Types and varieties of hydrangeas
There are a large number of varieties of this ornamental shrub. Most often, hydrangeas prefer to grow in partial shade; some varieties do well in sunlit areas. The size and flowering period of the shrub depends on the variety.
The most common types
Large-leaved (Hydrangea macrophylla). This variety blooms in the second half of summer. The flowering period occurs in July – August. The inflorescences are lush and spherical. Flowers of white, pink, and blue shades form inflorescences with a diameter of up to 20 cm. The height of the plant is 2 meters. It should be covered for the winter, since large-leaved hydrangea can tolerate temperatures not lower than -10 degrees.
Petiole hydrangea (Hydrangea petiolaris). It is a type of vine. The flowers have a white-pink hue.
The plant is suitable for decorating gazebos and arches. When growing, it requires support, otherwise it will spread along the ground.
Tree hydrangea (Hydrangea petiolaris). This type has many varieties. The bushes are tall, up to 3 m. The oval-shaped leaf plates are up to 20 cm in length. Flowers are collected in large inflorescences. In winter, this species is subject to freezing, after which it quickly recovers and blooms well. To maintain the bushes in proper form, in April it is necessary to perform strong pruning, almost to the root.
Hydrangea paniculata. Shrubs of this variety bloom from mid-summer to late autumn. The inflorescences are pyramidal in shape, up to 30 cm long and consist of flowers ranging from soft green to white. In late summer, the flowers change their hue to a dull purple. The height of the plant is from 2 to 5 m, it can grow in the form of a small tree up to 1 m. This species is easy to care for and resistant to frost.
The best places to arrange compositions with hydrangeas
There are quite a few options for creating interesting compositions involving flowers.
Lawn
Neatly trimmed grass goes well with single bushes. In this case, you need to choose compact varieties of hydrangea that can grow in the sun.
Flowers look spectacular against the background of a green lawn
Near a pond
The culture grows well near water, so it can be used to decorate ponds. In this case, you need to protect the flower from stagnant moisture. Irises are a good addition. You can also plant willow and juniper.
Along a fence or wall
The flower grows well near fences. It is protected from direct rays of the sun and gusts of wind. Coniferous plants and hostas are suitable additions. Different types of ferns will look good.
Flower garden
As part of a flower garden, the crop can be combined with bulbous crops - tulips or crocuses. It can also be combined with annuals - dahlias, marigolds.
Hydrangea looks simply great in the landscape. This plant fits perfectly into a variety of compositions and combines well with other plants, helping to create an interesting site design.
vote
Article Rating
Planting and care
Planting and caring for the plant is carried out according to special rules. It is best to plant hydrangea in late spring or early autumn:
- The planting site should be selected in advance. Acidic, sufficiently moist soil is perfect for growing flowers. You can plant flowers both in a well-lit place and in the shade.
- To plant a hydrangea bush in open ground, make a depression of about 60 cm, with a diameter of about 0.5 m.
- A gap of at least 1.5 m should be maintained between the bushes. When growing, thanks to proper care, the hydrangea will occupy a larger area than when planted.
- It is recommended to fill the recesses with a mixture that will include peat, sand, soil, humus (1:1:2:2), as well as fertilizers.
The following mixture can be used as fertilizer:
- 20 grams of potassium sulphide;
- 20 g urea;
- 60 grams of granulated superphosphate;
- 10 kg of humus.
Advice! It is forbidden to add lime to the mixture, since this substance has a detrimental effect on the growth and development of hydrangea.
When planting, you should carefully ensure that the root collar of the plant is located at ground level. After planting in open ground, the hydrangea flower should be watered well.
Watering
To water hydrangeas, soft water is used, the best option is rainwater, since such a liquid does not contain lime. Water taken from the tap must be settled before use, and this procedure does not always help combat leaf chlorosis. Each plant should receive at least 2 buckets of water per week. Watering is best done in the morning or evening, when the sun is no longer so bright.
The plant is a moisture-loving plant, so after watering the soil should be mulched so that the soil retains moisture for as long as possible. Pine needles, peat or sawdust are suitable for mulching.
What and how to feed hydrangea?
If a special soil mixture was used during planting, the hydrangea will not need feeding for several years. If the soil is not fertile enough, the inflorescences of the shrub will be small in size. Industrially produced products can be used as fertilizer, these include:
- Aqua;
- Agricola;
- Crystal.
Fertilizer for feeding can also be made independently.
In early spring, it is recommended to carry out the first fertilizing. To prepare the nutrient solution you will need:
- 10 g urea;
- 15 g superphosphate;
- 15 g of potassium sulfate, all these substances must be dissolved in 15 liters of water.
The second feeding is carried out after the first buds appear. For this, a solution is used:
- 20 g superphosphates;
- 20 g of potassium sulphide;
- dissolve in 15 liters of water.
In the summer, it is recommended to water the hydrangea with mullein infusion; it is best to carry out this procedure once a month.
Hydrangea should be fertilized 2 times a month. You can use fertilizers for heathers, azaleas, and rhododendrons. The use of ash is prohibited. Nitrogen fertilizers should be used with extreme caution.
Attention! Poor winter hardiness of flowers can be caused by fertilizing with nitrogen substances. Also, overfeeding with nitrogen-containing fertilizers can lead to diseases in plants, since the turgor of the stems is weakened.
Watch the video! How to achieve gorgeous hydrangea blooms
Hydrangea care
Macrophila is a rather unpretentious shrub. However, a number of measures are required for its normal development and decent appearance. Such procedures include:
- watering;
- feeding;
- pruning
For a shrub that loves moisture, its excess is nevertheless harmful. Therefore, it is normal to use up to one and a half buckets of water at the root of each plant once a week when watering. During drought, watering is increased . The water should be soft, it is good to use settled or rainwater. You should remember about timely loosening around the plant for aeration (depth - 7-10 cm).
Before budding, hydrangea is fed with potassium sulfate (30 g per bucket of water) and superphosphate (50 g) or complex mineral fertilizer (for example, “Lux”). Before wintering, it is also fertilized with a complex of minerals without nitrogen.
Experienced gardeners have learned to adjust the color of inflorescences. It directly depends on the acidity of the soil. You can increase the acidity of the soil and achieve blue and blue shades of flowers with alum (the composition includes heptahydrate of aluminum and potassium salts) at the rate of 3-5 pieces per liter of water. Light alkalization of the soil with a solution of potassium permanganate, on the contrary, will give a pink palette of hydrangeas.
To speed up the flowering of the bush by 2-4 weeks, use an aqueous solution of gibberellin. Spraying is carried out 2 times, the interval is a week, the solution concentration is 50 mg/l.
Hydrangeas need pruning as a cosmetic and health procedure. To form a crown, the shoots are shortened to a strong bud, and the roots are mulched. In September, weak branches are pruned so that the remaining shoots accumulate strength by spring. Overwintered frozen branches are pruned in early spring to healthy wood. In July, strong branches are shortened to lower growths.
In subsequent years, care must be taken to promptly rid the bush of dried and old branches. For varieties that bloom on last year's shoots, it is recommended to remove already faded shoots with 4 leaves in mid-summer - by August flower buds will still form on them. With proper pruning in the 5th year, the perennial will produce up to 30 inflorescences.
Preparing for winter
With the end of leaf fall, macrophyla are prepared for wintering. Small bushes are tied into a cone, tall shoots are divided into 2 parts and bent to the ground, securing them with wire. Peat, fine bark, and spruce branches are added to the base of the bushes and under the branches.
To insulate the shoots, you can use agrofibre, straw mats or other non-woven material. The structure is covered with film and tied. The plant rests until spring; when the frosts end, it can be “unpacked.”
Diseases and pests
Macrophila is resistant to fungal diseases.
Its main enemies are white rot, which affects the roots, gray rot and powdery mildew. The presence of white rot is detected by the uncharacteristic brown color of the stems and leaves of the plant. Gray fluffy coating and watery stems indicate gray rot. Powdery mildew appears as oily dark spots on the leaves. Rot is combated with fungicidal preparations (Fitosporin, Fundazol). Hydrangea is saved from powdery mildew by treating it with a soap-copper solution (15 g of copper sulfate, 150 g of soap per bucket of water).
Of the pests, the greatest damage is caused by snails, which with great pleasure feed young shoots, leaves and buds. Voracious snails should be “treated” with insecticides (for example, the drug “Thunderstorm”), poured into containers and placed near the bushes. A regular soap solution works well with spider mites (the leaves turn yellow and a peculiar marble-colored pattern appears on them).
With proper care of hydrangea and proper care for it, the plant will definitely thank the gardener with the captivating splendor and rich colors of its flowers.
Reproduction
Summer residents and amateur gardeners most often use bush division and cuttings to propagate hydrangeas. For a large plant, dig around 15 cm from the stem. Digging is best done on moist soil with a pitchfork. After which the bush is removed and cut with a knife or shovel.
It is best to harvest cuttings in April-June. To do this, annual shoots that are 10-12 cm long are cut at right angles. The leaves are removed from the bottom of the cutting and treated with growth stimulants, after which the cutting is planted in a special, fertile soil mixture in a growing bed in a greenhouse. In the first winter, it is recommended to protect the plant from frost and cut off the flowers.
Dividing the bush
It is recommended to propagate hydrangea by dividing the bush in the spring or autumn months. To do this, the plant is dug up and divided into several parts so that each separated bush has a renewal bud, after which it is planted in a previously prepared place.
By layering
To propagate by layering, a shoot that is more than 1 year old is bent to the ground and dug in, leaving only the upper part up to 20 cm on the surface of the earth. In the spring or autumn of next year, the rooted shoot is separated from the mother bush and replanted.
Why hydrangea is popular for garden landscaping
Garden hydrangea is a versatile plant. It has many advantages that make it indispensable in garden and park design. She is valued for:
- Long and colorful flowering;
- Variety of sizes and shapes;
- Unpretentiousness;
- Frost resistance;
- Durability.
This shrub has no equal in the brightness and variety of flowering shades. Numerous plant varieties have a wide variety of inflorescence shades.
And some of them change the color of the flowers over time, giving the bush a very interesting and sophisticated look.
Varieties of garden hydrangeas vary in size. There are large plants up to 3 m high that look great in single plantings. But there are also smaller and dwarf varieties used for planting in groups and even for hedges.
Most varieties are quite unpretentious and do not require careful care. And the developed frost-resistant varieties make it possible to plant this shrub even in areas with severe frosty winters.
More information about the types of bush hydrangea can be found here.
The lifespan of the plant is considerable - several decades. And with proper care, it blooms profusely at any age.
How to prune hydrangea correctly?
The formation of a hydrangea bush should begin 2-3 years after planting, since without pruning the plant looks ugly. It is recommended to prune in early autumn or in the spring months before sap flow begins. Each variety of shrub has its own pruning features.
In tree hydrangeas, weak and twisted branches, as well as three-year-old shoots, are removed to the base. Young growths are shortened, leaving only a few buds.
Recommendation! The weaker the shoot, the shorter it should be cut.
In paniculate hydrangea, shoots growing inside the crown, as well as young growths, are shortened by 1-3 buds. Some owners of summer cottages and gardeners form a standard tree based on the strongest shoot. To do this, it is driven out to 70-100 cm and all shoots located on the side are cut off, after which a spherical crown is formed.
Large -leaved hydrangea requires pruning of shoots in early autumn, as they interfere with covering the plant for the winter. In the spring months, frozen and broken shoots are removed for sanitary purposes.
How to combine hydrangeas with other plants
In addition to single and group plantings of hydrangea bushes, they can be successfully combined with other plants in the garden landscape. Such combinations can be very diverse. The main options for combined plantings are combinations with the following crops:
- Herbaceous flowering and non-flowering species;
- Flowering shrubs;
- Large non-flowering varieties.
In landscape design, hydrangea can be successfully combined with small plants. Sometimes it is even planted in the center of the flower bed. But you can create more complex combinations. Low-growing species are used for the following effects:
- Complementing the color scheme of hydrangea inflorescences;
- Framing the composition;
- Early season decoration.
Moisture-loving and shade-tolerant herbaceous perennials are suitable for combination with hydrangeas. Non-flowering species that look great in a composition with hydrangeas:
The most commonly planted flowering species are:
For compositions with other flowering shrubs use:
Often similar compositions are created with lilac or mock orange, in which different species do not bloom at the same time. This creates the effect of continuous flowering of the composition from late spring until the first frost.
Sometimes the bush is planted near large non-flowering plants. Usually these are conifers, the dark severity of which is appropriate to complement with a bright and colorful contrasting element so that they do not look too gloomy and dry. The hydrangea bush in this combination is a color accent that enlivens the composition and gives it sophistication and extraordinary beauty.
In the article we looked at the best hydrangeas in the landscape design of a summer cottage, and also saw their photos.
Amateur and professional gardeners recognize how good hydrangea looks in garden landscape design, and the photos presented on specialized sites only confirm this. Despite its eastern origin, the birthplace of this plant is China and Japan - gardeners from Russia loved hydrangea so much that it became one of the most typical elements of a traditional Russian garden, along with shady alleys.
Currently, there are more and more people wanting to reproduce a piece of Russian antiquity on their site. And if the territory of the gardens most often does not allow for an alley, then there is always a place for hydrangeas.

Hydrangea is native to China and Japan.
Abroad, hydrangea enjoys no less love. Different types of this flower can often be seen among plants at flower shows. Less demanding varieties are actively used in park and landscape gardening, as this plant quickly recovers even after cold winters and begins flowering early.
Garden hydrangea, or hydrangea (Hydrangeahortensishort), belongs to the Saxifraga family. Active use in garden decoration began after the development of hybrid plants with large flowers.

Hydrangea belongs to the Saxifraga family
The shrub blooms from early spring and throughout the summer. It has large and dense spherical inflorescences and juicy dark green leaves located oppositely. The colors are varied: white, purple, red, hot pink. Some varieties have learned to change color over time from darker to brighter shades.

The shrub blooms from early spring and throughout the summer
If space allows, interesting decorative effects can be created using hydrangeas alone. An important point is the willingness to constantly care for the plants, since they are quite demanding on the quality of the soil.

Hydrangeas are quite demanding on soil quality.
Diseases and pests
The most common disease among all types of hydrangeas is chlorosis. This disease develops due to excess lime or humus in the soil. To eliminate chlorosis, you need to water the bushes with a solution of potassium nitrate and copper sulfate; this procedure must be carried out one at a time, observing an interval of 3 days between watering. To treat hydrangeas, the drug Brexil and Agricol are used.
Excessive air humidity is the main cause of downy mildew in plants. As a treatment, you can treat the leaves with a solution of copper sulfate with the addition of soap.
Aphids can be driven away from the foliage of shrubs using garlic tincture. To prepare garlic infusion, use 200 g of chopped garlic added to 1 bucket of water. The solution should be infused for about 2 days, after which 40 g of laundry soap should be added to it. It is recommended to spray the hydrangea with the resulting mixture every 5 to 7 days until the aphids are completely destroyed. You can also use the drugs Fitoverm, Actellik.
Hydrangea, in general, has a fairly stable immunity against viruses and diseases.
Wintering hydrangea
Preparing hydrangea for winter and shelter
When the plant has flowered, it is prepared for wintering. Potted varieties are brought indoors. Dried flowers are removed from the branches of bushes left to spend the winter at their summer cottage. Otherwise, under the weight of wet snow, they may break off branches.
Almost all types of hydrangea are mulched for the winter. Especially young and slightly frost-resistant plant species. The tree trunk circle is loosened and generously covered with pine sawdust, wood chips or peat. This mulch will retain heat and prevent the roots from freezing. Panicle, ground cover and tree hydrangeas can actually do without shelter in winter - the branches become lignified by winter and tolerate the cold calmly.
Petiolate and large-leaved (also known as garden) hydrangeas winter well in southern latitudes. They are unlikely to survive the cold winter beyond the Urals and in Siberia without shelter. After the first frost, the branches are carefully tilted to the ground and laid on a layer of spruce branches or wooden flooring, securing them with hooks. The top of the bush can be covered with sawdust, pine needles, withered leaves, or special materials such as lutrasil or spunbond can be used.
If the winter is expected to be frosty, additional insulation is created for the bush - a metal frame of arcs is installed on top of the shelter at a short distance, filling the resulting space with dry leaves. This method of protection is also used for large mature shrubs.
It is recommended to remove the shelter on a rainy day, so as not to “scare” the bush with sunlight after wintering. This procedure is carried out closer to mid-spring or later (depending on the climate zone), only after daily positive temperatures have been established.
Hydrangea in winter
Preparing hydrangea for winter
How your garden will look in winter depends largely on the severity of the climate. If your hydrangeas winter in southern latitudes and the winter is snowy, then even heat-loving varieties can get by with light shelter, while frost-resistant varieties can do without it at all.
In a cold winter, it is better to take care of enhanced protection as early as possible, with the onset of the first autumn frosts.
And in order not to forget how cozy your garden was in the summer, dry the cut inflorescences and create an original autumn-winter bouquet suitable for your interior.
How to care
The characteristics of the species of the described plant are general - they consist in the following fundamental features:
- love of moisture;
- requirement for heat;
- unique attitude to soil composition;
- relatively low frost resistance.
It is on the basis of this list that the rules for watering and fertilizing, as well as maintaining the condition of the top layer of soil and the shape of the bush, should be taken into account. Care in the form of preparation for wintering is also important.
Video: Care, planting, pruning hydrangea

Watering
Irrigation should be regular, monthly with normal precipitation . At first, 30 liters of water are added every seven days. In order not to make mistakes with watering, you need to monitor the soil moisture - it should not dry out on top. Mulching promotes stability in the amount of soil moisture. It is also useful to spray the bushes.
The introduction of water to early varieties is reduced from August and then stops, and to late varieties - from September. In the fall, the buds ripen, so a little spraying is necessary .

Top dressing
The nutrient mixture described above and introduced into the planting soil is again given to the shrubs after two years. Until then, it is better not to disturb the plants.
The remaining rules for fertilizing the soil are as follows:
- in early spring, complex mixtures with phosphorus, potassium and nitrogen are introduced;
- when buds begin to appear , superphosphate compounds and those containing potassium sulfate are added;
- It is useful to introduce manure during active flowering (twice per period is enough).
Important! Do not overdo it with nitrogen fertilizers, which give the inflorescences a green tint. Such mixtures harm the normal wintering of hydrangeas.
Mulching and loosening the soil
Mulch is useful and important. It helps maintain humidity . The natural conditions of any soil are the presence of last year's leaves or other organic material. Therefore, in forests and open grassy meadows the soil is always loose, fertile, and saturated with oxygen. Mulching imitates such conditions.

Hydrangea prefers peat or compost, but other compositions are also suitable (sawdust is used, among other things, for decorative design of space in site design). It is useful to add mulch at the beginning of summer, and then before winter - which will help to survive frosts.
Important! Mulch is very important: in the first years it is necessary to cover the soil with it both in spring and autumn so that the roots of the hydrangea are not exposed.
Plant pruning
The formation of a decorative appearance is carried out as follows: after a sanitary haircut, all shoots are collected and shortened by half the length.
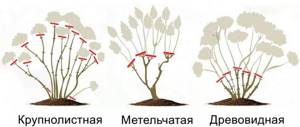
Correct pruning can be done by following the following standards:
- time - early spring (withered parts lie on the bud of the bush and protect it during winter), although hydrangea is often pruned in the fall;
- degree of truncation - to the first or second pair of buds;
- the depth of pruning gives a larger size of inflorescences (and the more shoots there are, the smaller the size of the flower part);
- Every year not only such truncation is carried out, but also preventive (damaged parts are removed);
- removal of all old branches - rejuvenation - is carried out every 3 years;
- cutting at the root - renewing the bush (once every five years it is cut down to 15 cm above the ground).
Important! You cannot prune annual hydrangeas.
Preparing for winter
You can cover the hydrangea before winter with the foliage of healthy trees, straw or special coverings made of comfortable materials. First of all, it is worth preserving and protecting young plants and those varieties that are not frost-resistant.
If the latter are already mature bushes, then it is recommended to carefully cover them from above using some kind of structure (a frame to which non-woven material such as spunbond will be attached). And under it, it is useful to fill the empty spaces with leaves or straw.

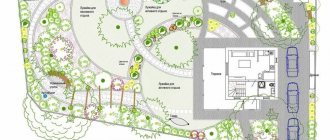
Schemes of flower beds with hydrangeas
Having figured out which plants hydrangea is combined with, you can begin to formulate a planting plan. Successful options for placing a bush in the garden in the form of a flower bed:
- A one-sided flower bed, framed by herbaceous perennials.
- Double-sided or tiered composition, including bergenia, hosts and astilbe.
- An extensive flower bed with barberry, thuja, and juniper.
Important! The location of the hydrangea in the flowerbed depends on the height and width of the “participants”.