History of growing decorative moss
Soft lace fur was chosen as a laconic decoration of temple gardens back in the 6th century by ancient Buddhists. The monks raised landscape design with moss to the status of a special art.
Now moss is an invariable attribute of gardens and parks in Japan. Near Kyoto, on the temple grounds, the ancient Saihoji Garden grows, where you can see more than 100 species of decorative lichens and mosses.

The importance of mosses in nature and human life
Mosses are food for many invertebrate animals.
After dying, peat deposits are produced, which is necessary in the production of plastics, resins, carbolic acid, and is used as fuel or fertilizer.
Moss completely covers the ground in places of growth, which leads to the accumulation of moisture and waterlogging of the area. Thus, the germination of other vegetation becomes impossible. At the same time, they prevent erosion and soil destruction by surface water and winds. When mosses die, they take part in the formation of soil.
Capable of growing in areas of fire, persistent and hardy, they inhabit the tundra (the main vegetation background, since other plants cannot survive in such conditions).
In wartime, sphagnum moss was used as a dressing material due to its bactericidal properties and ability to absorb moisture.
With the help of mosses you can navigate the terrain: they do not like light, so they are located on the shadow side of stones and trees. Moss points a person to the north.
In construction it is used as an insulating and insulating material.
- Bryophytes provide food for many invertebrate animals.
- Interesting facts indicate that when moss dies, it produces deposits of peat, which is needed for the production of plastic, resin, and carbolic acid.
- Moss completely covers the ground in places of growth, which can lead to waterlogging of the area and accumulation of moisture. This will make it impossible for other plants to germinate. At the same time, bryophytes prevent the destruction of soils by surface water, erosion and destruction by winds.
- During the war, sphagnum moss was used as a dressing material because it had bactericidal properties and absorbed moisture well.
- Thanks to moss, you can find your way around the area: these plants do not like light, and therefore they are usually located on the shady side of stones and trees. Moss points north.
- In construction, moss is used as an insulating and warming material.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with the “Friendly” vegetables in the beds. Compatibility of crops in the garden
What is decorative moss
This plant is a special type of site decoration that adds elements of magic and tranquility to the familiar landscape.

Moss grows quickly, prevents weeds from multiplying, and also inhibits the development of soil erosion. Even if you take a walk in a moss meadow, the plant stems easily recover after watering.

Types of moss for the garden
There are several popular types of plants for use in the garden:
- neat Leukobria pads;
- Hypnotic moss, which was previously used as insulation for wooden rooms;
- small flowering moss Kukushkin flax;
- Dicranum moss is ideal for decorating stones;
- beautiful fern moss;
- multi-colored peat moss.

Benefits of the plant
Decorative moss for the garden is very easy to care for and does not require cutting. It is also hypoallergenic and does not cause problems to animals and people.

To exist, it needs only shade and humidity. Even if there is little rainfall in the summer, the plant quickly recovers if you water it.

Dry and unsightly, moss is literally reborn under a stream of water or raindrops, demonstrating its velvety and emerald colors.

Moss is also practically not subject to any diseases or pest attacks. In addition, temperature changes do not create problems for the plant, so it feels normal in all regions of our country.

Moss propagation
Growing moss on your site with your own hands is not at all difficult. The easiest way is to bring ready-made plant pads from the forest and place them on the ground at a distance of 20-25 cm.

Moss pieces should be taken together with the “native” piece of soil. Before planting, the pads must be placed in water so that they are saturated with moisture.

It is better to replant in the spring or in the first days of summer in cloudy rainy weather. By autumn, the moss will consolidate in the soil and become stronger.

On dry days, the plant needs to be watered, and over time it will no longer be afraid of capricious weather. After 2-3 years, the islands of moss will close together and turn into a nice green meadow.

The second planting method is to purchase material from specialized stores. There you can buy different types of moss and get advice on planting and using it in garden design.
Where can you use moss?
- garden sculptures and other decorative elements covered with moss will add a pleasant velvety feel and create the feeling of an ancient garden
- place moss in the spaces between paving garden paths. This technique will hide uneven seams and soften the overall appearance.
- covering the roof of a cellar or shed. If there is a bulk cellar on the site, the “green” roof will additionally cool the space inside
- lawns and lawns
- when decorating a garden in Japanese or retro style
- when designing the shoreline of a reservoir, stream, swamp
- garden graffiti
- garden compositions
- hanging planters
- phytowalls
- moss flower bed
- design of the root zone of container plants
Mossy stones, tree trunks, driftwood and ceramic amphorae have a natural look and create a peaceful atmosphere of an ancient garden. For your experiments with moss, choose boulders with a porous surface (limestone, tuff). Moss spores will easily attach to them, and the plant will develop well.
If the surfaces that you plan to cover with moss are smooth, treat them with an abrasive to create the necessary unevenness and only then apply the prepared mixture with spores: Recipe: 2 cups of kefir, natural yogurt, milk or buttermilk (your choice) + moss (fresh or dry ) Mix 1.5 cups in a blender until smooth. In terms of thickness, aim for the consistency of sour cream or light cream. If you need to thicken more, add crushed moss, if diluted, add water. For smooth surfaces, moistened ceramic clay is added to the mixture. It will increase the viscosity of the composition and allow the mixture to consolidate.
After 6 weeks, you will be able to evaluate whether the moss has taken root where you placed it.
Mosses do an excellent job as a background that emphasizes the beauty of the forms and the brightness of the colors of other plants. Feel free to add mosses to the design of a rock garden, alpine slide or Czech rolling pin. They will give a finished, natural look to your landscape objects.
You can cover the entire retaining wall in the garden with moss, or you can fill the gaps between the stones to add color to the masonry and soften the corners. The following plants will look good against the backdrop of a mossy clearing: violet, lingonberry, fern, conifers, hydrangea, rhododendron.
How to care for a plant
The plant does not require any attention at all. Care is needed only after planting for the first few weeks. Agricultural technology consists only of regularly moistening the soil and removing dead pieces of the plant.

When the moss takes root, you can moisten the soil less often, and then water it only as needed.

General characteristics of mosses

Bryophytes are one of the oldest plants inhabiting our planet. The remains are found in fossils from the late Paleozoic era. The distribution of mosses is associated with a preference for moist environments and shaded areas, so most inhabit the northern part of the Earth. They do not take root well in saline areas and deserts.
Bryophyte classes
Leafy mosses are the most numerous class. Plants consist of a stem, leaves and rhizoids.
The stem can grow vertically or horizontally, divided into bark and ground tissue (contains water, starch, chloroplasts for photosynthesis).
Stem cells can produce thread-like processes - rhizoids, which are necessary for attachment to the soil and absorption of water. They are most often found at the base of the stem, but can cover its entire length.
The leaves are simple, often attached to the stem at right angles, in a spiral. The leaf blades are equipped with chloroplasts; a vein is located in the center (serves to conduct nutrients).
Deciduous mosses can reproduce by stems, buds, and branches that sprout, thus forming continuous carpets of mosses covering the ground. The class of phyllophytes includes sphagnum mosses (they have a variety of stem colors - light green, yellow, red), andreaceae and brie mosses.

Sphagnum moss
Liverworts are found on coasts, swamps, and rocky areas. Distinctive features: leaves have no veins, dorsoventral structure, special mechanism for opening the sporophyte.
The leaves are arranged in rows, have two lobes (the lower lobe is often curled and serves as a reservoir for water), the rhizoid processes are unicellular. During the eruption of spores, the sporophyte capsule opens into separate valves, and elaters (spring formations) contribute to the dispersion of cells.
Reproduction can be carried out using buds (vegetatively), which are formed on the upper pole of the leaves. Representatives of the class Pellia endievefolia, Milia anomalous, Marchantia moss, etc.

Marchantia
Anthocerotic mosses inhabit the tropical zone. The multinucleate body (thallus) has a rosette shape and consists of cells of the same type. In the upper spheres of the cells there are chromatophores (containing dark green pigment). The lower part of the thallus produces shoots, rhizoids, and the body itself forms cavities filled with a viscous liquid that maintains constant moisture.
On the surface of the thallus, under unfavorable conditions, tubers are formed that are resistant to low humidity; after a period of drought, a new generation is formed. The plants are monoecious, the reproductive organs develop in the thickness of the thallus, the sporophyte stage is predominant. Anthocerotes include folioceros, anthoceros, notothilas, etc.

Living graffiti from moss
Moss graffiti is now a current and fashionable style of site design. If you follow certain rules, you can make some kind of inscription or attractive design in the garden. This is painstaking work, but the result is amazing.

To do this, you should prepare a nutrient mixture on which the moss will grow. You need to take pieces of moss, 2 cups of buttermilk (natural yogurt without additives), 1 cup of rainwater (high-quality natural beer), 0.5 teaspoon of sugar. The nutrient mixture should be thick enough so that it can be applied to a vertical plane, for example, on a wall.

Pieces of moss must be carefully attached to the wall. The result is a fabulously beautiful drawing. Moss on small architectural elements

In addition to lawns, one of the best places for moss is various decorative garden elements, such as flowerpots, sculptures or fountains. It visually ages architectural forms and makes them mysterious.

The green mat will hold tightly if the elements are in a damp and not sunny place and also have a loose, rough surface.

A mixture nutritious for moss should be applied to the chosen form and its pieces should be strengthened. The main thing is not to forget to moisten the planting sites.

WHAT IS MOSS AND HOW DOES IT GROW?
People and mosses have lived next to each other for a long time, however, historically and evolutionarily, mosses live much longer, they appeared more than 400 million years ago, even before flowering plants, so mosses deserve to be told about them. Let's see if our opinion changes when we take a more complete look at what moss actually is. By the way, there are useful mosses, such as "Spanish moss" - a flowering plant related to the pineapple that produces very small flowers, not moss.

What is moss?
When we are asked: what is a plant? Many of us imagine a herbaceous or woody plant, such as chamomile or, for example, birch. We think that all plants have roots, stems, trunks, flowers, fruits and seeds. Most of us don't think about plants that grow on rocks, roofs, concrete and any other unexpected places; however, this so-called opportunistic group, choosing a variety of eclectic substrates, exists outside of our classical concept. Their leaves are mostly one cell thick, they have no true roots, stems, flowers or fruits, and they have spores instead of seeds. As has already become clear, “They” are mosses; plants that form "green carpets" with thin, wiry, vertical stems supporting a brown capsule that appears to be wearing a hat.
How do mosses reproduce and spread?
Mosses spread in several ways, but unlike flowering plants, they rely on moisture to reproduce sexually. Mosses reproduce by spores, which are similar to the seeds of a flowering plant; however, moss spores are single-celled and more primitive than a common seed. The spores are located in a brown capsule, which is located on the bristles. As the spores mature, they disperse from the capsule and some end up in areas where there is enough moisture for them to grow. Young moss looks very thin, like a tangled mass of branching green hairs. The green hairs will produce buds that will grow into tiny stems and thin leaves. Some mosses have cups on their tops that produce sperm; these are male plants. The female plant has eggs between her overlapping leaves. Water is necessary for fertilization: once the sperm becomes mature, its cells will have to swim to the eggs to fertilize them. The fertilized egg then produces a brown capsule. Mosses also spread asexually, by sending new shoots in the spring from plants of recent years, as well as by fragmentation. Parts of the moss body can break off, be moved by wind or water, and start a new plant if moisture permits.
How do mosses acquire nutrients?
Mosses have different mechanisms that they use to obtain nutrients. Some mosses are able to capture nutrients when air humidity is minimal because they have very efficient absorption surfaces. Other mosses, such as Cuckoo flax (Polytrichum polytrichum), obtain nutrients directly from the soil or substrate on which they grow and transfer them to the growing tips. With this in mind, we can see that the physical and chemical nature of the substrate, as well as its water-holding capacity, are extremely important for the formation of moss.
Where do mosses live?
Now that we've seen that mosses are resilient through multiple ways of reproducing, it's easier to understand that mosses can live anywhere from the Arctic Circle to the rainforests of the equator. Mosses can be found around hot springs, at the bottom of lakes, on rocks, sand dunes, trees, and even in some cases in seawater. Damaging mosses grow on our trees, sidewalks, rooftops, lawns and everywhere in between. The two main requirements of moss are sufficient moisture and available nutrients. For example, a damp environment on a roof under the shade of trees is a good place for mosses. Not only does the roof remain constantly damp during rainy periods, but nutrients are also added from the ash produced by the chimneys. Here lichens, consisting of wood, asbestos and conglomerate, create suitable homes for moss. Mosses prefer to colonize the space above the eaves where moisture accumulates, in eaves depressions or other depressions. Mosses feel good in autumn, warm winter and spring, when there is a lot of water, little light and low above-zero temperatures. In the hot summer, mosses dry out significantly and become less active, but if water comes in, their activity is restored instantly.
What types of mosses grow on the roofs of Russia?
In most of the samples we collected on the roofs of the European part of Russia, 4 types of moss were usually present. Of these, the most common were Tortula muralis, Bryum capillare, Hypnum cupressiforme and Dicranoweisia cirrata. These species tend to form dense carpets that cover large areas of the roof. We simply do not list rare species because they are unnecessary, since they constitute less than 3 percent. Bryum capillare has been found to grow in heavily shaded areas of the roof, while other species are found in both exposed and shaded areas. This may indicate that different types of mosses may grow in areas shaded by trees and other wetter, shaded areas. See Study Results.
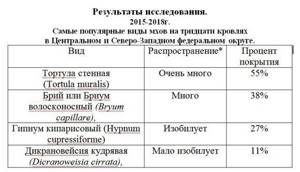
*average percentage of moss cover on all sampled roofs: Shingles: very much ˃ 50% much 10-30% Abundant 10-20% Slightly abundant <15% Clay tiles and others: Abundant ˃20% very much ˃ 30% Only five samples was taken from Clay tiles. Dicranoweisia cirrata and Bryum capillare were often found on Clay tiles. However, all species found were present on Flextile. Most roofs typically had less than 4 species of moss present. Of these, the most common were Tortula muralis, Bryum capillare, and Hypnum cupressiforme. These species tend to form dense carpets that cover large areas of the roof.
Bottom line
Let us summarize our brief acquaintance with the world and life of the Bryophytes who surround us and live with us. Our experiments and observations, as well as the construction practice of most roofing specialists, say that the presence of moss and lichen on the surface of the roofing material one way or another causes damage to the structure. The formation of tiny cracks under the root system of moss in roofing materials accelerates their destruction, ultimately causing micro- and macro-leaks. Moss can also hold moisture on the roof and decompose bio-debris, which helps more highly organized organisms like worms, etc., develop and take hold. Moss can grow under the edge of the shingles and lift them from the base (see photo), which leads to breakage over the years shingles from strong winds, and this is a direct path to the house for water.
We have previously written about methods of combating moss and lichen in our notes. If you have any questions, we will be happy to answer by phone and/or email.
Moss outside the garden
This ornamental plant can be used not only in the garden. Decorative stabilized moss is a natural material that has been specially suspended in development. It is used for decorating rooms.

The difference between stabilized moss
This plant is only half “alive”. Using chemicals, its growth and development were stopped at its highest point of prosperity.

The water in its base is replaced with a liquid, one of the components of which is glycerin, which allows it to maintain durability and reliability. You can only buy stabilized moss in the store.

Where do mosses live?
High humidity and regular rises in water in streams also contribute to the spread of mosses. For many species, trees, especially rotten trees, are an ideal habitat. At the same time, unlike fungi, mosses are not parasites. Mosses usually grow where flowering plants cannot take root: on rocks, in swamps, near springs and along stream beds, in trees . The fact is that mosses do not have a root system. They obtain water and nutrients directly from moist air or precipitation. Moss tissues contain a special type of cells that retain moisture for a long time. During prolonged drought, plants go into a dormant state. They change color and reduce metabolic rate to almost zero. At the same time, just a few drops of moisture are enough for them to emerge from the state of suspended animation.
Mosses usually grow where flowering plants cannot take root
Mosses are most often found in damp, shady places. However, some species are quite adapted to dry and sunny habitats, for example wall tortula . Its leaves end with transparent hairs that reflect the sun's rays and protect the plant from excessive light. Other survival strategies are also found in the moss kingdom :
- anthoceros often live in symbiosis with blue algae , which fix air nitrogen and transfer it to moss;
- sphagnums are capable of creating an acidic environment and thus preventing the appearance of fungi, bacteria and competing plants nearby.
Although moss is almost invisible in appearance, its role in ecosystems is very great . Since it is able to absorb and retain a lot of moisture, it plays a significant role in regulating the water balance of forests and swamps and reduces soil erosion in open areas. And without sphagnum moss, the formation of peat in swamps would be impossible.
A dense green carpet of moss provides reliable shelter for many small inhabitants of forests and swamps
Caring for stabilized moss
Caring for moss in the house consists only of regularly moistening it and protecting it from direct sunlight.

The intensity of watering differs only in the design of the moss mass. These can be fakes made of moss, such as furniture or wall decoration, panels or paintings, phyto-panels or a rug.

Moss in interior design
There are a huge number of options for decorating the interior with moss. Along with the living wall, it is worth highlighting other, no less popular ideas, which we will discuss further:
- Furniture or its individual parts;
- Greenboards;
- Silhouettes and inscriptions;
- Photo frame;
- Rugs.

According to Feng Shui, the more living plants there are in a house, the more it contributes to the development of a healthy atmosphere. Of course, if everything is done according to the canons of the Eastern tradition.

Moss in the office or home
It should be remembered that at home the humidity in rooms is always slightly higher than in offices. Therefore, in office premises it is necessary to take care of increasing the moisture content in the air using special devices and using various moisturizers more often.
The moss at home has dried up - what to do?
Slightly dry moss is not a problem. This happens in a room with insufficient humidity or when the stabilized moss is old.

To restore vital functions, you need to increase the percentage of humidity in the room and use a special humidifier, which can be purchased in the store.












