. The crown grows widely and over time acquires a dome-shaped shape. The needle-shaped needles are slightly curved and colored light green. The variety is widespread in the middle zone and northern Russia. Resistant to drought and low temperatures (withstands up to -35°C). The plant is unpretentious to the composition of the soil. Grows well in acidic and alkaline soils;
- Wegry. The height of the creeping shrub is 0.5 m, the volume of the crown is 2 m. The crown is large and spreading. The ascending shoots are covered with green needle-like needles. The variety is winter-hardy and drought-resistant. Suitable for growing on rocky terrain, as well as for landscaping slopes and ravines;

- There's No Blythe (Juniperus sabina Tam No Blight
). The height of the bush is 0.4–0.6 m, width 2 m. The shoots spread horizontally and grow in layers. The crown of an adult plant is dome-shaped. The plant grows slowly, adding only 10–15 cm per year. The needles are soft, dark green with a bluish tint. The pine aroma is pronounced. The bush is suitable for growing in rockeries and as a cover for rocky areas;
- Blue Sparkle (Juniperus Sabina Blue Sparkle
). The variety was bred in the 60s of the twentieth century. The height of the bush is 0.5–1 m, the diameter of the crown is 1.5 m. The crown is lush and grows widely. The branches grow vertically, the ends are located upward. The needles are scaly, needle-shaped with a slight bluish tint. The length of the needles is 4–6 mm. The smell is specific, coniferous, repels moths. It is used for landscaping park areas in combination with deciduous shrubs and trees. The variety is easy to care for and resistant to frost. All parts of the plant are poisonous;
- Hixie (Juniperus sabina Hicksii
). An adult bush reaches a height of 1.2 m and a width of 1.5 m. The shoots of a young plant grow vertically. As they age, they form a dome shape. Suitable for growing in urban environments for landscaping sidewalks and streets. The variety is quite resistant to low temperatures and can withstand down to -35°C;
- Broadmoor or Broadmoor (Juniperus sabina Broadmoor
). Externally, the shrub resembles the Tamaris variety. The height is approximately 0.5 m. The width of the crown reaches 3.5 m. Strong and tender shoots are covered with short needle-shaped gray-green needles, located horizontally;
- Erecta (Juniper Sabina Erecta
). An ornamental shrub about 2 m high. Ascending branches form a pyramidal crown. The dark green needles have a scaly structure. The variety is compact and suitable for group plantings;
- False Kozatsky (Juniperus Pseudosabina
). A variety of common juniper that is found in Western and Eastern Siberia. The species is slow-growing, resistant to high and low temperatures (down to -35°C). The needles are needle-shaped. The needles are not sharp, the length is 3 mm. The branches are creeping. The plant is planted as a cover for rocky areas.
Planting and care
Coniferous plants are increasingly winning our sympathy. Beauty, year-round decorativeness, relative ease of care - this is what seduces us. One of the representatives of this class is the Cossack juniper (Juniperus sabina).

Juniper Cossack
And I must say that this is truly the most reliable and unpretentious representative of the juniper genus for the middle zone. Beautiful, winter-hardy, drought-resistant, undemanding to soil, resistant to urban conditions.
And I would like to say separately about one more very important quality: Cossack juniper is less susceptible to spring scorching than all other species of this genus. No, to say that it does not burn at all would be wrong. He gets burned, especially in low-lying garden areas, where the sun in the spring is already actively giving a signal to plants to grow, and the ground remains frozen for a long time. But at the same time, the excellent growth energy of this plant also helps out; it very quickly grows needles, if the vessels remain intact, and grows new shoots, while simultaneously increasing the width and length of old ones. If you want to avoid this phenomenon, I recommend planting it near the northern wall of a small building, for example, a gazebo. In this way, it will be protected during the greatest solar activity and at the same time receive enough light.

Burning Juniper
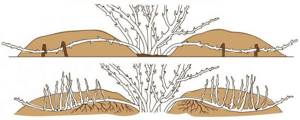
Speaking about this amazing shrub, one cannot help but touch on one more of its properties, which is important from a practical point of view. This is the use of juniper to strengthen slopes and ravines. Its powerful root system goes deep enough into the soil and at the same time grows strongly over the surface, thereby strengthening the soil.

Strengthening slopes with juniper
Even a beginner in gardening can care for Cossack juniper. This is a plant that forms the frame of a garden, widely used in landscape design and, at the same time, does not cause much trouble. But you still have to take minimal care.
The key to its successful residence in your garden will be the “foundation” - proper planting. Cossack juniper will feel best in light lacy partial shade. A sunny location is also acceptable. Only deep shadow will have a bad effect on it. Although the plant is undemanding when it comes to soil, it will certainly respond well to the addition of compost and peat. Juniper needles may turn yellow if both alkali and acid levels in the soil are too high. The plant will withstand short-term spring flooding with melt water. Extreme dry soil can also cause needles to yellow and drop. Watering in dry times and sprinkling the needles will make the plant look more presentable. It will also be useful to scatter granular mineral fertilizers under the bush in accordance with the season, in spring and autumn. If the planting site is damp and unventilated, then the plant will benefit from prevention with fungicides or biological products against fungal diseases.
Application in landscape design
In landscape design, Cossack juniper is used for landscaping parks and city streets. To decorate personal plots, it is planted individually or in group plantings. Forms a harmonious composition with foliage plants.
The squat shrub looks great under tall trees. Thanks to creeping branches, juniper groups form dense thickets that cover rocky areas and slopes with dense cover.
Learn in more detail the rules for combining juniper with other plants in the garden.
Juniper species
Common juniper
This species can withstand unfavorable conditions well.
Depending on its variety, it may look different. It can be a multi-stemmed tree, the height of which can reach up to 18 meters. Another option is a shrub, which is approximately six meters high. Its branching can be described as spreading and chaotic. When flowering it produces yellow or yellow-green flowers. Its cone-berries are blue-black. Their pulp is medicinal and viscous in appearance. They ripen within two years.

This type of juniper includes several varieties:
- The Pendula variety has a height of up to five meters. It has an elegant and weeping crown.
- The variety "Echinoformis" has a height of up to four meters. Its crown resembles a lush ball.
- The variety "Goldcone" has a column-shaped crown.
- A shrub variety called "Hornibrook" is characterized by shoots spread out on the ground and silver-green needles.
Let's talk about Daurian juniper
This species has no special requirements for soil type and tolerates cold or dry weather well. This includes the Expanza variety, which is widely used for decorative purposes. Its height is usually half a meter. The needles have a light green color. The shrub grows in width to a distance of up to three meters. The branches are thick and yet flexible.
The needles on this shrub are either needle-shaped or scaly. The tips of the branches of young growth are supported by powerful branches and usually rise slightly upward, which gives this variety of juniper its unique beauty.

About Caucasian juniper
This species is a low-growing tree or shrub that can reach a height of up to one and a half meters. Its needles are scaly and saturated with essential oils. Moths cannot tolerate the strong smell of this variety of juniper. One branch of this plant, placed in a wardrobe, will reliably protect its contents.
There are several varieties that belong to this variety:
- The Tamariszofoli variety is known for the fact that its needles consist of thin needles that have a silvery-gray color.
- The Erekta variety has a beautiful pyramidal crown up to two meters high.
- The Variegata variety is a creeping shrub with needles, the tips of which are yellow-white.

Red cedar
This variety originates from North America. It has another name: “Pencil Tree”. This is due to the quality of the wood of this tree. Pencils were once made from it. This type of juniper grows well in the climate of central Russia.
This species tolerates drought well, is shade-tolerant, and unpretentious to the soil on which it grows. But the best type of soil for it is sandy loam. In the climate of the Moscow region it tolerates winter well.
One of its important properties is that it is virtually invulnerable to pests or diseases. It tolerates the procedure of pruning branches well. In winter conditions, branches may break off due to the severity of the falling snow. To prevent this from happening, they should be tied with twine in winter. Grows in the form of a tree.
Its height can reach 15 - 20 meters. The trunk diameter of mature trees is half a meter. The needles on young shoots are needle-shaped, on long-term shoots they are scaly. Young trees are better suited for decorative purposes. With age, the crown may thin out from below. The cone-berries are up to six millimeters in size. Their color is dark blue with a bluish tint. They ripen in one season and are harvested in October. A plant strewn with berries looks very beautiful in the fall.

First, let's list the varieties that grow like trees:
- Pyramidiformis is like a narrow column ten meters high with needles that are light green in summer and change their color to pastel purple in winter;
- Shotti is the same height, it has light green scale-like needles;
- Polymorpha, having bluish needle-like needles below and green scale-like needles at the top;
- The Chamberlaini variety is distinguished by its long, thin, flowing branches in needle-like needles, which look like a lush and wide gray-green pyramid.
Now let's talk about artisanal types of juniper:
- The Dumoza variety is characterized by a pyramidal, rounded crown and branches that are covered with dense needle-type needles;
- Variety Albospicata - has a height of up to five meters, the needles that grow on the tops of the shoots are whitish in color;
- In Helle, the outstretched shoots actually form a wide base, which is pure green;
- The Glauka variety is a column up to five meters high, the color of its needles is bluish-green.
- Variety Kosteri - spreads along the ground. This shrub is widely used for decorative purposes.
There are varieties of juniper known for the beautiful color of their coniferous cover:
- In the Cinerascens variety, the needles have a beautiful greenish-ash color;
- In Aureospicata, the tips of the coniferous needles are golden;
- The color of Aureovariegata needles is golden-variegated.
Growing a plant
Growing juniper begins with planting. However, you need to properly prepare for planting so that in the future the plant grows well and does not cause additional trouble.
Preparation stages:
- choice of location;
- soil preparation;
- selection of planting material;
- landing.
How to plant Cossack juniper
First of all, you need to decide on the place where the young bush will grow. Juniper is a light-loving plant, so it requires the most open space with good lighting.

In addition, it should be taken into account that the branches of the bush grow greatly and for full development, as well as maintaining the natural shape of the crown, it needs to be provided with enough free space.
Soil preparation involves preparing a soil mixture. It is prepared from peat, turf soil and sand in a ratio of 2:1:1. It is recommended to lime the prepared mixture with dolomite flour or ground limestone at the rate of 80–100 g of substance per volume of one pit. The average size of the pit is 50 cm deep and 60 cm wide.
Healthy seedlings should be selected as planting material. The root system should not show signs of damage by diseases or pests (dry and rotten roots). Seedlings that are in a container must be watered generously and the roots should be allowed to absorb moisture.
If the planting material was purchased with an open root system, it should be temporarily placed in a bucket of water for several hours, then the roots should be treated with a stimulant, for example, “Kornevin”. Having completed the preparation, you can begin planting.
Important! When planting in groups, shrubs must be planted at a distance of 0.5 m from each other.
Planting pattern:
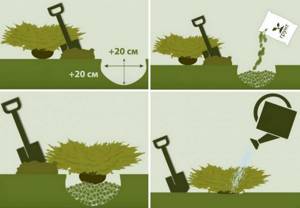
- Dig a pit 50x60 cm.
- Place a 20 cm layer of drainage at the bottom of the hole. Crushed stone, brick fragments or stones can be used as drainage material.
- Pour out the prepared soil mixture (peat, turf soil, sand).
- Plant the seedling in a hole so that its root collar rises 10 cm above the ground.
- Fill the pit with the remaining soil mixture and compact it.
- Pour 12 liters of water. When the ground has completely absorbed the moisture, cover the tree trunk circle with pieces of pine bark and peat in a layer of about 5 cm.
Juniper care
After planting, the young plant must be provided with conditions suitable for development and growth. To grow a healthy and beautiful bush, you need to learn how to properly care for it.
Features of care:
- pruning;
- watering;
- feeding
Next, you should understand the intricacies of the listed procedures.
4 popular shade-tolerant conifers
| 2. Canadian yew |
| 3. Yew berry (European) |
| 4. Cross-paired microbiota |
| 1. Spruce Pygmy. |
Peculiarities:
- maximum height - 50 m;
- crown diameter 6 - 8 m;
- crown shape - conical;
- needles - needle-shaped, hard;
- blooms in May or June;
- tolerates very low temperatures;
- loves fresh, well-drained, loamy, sandy soils;
- does not tolerate flooding and wind;
- tolerates pinching well;
- lives 235 - 300 years;
Almost all types of spruce trees grow well in low light conditions
Peculiarities:
- tree or shrub;
- height - up to 35 m;
- the needles are shiny, green, with large white spots underneath;
- cones - round, woody;
- grows well in partial shade, but can also grow in open areas;
- loves moist, fertile clay soils;
- has shiny scale-like needles;
- lives more than 500 years
Peculiarities:
- trees and shrubs;
- height - from 4 to 10 m;
- growth - 6 - 12 cm;
- shade-tolerant, but prefers sun;
- not demanding on the soil, grows even on swampy, poor and compacted soils;
- frost-resistant;
- adapted to urban conditions.
After planting, young plants require feeding with special fertilizers for conifers.
Peculiarities:
- height - 0.3 - 0.4 m;
- width - more than 1 m;
- crown shape - cushion-shaped;
- needles - small, scale-like, bluish-green or light green, in winter they acquire a purple tint;
- grows slowly;
- prefers sandy loam, moderately moist soils;
- shade-tolerant, but light-loving;
- does not tolerate dry air and stagnant moisture;
- very frost-resistant.
The variety is planted in group plantings and individually on rocky slopes and hills
How to propagate Cossack juniper
Planting material can be purchased at the store or you can try to propagate the plant yourself at home.
Reproduction methods:
- Seeds. In the fall, you need to collect the cones and carefully extract the seeds from them. Then soak in sulfuric acid solution for 10 minutes. After this time, rinse with plenty of water. Next, the seeds must be stratified by sowing them in the snow for 5 months. In the spring, when young shoots appear, transplant into open ground.
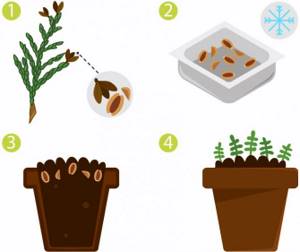
- Cuttings. In the spring, preferably in cloudy weather, you need to prepare cuttings. To do this, you will need woody branches growing at the top of the bush. The selected shoots should not grow vertically; it is advisable that they droop. When cutting a cutting, you need to make sure that there is a “heel” on it - a fragment of a shoot or branch. Then you need to remove 5 cm of needles without touching the “heel”. Next, you should immediately plant the cuttings in a substrate of peat and river sand in equal parts. You need to deepen it by 3 cm, maintaining an angle of 60°. Then the plantings need to be watered with sodium humate or “Heteroauxin” - a drug that stimulates root growth. Cuttings should be stored in greenhouse conditions with high air humidity, at least 90%. The temperature regime must be maintained within the range of +17…+19°С. After the buds open, increase the temperature to +25°C. The root formation process takes from 50 to 90 days. You can plant young plants in open ground next spring. During the rooting period, cuttings need to be watered 5 times a day. After the first roots appear and buds open, reduce watering to once a week.

- By layering. Shrubs can be propagated using this method throughout the entire growing season. To do this, you need to choose green, but developed and formed shoots. Then prepare the soil: loosen the soil, fertilize it with acidic peat and river sand, and water it. Next, you need to remove 20 cm of needles from the base of the selected branch and, bending it to the ground, secure it. In this case, the top should be above the surface. The soil around the attached branch must be loosened periodically. Layers take root within a year. After the roots have formed, the seedlings can be transplanted to a permanent location.
- Vaccination . The grafting method is used to propagate valuable varietal forms. For this purpose, a cutting cut from a certain variety is grafted onto a common juniper seedling. To do this, you need to press the cutting against the rootstock and secure it tightly with tape.
Find out when is the best time to replant your juniper to a new location.
Reproduction
There are several common options for propagating Cossack juniper.
- The simplest of them is propagation by air layering. Thanks to the rooting of branches in contact with the soil surface (air layering), it itself quickly grows in width, forming dense thickets. Sometimes you just need to carefully look for such material near the main bush, cut off the rooted part and plant it. If it (the material) is not found, then bend the branch to the ground, pin it and sprinkle it with earth, and water it periodically.
- Another way to propagate this juniper while maintaining the variety is by cuttings. That’s exactly what I used, having received juniper branches from neighbors. Cuttings can be done in winter-autumn, spring and summer. We cut off the stem from the bush at the base, place it in fertile light soil and, if it is spring and summer, water it abundantly until we are sure that the plant has taken root and taken root. Most often, with such cuttings from lignified stems and with proper watering, there is not even a need for root formation stimulants and greenhouse conditions. When cutting in winter-autumn, we also keep the soil moist until the snow falls, and next year after it melts. We cut the stem from the plant and bury it approximately 15 cm into the soil just before it freezes. So, if you wish, you can produce many of our juniper planting units without much difficulty.
- Also, this type of juniper propagates well in spring and early summer by green cuttings with a small piece of old wood. In this case, it is better to use means to accelerate root formation. However, it will take much more time to form a bush here than when propagating using the two methods mentioned above. Moreover, by using these methods, you can get a fairly ornamental plant almost immediately after the material has rooted. To do this, it is necessary to plant not one stem, but three, on one seat, placing them at an angle of 45 degrees, as if forming a bowl. But an exception here may be some varieties that do not have this shape (bowl shape) in adulthood.
- Another method of propagation is by seed. But with this method the grade is lost. It is more labor-intensive, time-consuming, and therefore little used by gardeners.
Benefits and harms
Before you start growing Cossack juniper, you need to familiarize yourself with its beneficial and harmful properties. For example, to understand why rust attacks an apple or pear tree, you need to pay attention to the proximity of the plants.

If juniper grows nearby, then most likely it is the source of the spread of the fungus Gymnosporangium sabinae, which is the causative agent of this disease. Fungal spores spend the winter in the cones of the bush, and in the spring they spread throughout the garden.
Read how to treat juniper for rust.
- Positive traits:
- Decorative;
- The needles are suitable as mulch and fertilizer for flowers;
- The shoots contain phytoncides that have an antibacterial effect;
- The aroma of juniper repels parasites and pests.
- Negative qualities:
- In winter, the plant changes its needles and looks untidy;
- Fallen needles rot within 3–5 years, so the fertilizer will not be ready soon;
- All parts of the plant are poisonous;
- Substances contained in shoots, needles and berries are toxic and affect the central nervous system, digestive organs and kidneys.
“Cossack” juniper is planted to decorate the landscape. Growing this unpretentious plant is relatively simple. Having decided to plant an ornamental shrub in your garden, it is important to remember that it has both beneficial and harmful properties.
Advantages and disadvantages of the variety
Juniper Cossack Tamariscifolia: description, planting and care
The undoubted advantage of Cossack juniper is its ease of care. Dense bushes perform a decorative function well, covering the ground with a dense layer of greenery. This cover prevents the spread of weeds, freeing the farmer from weeding activities. The ability to tolerate smoke and air pollution makes it possible to plant shrubs within the city.
Significant disadvantages of the variety are:
- poor tolerance of close groundwater;
- demanding watering conditions;
- pronounced aggression towards neighboring plants for territory, water and nutrients;
- pronounced poisonous property of the fruit;
- specific pungent odor.

Advantages and disadvantages of the variety
Pruning juniper: how to properly trim common, creeping, and Cossack juniper
Many people consider pruning junipers unnecessary. Others are afraid of damaging the bush. But juniper should be trimmed for health and decorative purposes.
Juniper is an evergreen coniferous tree or shrub from the cypress family. Particularly common in mountainous regions. Leaves are scaly or needle-shaped.
It is important to prune correctly and not get carried away with it. The shrub has a plastic crown, which allows you to give the plant a certain shape during the pruning process.
The plant is grown for decorative purposes. The bush is evergreen and resistant to cold.
Diseases and pests: treatment methods
Junipers are susceptible to diseases, especially fungi. More often than others, ocher growths can be found on branches, indicating rust infection. This parasite requires two hosts, one of which is a pear, apple, rowan or hawthorn. You can avoid infection by planting the conifer as far as possible from another host. All affected branches must be removed with a sterile pruner and the instrument must be disinfected again after work. Without waiting for autumn, juniper and pear need to be treated with Topaz 2 times a month.
High soil moisture can cause a disease such as Brown Schutte. It looks like a gray, almost black cobweb that has enveloped the entire bush. Young shoots die, then the entire plant may die. Severely affected branches are removed and the entire plant is treated with Bordeaux mixture.
To avoid infection of plants with fusarium, they are treated with Bactofite before planting. If the plant is already infected, it can be watered with a solution of Fundazol.
Insects infect junipers less frequently, but scale insects or spider mites can still be found on their branches. The plant must be treated with Aktara, Fufa-nova or Fitoverm.
Is it necessary and possible to trim various varieties of juniper?
Depending on the variety, juniper can form the crown in different ways. Therefore, when choosing a variety, it is important to clarify in advance where it is planned to be planted and what formation is expected. For example, the Chinese Blue Point plant can be formed into a ball or pillow in water. And Hibernica is perfect for shaping into a cylinder.

Hibernica in the form of columns
It is necessary to trim juniper of any variety. But the goals of rejuvenation can be different - to improve the health of the bush, to make it more decorative, getting rid of unnecessary shoots. But pruning is needed in any case, because it helps renew the bush.
Some designers believe that juniper should not be pruned, because then the natural shape of the plant will be preserved. This usually applies to creeping varieties. But it is still necessary to cut off shoots that are diseased or damaged, otherwise there is a risk of death of the entire plant. Also, a little intervention is needed for columnar varieties. Usually they only cut off what has gone beyond the crown shape.















