Felt cherry (Cerasus tomentosa) in Russia owes its popularity to I.V. Michurin, who described the fruit-bearing shrub.
Felt cherry belongs to the genus Plum, the Rosaceae family. Genetically close to it are plum, cherry plum, apricot, and peach. The culture is similar to ordinary cherries only in the shape of the berries. The plant is covered with down, so it also has names: “textile”, “velvet”.
Velvet cherry is also called Chinese because its homeland is China, Mongolia, and Korea. The tree began its journey around the world at the end of the nineteenth century: at first it was grown as an ornamental, landscaping plant decorating the garden. The development of new varieties of velvet crops has made it possible to use the berries for food. Now the regions where felt cherries are grown are European countries, Japan, America, and Canada.
Gardeners fell in love with the velvet plant because of a number of advantages:
- good productivity of the velvet tree;
- high frost resistance of velvet crop;
- drought-resistant trees with velvety berries;
- resistance of the velvet tree to many diseases, for example, coccomycosis;
- indifference of insect pests to the velvet tree;
- rapid growth, early fruiting of the velvet tree - in the second year;
- no shedding of velvet berries;
- pleasant taste of velvet berries;
- velvet berries are rich in vitamin C, polysaccharides, antioxidants;
- the beneficial qualities of the berries are used for high blood pressure, heart disease, problems with blood vessels, digestive organs, sleep disorders, and joint diseases;
- the small size of the velvet crop allows the use of small areas for planting;
- the tomentose plant has no root shoots;
- decorative properties of the shrub: the plant fits well into landscape design;
- unpretentiousness in caring for a velvet plant;
- simple propagation of velvet culture using cuttings and layering.
The disadvantages are:
- short plant life - an average of ten years;
- the need for annual pruning of the plant;
- thaws lead to peeling of the plant's bark;
- For pollination of a velvet plant, fellow plants must grow nearby;
- poor keeping quality, impossibility of transporting berries;
- the plant lacks resistance to moniliosis;
- the inability to consume velvet berries for people suffering from gastritis, ulcers, prone to stomach upsets, or having sensitive teeth.
Felt cherry description and photo
The small felt cherry tree is more like a bush: its size does not exceed three meters, which makes harvesting easier. Several powerful skeletal branches extend from the trunk of the tree, which form a rounded crown that requires systematic pruning to avoid neglect. The trunk and branches are covered with rough gray-brown thick bark.
A relief appears on the small leaves of the velvet cherry. Flower buds are arranged in bouquets of three. The peduncle is short. Therefore, it seems that the berries grow from the branches.
Delicate pink and white flowers bloom on the short stalks of the plant in mid-May. The velvet beauty becomes like a huge fragrant bouquet.
At the end of June - beginning of July, juicy berries begin to ripen on the tree. Depending on the variety, they are pink, white, red, burgundy and even black. Children love the delicate sweet taste with a subtle sourness of the berries, hence another name for the culture – “children’s”.
The shoots, stalks, leaves, and berries of the plant are covered with delicate down. This is how felt cherry differs from ordinary cherry.
Velvet berries make delicious jam, marmalade, jam, compote, juice, fruit drink, and homemade wine.
Features of felt (Chinese) cherry
The homeland of this culture is China (hence the second name of the species - Chinese). It appeared in Russia at the end of the 19th century. The first specialist in our country to develop a variety with fairly large fruits was I.V. Michurin. This cherry got its name because of the pubescence that covers all parts of the plant, including the fruits.
All parts of the plant are slightly pubescent, which is why this crop got its name
The tree is small in size (up to 3 m), the crown is spherical or oval, rather spreading. The shoots are powerful, the leaves are small, wavy at the edges. The berries are small, the color varies from light milky to dark burgundy (depending on the variety). The fruits are sweet, slight sourness is present in some varieties. The bone is small and difficult to separate. In the photo you can see that the berries have short stalks, and therefore it seems that they are “sitting” on a branch.
Compact cherry bushes are completely covered with fragrant flowers, thus creating huge natural bouquets. Felt cherry flowers, emitting a honey aroma, attract a lot of bees.
Table: advantages and disadvantages of Chinese cherries
| pros | Minuses |
| The small size of the tree makes it convenient for care and harvesting, and this is also a plus for gardeners with a small garden plot | High susceptibility to moniliosis |
| Easy to grow and propagate | Short lifespan of a tree - about 10 years |
| Sweet, almost without sourness, taste | Some varieties are self-sterile and require pollinators to be planted |
| Decorative type of shrub | The bone is difficult to separate from the pulp |
| Early fruiting (can produce harvests already in the second year after planting) | Poor transportability |
| Stable yield | Intolerance to excess moisture |
| The berries practically do not fall off | |
| Resistance to coccomycosis | |
| Early ripening of berries | |
| Good drought resistance |

The felt cherry tree is compact and great for small gardens
Felt cherry how and where it grows growing conditions
Felt cherry grows well on fertile sandy, loamy soils. The soil should be non-acidic and drained. Peat bogs and waterlogged soil are not suitable for growing crops. With excessive moisture, the tree lags behind in growth, flowering, fruiting, and loses cold resistance.
Velvet culture loves sunny places; it will grow in the shade; there will be no partial shade.
In the case of groundwater close to the surface, the soil must be drained. Excessive soil acidity should be neutralized with lime.
Felt cherry varieties
According to the time of fruit ripeness, fruit and berry crops are divided into early, medium, and late ripening varieties. Felt cherry has varieties with all three maturity periods.
A successful harvest is possible if there are different varieties close to each other: self-fertile and self-sterile, with different ripening periods.
Velvet cherry has many types. Here is a description of the most popular ones, with varietal characteristics.
Summer
Felt cherry Leto is a self-fertile, mid-late variety. The variety was created in the mid-twentieth century. The original geographical destination of the variety is Khabarovsk, Primorsky Territories. Now widespread in many regions of Russia. Cherry Summer combined felt and sand. The young tree grows quickly. It grows up to one and a half to two meters - medium tall. The yield of an adult crop is on average eight kilograms. The ripening period for large, up to 4-5 grams, light red velvet berries occurs at the end of July. The berries of the variety have juicy, thick, sweet and sour, slightly fresh pulp. The pulp is covered with a thin fluffy skin.
Ogonyok
Felt cherry Ogonyok is a mid-late variety. Self-sterile. The tall tree grows up to two and a half meters. Productivity is up to eight kilograms. The variety's velvet berries ripen by the end of July. Light red in color with thick, juice-filled, beautiful pulp. Fruits with a sweet taste have a pleasant sourness. The pubescence of the thin skin is gentle.
Tsarevna (Tsarina)
Felt cherry Tsarevna belongs to the mid-late varieties. The princess is self-sterile. The fruits ripen at the end of July. A low-growing tree - just over a meter tall - has a yield of about ten kilograms. The variety's crimson-pink berries, juicy and sweet, weigh about four grams. Short hairs are visible on the thin skin.
The Tsarevna variety has high decorative qualities and is actively used in landscape design.
Alice
Felt cherry Alice is a compact tree of medium size, the average height is on average one and a half meters. In a mid-season, self-fertile variety, the berries ripen in mid-July. The yield of the variety is good - up to nine kilograms. With proper care, fruiting begins two years after planting. Velvety berries of a dark burgundy tone are rich in juice, have a balanced taste, which harmoniously combines sweetness and acidity, large in size - 3-4 g.
Children's
Children's felt cherry is a low, wide tree, about 1.5 m tall. The fruits are collected in mid-summer. The rich red juicy berries of the plant have elastic, flesh covered with thick skin. They weigh from two to four grams. The sweet taste is complemented by a gentle sourness. The yield of the variety is good, ten kilograms per tree.
Natalie
A vigorous tree about two meters high produces a harvest in mid-summer. The variety is self-sterile. The yield of the variety is 7-8 kilograms, reaching 10 kilograms. The berries are not small, weigh about four to five grams, and are dark red in color. Tender skin covers juicy, elastic, gristly flesh with a sweet and sour taste. A special feature of the Natalie variety is its long fruiting period.
What defects and parasites attack felt cherry
This variety is quite resistant to various defects and parasites. But at the same time, there are some ailments that can regularly attack cherries. Therefore, you need to know what to treat and what to do if the cherry is infected. So, what defects and parasites can attack the felt variety:
- Moniliosis is able to penetrate deep into the sprouts and infect them. It appears during the period when flowering begins. If this defect affects the felt cherry, then by the beginning of June the branches and foliage begin to dry out. In the case when the moment of damage to the bush was missed, the novice gardener will later have the question of how the felt cherry tree does not bear fruit and what to do. This disease can be overcome with timely treatment with fungicides.
- The second defect, which is also common, is Coccomycosis. When affected by this disease, felt cherry leaves begin to fall off early, the tree's immunity decreases, and the affected bushes no longer pollinate. In order to defeat this disease, it is necessary to spray with Bordeaux solution.
Of the pests that attack felt cherries, the most dangerous are aphids, leaf rollers and plum moths.

In order to protect the cherry front garden, the following rules must be followed:
- neighbors such as gooseberries, currants and raspberries should not grow next to the cherry;
- regularly treat cherry bushes with a weak solution of potassium permanganate;
- every year, after the harvest is harvested, it is necessary to remove and destroy all fallen leaves from the cherry front garden;
- you need to regularly spray with organic fertilizers to strengthen the immunity of the cherry bush;
- if parasites have already appeared, then the plant can be cured of them using an ash solution.
Above we looked at everything about such a culture as felt cherry care. It is worth noting that sometimes a novice gardener has a question: why does a cherry tree, which appears to be absolutely healthy, not bear fruit? In this situation, experienced gardeners notice that such a problem can arise if the shrub was planted incorrectly.
The fact is that compatibility plays a big role when planting this crop. Therefore, if the cherry tree does not bear fruit, then it is urgently necessary to plant a new seedling opposite such a shrub, which will further ensure compatibility of the crop and a generous harvest.
Planting and caring for felt cherry
Velvet cherries are planted in the autumn, in September, or in early spring, until the buds actively swell. Plant seedlings must be one or two years old.
The place is chosen to be sunny. Drafts and strong winds should not create inconvenience for the plant. There should be no stagnation of moisture - it is best to choose a small hill.
Landing
When to plant felt cherries, in spring or autumn, depends on climatic conditions. In the southern regions, planting can be done in spring and autumn. In the northern regions, it is better to plant the plant in the spring.
Landing algorithm.
- Choosing a location.
- After choosing a place for planting, a planting hole with a diameter of 70-80 cm and a depth of half a meter is prepared.
- A nutrient mixture of rotted manure, phosphorus, lime, and potassium is placed at the bottom of the pit. Ingredient proportions: 30 liters – 50 grams – 500 grams – 30 grams, respectively.
- The roots of the tree are dipped into a clay mash.
- A felt cherry seedling is placed in a planting hole so that the root collar of the plant is above ground level. The roots are covered with a mixture of earth and nutrient soil, compacted, and generously watered.
- The area around the plant trunk is mulched. You can use peat for this.
- Spring planting requires systematic watering: in the absence of rain - at least once every 10-14 days. No watering is required in autumn.
It is necessary to plant at least three felt trees nearby, placing them at a distance of two to three meters from each other.
Care
Caring for velvet cherries does not require much effort.
- It is necessary to regularly weed, loosen the soil around the plant trunk, and water.
- It is necessary to fertilize the tree regularly. In the spring, during the flowering period, phosphorus, potassium, and nitrogen are added. In autumn - organic fertilizers.
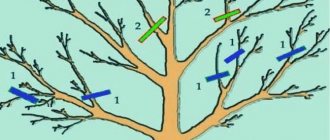
- Felt cherry trees need pruning in spring or fall. Pruning rejuvenates the tree, thins the crown, and removes dead shoots. Anti-aging pruning is done no more often than every four years. Formative and sanitary are performed annually. The lateral shoots growing inside the tree, as well as dry, frozen, damaged, old branches are removed. Branches that have reached seventy centimeters in a year are shortened by 20 cm. Pruning should not be done too intensively, in order not to harm the tree.
Felt cherry propagation
How does felt cherry reproduce? There are several ways.
- Using cuttings. Side shoots are suitable for felt cherry cuttings. The top edge is cut straight, the bottom - obliquely. The shoot needs about 20 cm, it should have four internodes or more. Peat, earth, sand are mixed. The cutting, treated in a special solution to stimulate growth, is placed in prepared soil. Depth - one to two centimeters. The cuttings are thoroughly watered and covered with film. The soil should always be moist, but not soggy. Root shoots appear on cuttings within a month on average.
- With the help of layering. In the spring, a layer is made from the developed lower shoot of the plant by bending it to the surface of the earth into a prepared depression. The stem is pinned and covered with soil. The aerial part of the stem is attached to a vertical column. The rooted cherry is planted in the prepared place.
- Felt cherries from pits are a propagation method for gardeners who like to do everything themselves. For planting material, seeds taken from ripe berries are suitable. They are washed with water and dried in a shady place. By the beginning of autumn, planting material is placed in a damp mixture of sand and sawdust and placed in a cool place. The mixture should always be moistened. At the end of September, a small groove three centimeters deep is made in the open ground: velvet cherry seeds are planted in the furrow at a distance of two centimeters from each other. The furrow is filled with a mixture of earth, sawdust, and humus. In April-May, the emerging seedlings need to be thinned out and the stronger ones left. A year later, the cherries are planted in areas chosen for growth.
Knowing what to plant a felt cherry on will help you replicate all the beneficial properties of a velvet plant. Felt culture is used as a rootstock for plums, cherry plums, sloe, and sometimes for apricots and peaches. Felt cherry should not be grafted onto ordinary cherry.
Landing
In order for the felt cherry to grow and bear fruit well, you need to choose the right place for planting. The main “requirements” for the landing site: good lighting and light, well-drained soil (for example, peat bogs are not suitable). The tree does not tolerate partial shade. As well as excess moisture, acidified and heavy soils. It can survive in such conditions, but it will grow slowly, and the number of berries will decrease significantly even with proper care.
The ideal landing site would be loamy or sandy soil, with a good drainage system (no stagnant water). You need to choose unshaded places. The trees are small, so planting them next to taller specimens with lush crowns is not recommended.
Advice: several seedlings (at least three) should be planted at the same time. Without this, self-sterile varieties practically do not produce a harvest. The distance between bushes is maintained at an average of 2 m.
Disembarkation rules
To plant felt cherries you will need:
- dig holes to a depth of 50 cm with the same diameter (you can dig a trench instead of individual holes);
- pour soil mixture on the bottom: for 3 buckets of organic matter you will need 400-800 g of lime, 30 potassium and 50 phosphorus (proportion for each m2);
- trim the roots from below to a level of 20 cm;
- treat them with a clay mash;
- sprinkle the seedlings, compact the soil, water moderately and be sure to mulch (peat or organic fertilizers are preferable as mulch).
Important: the root collar should be located above the surface. This is a mandatory condition, otherwise the seedling will die. The depth level is maintained (the same as during germination).
Seedlings are planted in spring or at the very beginning of autumn. In the spring, they need to be planted before the first buds appear, in the fall - until the end of September at the latest. It is recommended that planting material obtained in October not be planted in open ground, but dug in until spring planting.