Main types of pruning garden trees
Formative pruning of fruit trees is used to give them a certain shape. This is also one of the ways to force a tree to grow in the desired direction. The result of this work will be large leaves, strong shoots, abundant flowering and fruiting. By the way, to achieve this result during the procedure, you need to leave the optimal number of buds on the branches.
Sanitary pruning of fruit trees is necessary if some of their branches are broken, intertwined or dried out. As a rule, it is carried out before the onset of frost, while the temperature is still positive - in the fall or during a warm winter. During this event, only unsuitable branches are removed, but the main crown is not touched.
Rejuvenating pruning of fruit trees is carried out in an old orchard when it is necessary to extend its fruiting for at least a few years before the young seedlings get stronger and give you a harvest. It is unlikely, of course, that old apple, pear and other trees will last long, but you can still win 3-5 years. How to properly trim trees in this case? First you need to make sure that they are viable and can withstand such a procedure. All work must be carried out at a time when sap flow is slowed down or stopped, i.e. early spring or late autumn, after leaf fall. Anti-aging pruning of trees can be gradual, half or radical. But it is still better to carry it out gradually, over 2-3 seasons, observing the reaction of the trees.
How to extend the life of an old tree - all about rejuvenating pruning and regrafting Do you know how to rejuvenate your garden? It is quite possible to extend active fruiting for several years with the help of a couple of techniques.
In addition, you can also prune fruit trees, which slows down their growth. This can be done throughout the growing season.
By the way, pruning is considered the most difficult procedure in caring for plants, and this applies to different types of plants.
Proper pruning of ornamental shrubs - everything you wanted to know 9 techniques for pruning shrubs with a description of the process and diagrams.
When is the best time to prune fruit bushes?
Proper pruning shapes the bush in such a way that each branch has enough light and air for normal fruiting. Autumn pruning frees the bush from fruit-bearing shoots and relieves the plant of the need to feed them during the dormant period. However, if for some reason you were unable to prune in October or November, reschedule it for late winter or early spring - from late January to early April, when the snow has melted and the air temperature has risen to at least -8 ºC, will remain at this level for several days.
Avoid pruning in cooler temperatures or on a day when it is snowing or raining, and try to complete the process by the time the bushes begin to bud.
Proper spring pruning of fruit trees in the garden
Sanitary pruning is carried out when the need arises, regardless of the time of year.
- Cranberries: growing in the garden, types and varieties
Rules and technology for pruning trees and shrubs
Before you start trimming trees, you need to not only acquire the necessary equipment, but also learn some of the subtleties of pruning plants. So, in order not to harm the bush (especially young ones), when removing unnecessary branches, follow the following rules and follow the pruning technology:
- Do not cut many large branches at once - this will weaken the bush and may contribute to its death. It is better to remove a few branches every year than to remove them en masse every few years.
- It will be better for the bush if you pinch a small shoot than if it grows later and you cut it off.
Periodically pinch out unwanted small shoots
- A healthy bush has 10-15 branches of different ages.
- It is better to complete the formation of the plant crown by 4-5 years.
- Old branches (6-7 years) must be completely removed.
- The first thing that should be removed is painful and damaged branches.
- It is forbidden to leave split sections.
- If you need to saw off a branch completely, you should not leave a stump. Make a ring cut.

Make the cut correctly: without stumps and splits
- When a branch of significant thickness needs to be cut, start sawing from the bottom and finish at the top. Otherwise, when falling, it can tear off the bark from the trunk, thereby causing unnecessary damage to the plant.

Cleaning and processing the saw cut is the most important activity
- If you have cut a very large branch (more than 2 cm in diameter), clean the cut with a knife and cover it with garden resin.
- Never use blunt instruments; they cause wounds to the plant that will have to be healed later. It is best to purchase high-quality equipment for gardening.
- If you are cutting standard grafted shrubs, remove the growth around the root collar. This needs to be done in early October.

Cut off the side shoots at the root and then cover them with dry soil.
- Monitor the condition of pruners, scissors and all garden items: they must be clean, because dirt can contain harmful substances. In addition, a clean tool is easy and pleasant to work with.
- If the bush is too tall, be sure to use a stepladder. Do not try to climb tree branches; this is dangerous for you and may harm the plant.

A stepladder will greatly facilitate gardening work.
- All deleted branches must be recycled. It would be best to burn them. This way you will prevent the spread of parasites and diseases, and the resulting ash can be used as fertilizer.

Dispose of cut branches
Depending on the tasks, there are different types of pruning:
In order to form the crown of a tree
It can be done with the aim of creating a very unique crown, unlike the natural one. This is a type of garden art called topiary. When shaping the crown of a tree, it is necessary to begin work as early as possible and carry it out throughout the life of the tree. Accordingly, a distinction is made between forming and supporting trims.
In order to improve lighting conditions, breathing and mechanical stress of tree branches, stimulate growth
Such pruning should be carried out annually or once every few years, as the tree crown grows and becomes excessively thick. With it, “extra” branches are cut off, leaving space for the growth of other branches and space for normal breathing and lighting of the leaves. In the case of fruit trees, this type of pruning is very important to ensure optimal and uniform fruit load on the branches. When pruning, it is always necessary to maintain the correct geometry of the crown being formed and leave the required number of buds between the trimmed branches, so that if the existing branches break, there will be something for new ones to grow from in the same place.

To improve the health of the plant
It consists of removing diseased, dried out, frozen branches that disrupt the uniform load on the trunk and root system of branches.
To rejuvenate the plant
It consists of removing (sometimes completely) old branches, which allows dormant buds to grow, which form fresh, young shoots. As a result, after a few years, a new young crown is formed on the old “stump”, which has both higher decorative value and higher strength.
For the correct balance between growth and fruiting processes
For fruit trees, pruning can be used to regulate the ratio of growth and fruiting processes
. To do this, there is a whole range of techniques that allow, depending on the age, type, condition and wishes of the owner, to change the “behavior” of the tree in the desired direction.

The basis of pruning as an agricultural technique is the ability of plants, unlike most animals, to restore lost parts. More precisely, not to restore, but to grow new ones in place of the lost ones. However, in order to ensure that pruning does not lead to weakening and death of the tree, it is necessary to follow some rules and take into account the individual characteristics of both the specific tree and the species. Here are the basic rules to follow when pruning:
- Since, when restoring pruned parts of a plant, restoration occurs due to the work of specialized tissues capable of division (in botany, such tissues are called meristems), pruning should be done in the period immediately preceding or coinciding (depending on the type of plant) with the time of activity of these tissues. The main period during which pruning of living tissues is carried out is from the end of winter until the buds begin to awaken. If dried branches or small areas (primarily small in diameter) are removed, then this can be done in the summer-autumn period. Thus, we get two main periods for pruning: main and maintenance - from February to the end of April and from May to the end of October. During the period of preparation for wintering, it is strictly not recommended to prune plants.
- Due to the peculiarities of hormonal regulation (yes, plants also have their own hormones, auxins and statins), the apical buds produce the most powerful growth. The growth of shoots located in the lower parts of the tree crown is inhibited. This must be taken into account when pruning. Also, depending on the location, not only the intensity of growth is regulated, but also the direction of growth of shoots from the bud, depending on its location along the height of the trunk. Higher buds produce long, fast-growing shoots with sparse branching points, tending upward. The buds located directly above them also grow upward. But the buds of the lower tiers grow slowly and parallel to the ground, forming, however, frequent branching zones and ensuring the density of the crown.

We recommend that you either carefully read specialized literature on tree pruning, already in relation to the species that grow on your site. It’s even better to seek advice and help from our professionals. Remember! Proper pruning can significantly improve the appearance, fruiting and condition of your garden, but poor pruning or lack thereof, on the contrary, can cause premature death of trees.

Sanitary pruning of trees and shrubs
Sanitary pruning of trees and shrubs makes it possible to restore the decorative qualities of the crown of plants, as well as improve their fruiting quality (Figure 6). In addition, with regular practice of this type of pruning, the risk of wood and bark disease is reduced.
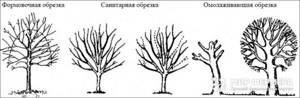
Figure 6. Features of sanitary pruning of trees and shrubs
Indications for sanitary pruning are the presence of dry (damaged) shoots, excessive thickening of the crown, broken (or completely broken) branches hanging in the crown, overgrown and intertwined shoots. In other words, the main goal of sanitary pruning is to remove branches (shoots) that pose a danger to both humans and the plant itself.
What's special
In a home garden, the need for sanitary pruning arises when plants are infected with diseases or damaged by pests. For example, fruit trees are often affected by fungi during the flowering period, when the use of chemicals is unacceptable. In this case, sanitary pruning is carried out, removing the affected and diseased branches and thus saving the entire plant.
However, this does not mean that healthy plants do not need this type of pruning. Very often, the skeletal branches of fruit trees break under the weight of the fruit or due to strong winds. Therefore, there is a need to carry out sanitary pruning, cutting and sawing out broken shoots.
When needed
As a rule, planned sanitary pruning of fruit trees and shrubs is carried out in the spring, in March - April, when all branches are clearly visible. In addition to the cleansing effect, spring sanitary pruning stimulates the growth of shoots. If it is carried out during the period of mass flowering or after it, then this leads to the rapid growth of flower buds. However, you should know that summer sanitary pruning interferes with the growing season, so it is carried out selectively, only to remove unnecessary branches.
Lilacs and deutia are pruned in spring and summer, but hydrangea, tamarisk and spirea are pruned only in spring. Trees and bushes that bloom in the spring should be pruned after flowering.
Rules
Gardeners with many years of experience are advised to follow the following rules for sanitary pruning (Figure 7):
- It is carried out only on rooted plants.
- Sick and dry branches are cut off from the healthy part. The branches are removed into a ring, the shoots are removed above the outer bud, without touching it.
- The cut area should be smooth, without burrs or torn edges. In this case, vertical branches must be cut obliquely to prevent water stagnation.
- Large branches are cut down in three steps. The first cut is made 30 cm from the trunk, at the bottom of the branch, a quarter of the thickness deep. The second time the branch is sawn from above, 5 cm further from the first cut. During the third step, the remaining stump is cut down.

It is customary to lubricate the cutting areas with a disinfectant and drying agent, for example, garden pitch. The exception is coniferous trees, whose wounds are not covered.
Principles and timing of pruning vines and hedges
The general principles and timing of pruning vines are approximately the same as for shrub plants. Lianas that bloom on last year's growth are pruned immediately after flowering, and weak and thickening shoots and, first of all, faded branches are removed.
All species that bloom on the shoots of the current year, for example, honeysuckle and clematis, are pruned in early spring. This allows the plant to produce a large number of young flowering shoots. Deciduous vines, grown for their beautiful leaves and shoots, and especially leaves with rich autumn colors, for example, maiden grapes, should be pruned only in late autumn, in October-November.
If the vines are evergreen, then they should be pruned in early spring. Lianas used for vertical gardening of gazebos, sheds, and walls require pruning in the spring, in late March - early April.
Hedges serve both to delimit areas and to decorate them. The most suitable for constructing a high wall along a fence are hawthorn, sea buckthorn, turf, viburnum, tall rose hips, etc. Spiraea (oak-leaved, medium, Vangutta), currant, cotoneaster, privet, honeysuckle, mock orange, and barberry are especially suitable for medium-height hedges.
For low borders, 1-1.2 m high, it is best to use Boumalda spirea, Thunberg barberry, holly mahonia, Japanese quince, privet, purple willow, common holly, etc.
Recently, gardeners most often plant and form hedges of a strict geometric shape, mostly rectangular or slightly tapering at the top. With this formation, the hedge becomes bare more slowly, as it receives maximum light, air and water in the form of precipitation. Such a fence reliably closes the area from prying eyes, protects it from the wind, and also gives the area the most well-groomed appearance.
In the first years of crown formation, it is important to achieve good branching over the entire height of the plant being formed. It is best to prune shrubs in late autumn (October-November) and early spring (March-April). When creating hedges from deciduous shrubs, they are cut very low, leaving up to 10 cm of the current year's growth. The next year, the resulting shoots are shortened again and this is done to the designed size of the fence.
Pruning lavender, clematis, roses, peonies, jasmine
Lavender pruning
Lavender is pruned in the fall, when its fragrant lavender blossoms have been collected, to maintain even shapes and harmonious proportions. Prune flowers immediately after bloom without overexposing the foliage to maintain compact clumps. Cut the flowers at the end of the stems 4 or 5 cm just below the flower braid.

Pruning lavender in autumn
The lavender bunches can be seen in several types of sizes, depending on the age of the plant. These are mainly molding and maintenance sizes, not flowering at all.
On older bunches, after cutting off faded flowers, it is necessary to cut off all branches by 10 cm, giving the plant an even silhouette.
Be careful never to prune old stems without leaves. Roots that are too old and produce only fragile and sparse stems will have to be torn off and replaced.
Pruning roses in autumn
To get abundant flowering, we prune roses in the fall. Each variety has its own pruning rules.

Autumn pruning. The illustration for the article is used under the standard license sadvokrug.ru
In autumn, after flowering, rose bushes should be trimmed, shortening them to 25 cm, and young shoots should be cut off completely. Hybrid tea, polyantha and floribunda varieties are pruned short, leaving four buds on each stem. Shoots of roses of remontant varieties and grandiflora are cut in half, leaving five developed buds. For climbing roses with small flowers, cut off the ends of the shoots, and with large ones, shorten the shoots by a third. For shrub roses, shoots are cut to three-quarters of their length.
When to prune clematis

Climbing clematis on an arched support
There are more than 150 types of clematis on the market and countless varieties
Therefore, before pruning, it will be important to know the characteristics of the variety in order to do the correct pruning and not jeopardize future flowering. Sanitary pruning of clematis is carried out throughout the entire growing season.
But it is in the fall that the main pruning is done.
Early flowering clematis varieties are pruned immediately after flowering. Remove dead wood, weak and damaged branches (for example, these are varieties: Clematis alpina, macropetala or montana).
The purpose of pruning summer flowering clematis is threefold: to limit the clutter of these climbers; clean them by removing dry stems and, above all, stimulate their future flowering.
Prune in early March (depending on region) large or small flowering clematis, herbaceous varieties and most late flowering very large hybrids such as: Clematis x 'Jackmanii', 'Azure Pearl', 'City of Lyon'.
For herbaceous clematis (Integrifolia or heracleifolia), which bloom in the second part of summer, cut the bunch 50 cm from the ground in the fall. Like a perennial plant, the latter will eventually die out in winter.
Peony pruning

Before pruning in dry weather, water the peony well and cut off the foliage at ground level, add compost and sprinkle a little soil at the base of the plant. This procedure will effectively affect the plant in the spring.
Jasmine pruning

Spring jasmine after autumn pruning
Garden jasmine is pruned after flowering. Remove old, dried and crooked branches. Anti-aging pruning is performed. This procedure is done annually, otherwise you may not see it bloom.
How to prune fruit trees correctly?
Formative pruning of fruit trees - apples, pears, cherries, plums - is carried out by amateur gardeners in early spring. In industrial gardens, the amount of work is enormous, so pruning begins in winter, when the snow begins to melt.
Why is pruning done at this time? When the branches of an apple and pear tree are cut, deep cuts are made at the pruning sites, through which the cold penetrates in winter and the living tissues surrounding the cuts are damaged.
At the end of summer - beginning of autumn, dried, barren branches, as well as small and weak branches up to 3 cm thick, are pruned. In the spring, it is difficult to predict which branches will not bear fruit, but at the end of the season this is already visible. In order not to forget these branches when pruning in spring, gardeners do not shorten them to the very base - they cut off only the top and leave about 15 cm of the base. Thus, in winter the cut site is quite far from the base. In spring, such a branch can be cut to the end.
Cutting should only be done in dry weather, after which primer or a special compound must be applied to the cuts.
How to prune berry bushes and when is the best time to do it?
Shrubs, unlike trees, are for the most part less durable, and their life is often only a few dozen years. With good care, black elderberry lives up to 50 years, while red elderberry, snowberry, meadowsweet, and mock orange live less than 15 - 25 years. How to determine when is the best time to prune bushes? Usually the gardener himself determines whether he likes the plant or not, hence the need for pruning. It is not difficult for a person who even knows little about the plant to identify defects that need to be eliminated: damaged or broken branches, dry and rubbing shoots, rotting branches, protruding branches, especially on trimmed hedges.
Before pruning berry bushes, it is very important to determine the reasons for the unsatisfactory condition of the plants. It is known that plants are most vulnerable when they are not properly cared for, that is, they are insufficiently provided with nutrition, moisture, and lack air and light.
Weakened plants are more likely to be attacked by pests than healthy ones. Therefore, before pruning ornamental or berry bushes, you need to identify disease-damaged or dead branches and remove them first - this will allow the bushes to grow, bloom and bear fruit normally.
The degree of pruning can be very different: from removing faded flowers from lilacs or roses to trimming large skeletal branches of fruit crops, as well as rejuvenating pruning of old bushes. It should be remembered that pruning for plants is the same surgical operation, and before proceeding with it, the gardener must know exactly whether it is necessary and what he wants to achieve with this operation
It is very important for the further normal development of shrubs to carry out their formation and pruning at an early age to give the plant an optimal crown shape in the future.
Different types of plants react differently to pruning, since the shape of the crown of the bush is of great importance, which can be either pyramidal, or spherical, or creeping, etc. For example, Hungarian lilac, cotoneaster, honeysuckle have new shoots after low pruning arise along the entire length of the branches, and in rhododendrons and yellow roses, low pruning causes the death of entire branches and even the entire bush, since these plants do not have the property of budding on the lower old branches.
Quite often in central Russia, and especially in the Moscow region, ornamental shrubs suffer from winter frosts or late spring or early autumn frosts. Winter damage to plants is very diverse: death as a result of ice formation in the tissues of shrubs, the appearance of frost holes and cracks on shoots, the death of flower buds, and freezing of individual branches, roots or parts of the crown.
Measures to combat plant freezing include, first of all, the correct choice of site for planting shrubs, careful care and proper preparation of plants for winter. Various pests and diseases worsen the condition of plants, which significantly weaken the winter resistance of plants. Therefore, regular control of pests and diseases is one of the conditions for good overwintering of plants.
Features of molding pruning of fruit bushes (with video)
Aronia – Aronia
Immediately after planting, the plant is pruned, leaving stumps 15-20 cm above the soil. In the future, the shaping will be to ensure that the bush consists of shoots of different ages. In mature bushes, about 15-20 such branches are left.
Chokeberry is a light-loving plant, so to ensure uniform illumination of the bush, young shoots should be periodically removed. When the bushes reach 14-15 years of age, they should be rejuvenated.
This shrub is especially beautiful when pruned using standard molding, when it turns into a small beautiful tree. At a young age, it is recommended to tie the standard plant to a stake.
Hawthorn – Crataegus
To create a hedge in the first year after planting, it is necessary to trim the bush heavily, leaving stumps no higher than 10-15 cm from the soil level. This pruning is done in April; it promotes the formation of powerful basal shoots.
In the second year, at the same time, to create a strong skeleton, deep pruning of the fruit bush is again carried out, which ensures the appearance of new shoots and increased growth of last year's shoots. If the hedge remains insufficiently thick, such severe pruning is carried out in the third year.
Gooseberry – Grossularia
The main goal of forming a gooseberry is to grow a bush with well-developed, healthy shoots of different ages. An adult gooseberry bush should have 20-25 well-developed skeletal branches of different ages. Gooseberries begin to form from the moment the plant is planted in a permanent place. In early spring, planted shrubs are pruned, leaving 2-4 well-developed buds above the soil surface, and all weak branches are removed.
Next year, the strongest and most vital of these shoots are left: 3-5 zero shoots. Unripened or damaged ends are cut back to healthy wood. All newly emerging shoots, excess, weak and lying on the ground shoots are removed.
Pruning is best done in spring or autumn, after leaf fall. As gooseberries age, it is necessary to carry out anti-aging pruning. It is advisable to cut out old shoots once every 2-3 years.
Hazel – Corylus
The above-ground part of the hazel is cut 20-25 cm from the soil level. Formation occurs due to shoots that arise on skeletal roots in the form of root suckers. In the future, pruning is reduced to removing root suckers, as well as shoots appearing on the stems below the root collar. Overgrowth must be removed annually. When hazel begins to bear fruit, it usually retains from 6 to 12 main strong trunks.
On properly formed bushes, further pruning is reduced to the annual removal of all shoots, dry and mechanically damaged trunks. Crossing or closely growing branches inside the crown are also removed. During gradual rejuvenation, part of the old fruit-bearing shoots is removed.
At the same time, 2-3 old, unproductive shoots are removed annually, and new ones are reproduced in their place. Thus, complete rejuvenation of plants occurs within several years. Pruning and rejuvenation of hazel in the conditions of central Russia can be carried out in late autumn or early spring (March).
Blueberry – Vaccinium
In young plants, small growths formed at the base of the bush and shoots lying on the ground are cut off. Starting from the 3-4th year, lightening pruning is carried out, and dry, diseased and damaged branches are cut out. Then old shoots that do not produce strong growth and thin shoots that greatly thicken the center of the crown of the bush are removed.
Form a bush with 6-8 main branches. Subsequently, the oldest shoots are cut out at the base of the bush or at a height of 20-30 cm, keeping no more than 2-3 branches on the bush at the age of 3-4 years.
If more than 6-8 shoots grow, then the excess ones are also removed, primarily lodging and weak ones. Pruning of these berry bushes is carried out in early spring, usually in March - early April, before the sap begins to flow.
Raspberry – Rubus
Raspberries are formed in the form of individual bushes or a trellis 0.4-0.5 m wide. After planting in a permanent place, seedlings are pruned into 3-5 buds. Next year, stems 1.2-1.5 m high grow from the left buds. Fruit buds are located in the axils of the leaves. In the spring, when pruning this fruit and berry bush, the shoots that grew in the previous year are slightly shortened, usually the unripe top is removed, which promotes the appearance of new fruit buds.
In subsequent years, all fruit-bearing biennial shoots are removed immediately after picking the berries, cutting them down to the base of the soil. Thus, the annual replacement of fruit-bearing shoots with new ones occurs.
Typically, 10-12 stems per 1 m of trellis are left for fruiting next year, or for bush growing - 4-6 shoots per bush. In the middle zone at the end of September, young shoots should be bent to the ground, pinned with pegs and then covered with snow.
Almond – Amygdalus
When forming a bean tree in the first year after planting, pruning should be minimal. In this case, the shoots are shortened by only 2.5-5 cm.
Incorrectly located, dried out and diseased branches are also removed. Do the same pruning the second year. In March or April, last year's growth is severely cut off.
In the future, every year in the spring, after the threat of low temperatures has passed, the tips of the shoots damaged by frost are cut off. At the same time, weak, non-viable and incorrectly located shoots are removed.
Red Ribes
Red currants, unlike black currants, are easier to shape; every year they produce less and less replacement young shoots, and fruit-bearing branches are more durable - they can last 7-8 or even 10 years. First, the shoots of the seedlings are shortened, leaving 2-3 strong, healthy buds on them. Every year, 2-3 of the most well-developed shoots are left from the resulting root shoots, all the rest are removed.
This formation should be carried out over 3-4 years, and by the end of the 4th year the bush should have at least 12-16 well-developed skeletal branches. Usually, many fruiting branches are formed at the ends of annual shoots, so it is not recommended to shorten annual growths, as this will lead to loss of yield.
In autumn or spring, these fruit bushes are pruned annually and aging, broken and diseased branches are removed. Thus, the main harvest of red, pink and white currants ripens on 2-3-year-old branches. Currants produce a large number of basal shoots. You should leave no more than 3-5 in one year to replace. Branches that bear fruit should be cut off close to the ground, leaving no stumps.
Watch how fruit bushes are pruned in this video:
Forming currants with a trellis
Plants are planted along the trellis at a distance of 1 m from each other. Three rows of wire are pulled to the posts 1.5 m high. Immediately after planting, the seedlings are pruned, as with normal shaping, leaving 2-3 well-developed buds on the stumps. By the end of the growing season, 3-4 or 5 of the strongest zero shoots are left.
The shoots, evenly distributed over the trellis, are tied to the first row of wire. Everything else is cut down to soil level. In the second year, another 2-3 zero shoots are selected, and the rest are removed from the new growth; shoots that are too long are shortened slightly.
As the main shoots grow, they are tied to the next row of wire. Later, when shaping and pruning these shrubs, aging shoots are cut out and replaced with new ones. In the middle zone, in the first years after planting, red and black currant bushes are covered with soil to a depth of 10-12 cm to protect them from freezing.
Black currant - Ribes nigrum
The formation of black currants begins immediately after planting on the site. The seedlings are immediately pruned heavily, leaving 2-4 normally developed buds on the shoots. New shoots are formed from these buds located at the base of the bush.
In the second year, 3-4 young strong shoots are left, and the rest are cut out to the ground. In the third year, 2-3 more new strong ones are added to the existing shoots. The formation of a blackcurrant bush is usually completed in the 4th-5th year.
By this time, the bush should have 12-15 strong skeletal branches of different ages, as well as a large number of fruit branches that bear a harvest.
They are usually short-lived, dying off after the first or second fruiting. When shaping and pruning, it is very important that the currant bush is evenly developed and all branches have free access to light and air. Subsequently, 4-year-old branches that bear fruit, as well as broken, damaged or diseased branches are cut out at the base.
We must remember that young branches produce larger berries and that the main branches of black currant live for 5-6 years and then die off. Pruning bushes in central Russia is best done in early spring, before buds open, or in late autumn, after the end of leaf fall.
When pruning in spring, shoots that have frozen in winter are also removed. For blackcurrant varieties that produce many basal shoots and weak branches, it is recommended to shorten annual shoots by 1/3.
The next section of the article explains how to properly prune ornamental shrubs.
Tools for pruning trees and shrubs
When pruning and shaping trees and shrubs in their garden plot, gardeners use special equipment, which includes: secateurs, loppers, garden knife and garden saw (Figure 5).
The pruner is the most popular tool for pruning trees and shrubs due to its versatility. They can be used to trim small branches of medium thickness (up to 2.5 cm), remove shoots and dry shoots. A pruner with extended handles is called a lopper. It is convenient for working at high heights where it is difficult to reach.

Figure 5. Basic garden tools for pruning trees and bushes
A special garden knife is used for trimming stems and branches, as well as for cleaning out irregularities at the cutting and grafting sites. The advantage over a regular knife is its comfortable handle and durable blade. A small garden saw is equipped with the same handle, it has a convenient weight and is sharpened with a very correct setting. It is useful for trimming branches whose diameter exceeds 3 cm. In this case, the cut area will be even and smooth.
When choosing tools for working in the garden, give preference to quality and good quality, because with proper care they will serve you for a long time. Make sure that the springs on the tools are always lubricated and the nuts are tightened; the cutting edge must be sharpened only on one side. And, of course, do not forget that all tools must be kept clean. Therefore, immediately after use, clean them with a soft, dry cloth.
A necessary tool for pruning and shaping the crown of shrubs
To shape and trim ornamental shrubs, you must have the appropriate tool and know the rules for using it. The quality of equipment is also of great importance for work.
The necessary tools for pruning ornamental shrubs are various types of pruning shears, loppers, garden shears, garden saws, garden knives, as well as an electric hedge saw.
And among the auxiliary devices we can mention garden ladders, putty and gloves for work. Gardeners most often use pruning shears. It is indispensable for shortening shoots and cutting out branches that thicken the crown. The diameter of branches cut with pruning shears should not exceed 1-2 cm.
In gardening stores you can buy pruning shears with long handles, suitable for cutting branches up to 3-4 cm thick. For cutting high-lying branches, rod or pole loppers are used, which are driven by a rope. The blades of such loppers must be well sharpened.
Garden tools must meet the following requirements:
- Have comfortable handles and be sharp
- Be as easy and safe as possible to work with
- Withstand significant loads, especially when cutting old thick shoots
The following describes the rules for pruning fruit bushes on a personal plot.
Pruning bushes in spring
With the arrival of spring comes more work in the garden.
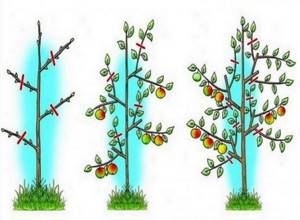
Among the many troubles, do not forget to pay attention to berry and ornamental shrubs. As soon as the snow melts at their base, you can begin thinning the berry bushes, if such work was not carried out in the fall (Figure 3)
If time has been lost and the buds begin to bloom, pruning cannot be done.

Figure 3. Rules for pruning shrubs in spring
You should know that among the ornamental shrubs, lilac needs pruning the most. Therefore, in the spring it is necessary to remove all weak shoots growing inside the crown, which intersect with each other and interfere with full growth. Old bushes need to be rejuvenated by cutting down trunks with loose bark. The surface of uneven cuts must be cleaned with a knife and cleared of sawdust, then treated with any disinfectant, for example, garden pitch. If juice comes out from the cut area, you need to wait until it dries and only then cover the surface.
Features of spring pruning of shrubs are shown in the video.
Garden routine: tree pruning
To begin with, it should be noted that garden crops need pruning for several reasons:
- Maintaining a compact shape - some garden plants whose crown is initially set (for example, curly hedges, topiaries) require periodic pruning; the procedure allows you to remove too long shoots.
- Rejuvenation of plants, thinning of the crown - this procedure is carried out in the garden every year. On mature trees, branches growing inside the crown are removed, and tops are cut out. Fruit-bearing raspberry shoots are cut out at soil level.
- Removing diseased or broken branches - shoots affected by infectious diseases must be pruned. It is necessary to promptly file frostbitten or wind-broken branches in the crown.
- Formation of garden bonsai - young plants intended to decorate the landscape should be periodically pruned, giving them the desired shape.
- Formation of bushes and tree crowns for better fruiting - pruning of vines and fruit trees is carried out annually.

Which garden crops need pruning?
Many garden crops require pruning at least once a year, but some green pets require increased attention and crown treatment 3 to 5 times per season. It is worth planning this procedure depending on what plants are planted in the garden plot. This procedure is recommended for the following crops:
- Spring-flowering trees and shrubs: rhododendrons, forsythia, lilac, but it should be taken into account that crops that bloom on last year's shoots may stop producing buds if radically pruned.
- Summer flowering crops - you can prune those types of plants that are capable of a second wave of flowering after the procedure (for example, remontant roses of the floribunda group, grandiflora, hybrid tea, bush, climbing, mini; lagerstroemia).
- Fruit trees and shrubs: pear, apple, raspberries, gooseberries, currants.
- A group of deciduous ornamental plants: oak, ash, elm.
- Coniferous and evergreen garden plants: mahonia, yew, holly, juniper, cypress.
Pruning fruit trees is especially important when the seedlings' crown skeleton is formed. Garden figured trees and shrubs are painstakingly and systematically pruned - topiaries are used to decorate the landscape and create hedges or high borders.

Timing of pruning
It is very important to start pruning the bush correctly and on time, because pruning done at the wrong time can significantly harm the plant. Therefore, there are different periods for this procedure: spring, summer, autumn.
Spring
Traditional time for “hairdressing” garden work. As a rule, this is March-April (in central Russia)
However, it is important not to miss the moment, because when the buds begin to bloom, it is no longer possible to cut the plant. In the south of the country, where sap flow and flowering begin much earlier, some trees and shrubs are pruned in February, before the dormant period comes to an end

Spring pruning is done before the buds open.
The climate of the northern regions of Russia dictates its own conditions: early pruning is not carried out. This is due to the fact that in severe frost the edges of the cut become weathered (even if they are covered with garden pitch), which leads to necrosis of the wound and its long healing. Thus, in Siberian and Ural gardens, pruning begins when the temperature reaches above zero. Moreover, if the winter has been severe, the bushes are not pruned at all this season.
Usually, the first crops to start pruning are those whose buds swell early—berry bushes. Then the fruit trees are pruned. They are followed by grapes, roses, and ornamental bushes.
Summer
During the period when the growing season begins for all crops, cutting can also be done. As a rule, it is additional in nature and is applied to mature trees. At this time, the apple tree crown is adjusted, unnecessary shoots are removed, and crops that have faded in early spring are pruned. The beginning of summer is an excellent time to trim evergreen shrubs (such as boxwood), hedges and lemongrass.

Summer is the ideal time to trim boxwood
This plant is dangerous to cut in the spring: it has early sap flow, so it is easy to injure, which will lead to death. Sanitary cutting, if necessary, can also be carried out during the summer months.

Boxwood pruning
Autumn pruning
During this period, it is recommended to trim the berry bushes, preparing them for winter. So, fruit-bearing shoots are removed from raspberries.

The main purpose of autumn pruning is sanitary
Also in the fall it is allowed to trim shrubs that form their flower buds on last year's shoots. They are cut 30 cm from the soil. After this procedure, new branches grow, and the main flowering will appear on them. Autumn pruning is carried out every season, or less often - it all depends on the intensity of thickening of the bush.
You need to monitor the appearance of the crop, and, as necessary, carry out the type of haircut that is required at the moment.
How to prune ornamental shrubs correctly
Heather – Calluna
Evergreen shrubs generally require little pruning. For the first 2-3 years after planting heather in a permanent place, pruning is not carried out at all. Carefully break off faded flowers with your hands to prevent seed setting.
In old plants, after the end of flowering, cut out part of the stems located below the faded inflorescences with garden shears, while capturing damaged and diseased shoots. When pruning, try to maintain the shape of the bush.
Wolfberry – Daphne
After planting the seedling in a permanent place, it is necessary to remove all weak and intersecting branches; this must be repeated the next year.
It is best to do this forming in the fall (November) or spring (April). The wolfberry tree does not require special pruning; only diseased and old branches are removed annually after flowering.
Maiden grape – Parthenocissus
After planting in the summer, the strongest shoots are selected and placed on prepared supports. In the second year, all weak shoots are cut into a ring. In the future, annual pruning consists only of removing diseased, broken and dry shoots.
Rejuvenating an older plant is simple: trim off all the shoots and vines of the bush to the stump. Partial rejuvenation can be carried out by removing weakly growing and old shoots, thereby allowing younger, stronger lateral branches to grow.
Kerria – Kerrio
A feature of Kerria is the growth and development of almost all new shoots from the soil level. Therefore, immediately after planting in a permanent place, in March-April, it is necessary to remove all weak, frost-damaged and thin young growths.
However, strong shoots and the side branches located on them should not be removed, since it is on them that a large number of buds and flowers will appear in the same year. After the end of flowering, in May - early June, when pruning this ornamental shrub, all faded branches are removed, but strong lateral young growths are preserved and carefully mulched.
This is done to accelerate the growth of root shoots. In the second and subsequent years, all operations are repeated again in the spring.
Cotoneaster – Cotoneaster
Cotoneaster is formed at a young age in the same way as lilac. The plant is grown primarily for its beautiful fruits, which remain on the plant almost all winter. Therefore, they cut it based on these features. In cotoneaster, the main growths are formed on the periphery of the crown.
If timely pruning is not carried out, its shoots will become smaller, the bush will thicken, flowering and fruiting will sharply decrease and move to the top of the crown. All competing, weak, intersecting shoots that grow inside the bush, as well as shoots that spoil the appearance of the plant, are cut off from the cotoneaster.
It is best to prune this garden shrub in March, before the sap begins to flow. It should be remembered that when pruning, no more than 1/3 of the length of the annual growth should be removed. Old plants are easy to rejuvenate. To do this, severe pruning is carried out, removing dried, diseased, damaged and old shoots. In the first year, new strong shoots grow from the underlying buds.
Clematis - Clematis
Many clematis, including varieties of the Jacquemin group, form flowers on the current year's shoots, so shaping and pruning should be done with particular care. In the first year after planting in the fall, the plant is cut back to its two lower strong buds, mulched and left to overwinter.
In May-June next year, it is necessary to select young strong shoots and growths formed from the basal buds. In late autumn, after the first frost, all stems must be severely pruned, again leaving two strong buds on each plant, and then mulched to protect them from damage by low temperatures.
In May and June, all growing shoots are tied up, and clematis begins to bloom in July. Pruning can help advance the flowering time of clematis. If you want an early-flowering variety to bloom later, it should be heavily pruned at a later date, and, conversely, if earlier flowering is desired, clematis should be pruned moderately, removing only shoots with faded flowers.
It should be remembered that clematis blooming on last year's shoots need light pruning, and clematis blooming on current year's shoots need strong (short) pruning, which should be done in late autumn or spring, before flowering. When forming clematis, it is necessary to leave more than 10-15 simultaneously flowering shoots on an adult vine.
When clematis freeze in the spring, the shoots must be pruned to the first healthy buds. As the plant begins to grow, and especially at the beginning of summer, it is necessary to regularly orient all growing shoots in the desired direction and, if necessary, tie them to a support.
At the same time, thinning of thickening branches is required, which improves aeration and illumination of the plant.
Prince – Atragene
Princes form identically to clematis. The liana blooms on last year's growths. Therefore, plants are pruned only after flowering. Remove faded shoots, weak, old and diseased stems. If the shoot growth of the prince slows down or stops, the stems are exposed, the plant requires urgent rejuvenation, which is carried out by shortening the stems and transferring them to lateral, rapidly growing shoots.
At the same time, thinning is carried out by removing old and damaged shoots. Plants cut in autumn are mulched with peat or covered with spruce branches, sawdust, and dry leaves.
If the princely bushes become thick, they need to be thinned out, providing better illumination and maximum aeration. The prince tolerates annual pruning well. If for some reason it was not carried out, then the plant must be severely pruned, leaving a few old shoots. It should be remembered that regular pruning and garter of the princeling contribute to the duration and continuity of its flowering.
Schisandra – Schizandra
The formation of the crown of this shrub is usually done arbitrarily. Shoots that grow up to 2 m or more during the growing season are directed along vertical supports. Schisandra tolerates pruning well. To regulate the growth of vigorously growing shoots, pinching should be done periodically, as a result of which the growth of pinched shoots is delayed and the growth of unpinched shoots is enhanced.
In addition, this technique prevents crown thickening. Schisandra produces a lot of root shoots, which spread far from the mother bush, so it is unsuitable for making hedges.
In winter, the schisandra vines do not need to be removed from their supports, since in adulthood they can tolerate low temperatures. Old branches of lemongrass, older than seven years, must be cut out at the base, replacing them with new ones.
It is best to do this either in the fall or at the end of May - beginning of June, when diseased, old and damaged shoots are already clearly visible, and by this time the lemongrass usually stops “crying” (leakage of juice).
If for some reason a large number of shoots of Schisandra have dried out, the plant needs rejuvenating pruning. In this case, all these stems are cut to the stump, and the plant sends out new healthy replacement shoots.
Rhododendron – Rhododendron
To stimulate the flowering of rhododendrons, a particularly important technique is to remove faded flowers. At a young age, such removal promotes the formation of new shoots and branches; later, after this operation, the plant forms more growing buds, and vegetation begins faster in the spring.
Pruning should be carried out to give the bush a certain shape and remove old, damaged, dried and diseased branches. In this case, only individual branches are shortened. Heavy pruning significantly delays plant growth and first flowering.
If there is a need to trim old and out-of-shape bushes, it is best to do this at the end of April.
Chaenomeles - Chaenomeles
In the first or second year, several powerful basal branches form at the base of the bush. Subsequently, 3-4 well-developed shoots are left annually at the base of the bush. Shoots that thicken the crown should be cut out. Second-order shoots are formed from adjacent buds.
At the end of July - beginning of August, the ends of the shoots are shortened by 2-3 leaves. Flowering, fruit-bearing branches will appear from the remaining buds next year. Fully formed bushes should have 12-15 branches of different ages.
Flowers and the main fruit crop are formed on 3-year-old branches. On 5-6-year-old branches, the yield decreases and the decorative appearance of the plant is lost. Therefore, to maintain good healthy growth, it is recommended to carry out anti-aging pruning in early spring, while cutting out old shoots that thicken the crown. Bushes aged 15-17 years require rejuvenation. In this case, the plant is cut to a stump.
Rosehip – Rosa
In the first year after planting, rose hips are formed like ordinary roses. All rose hips need shaping and pruning, but the p. variety requires almost no pruning. wrinkled and r. prickly.
In the first year of cultivation, young plants undergo severe pruning, stimulating powerful growth of root shoots, and the formation of a bush with shoots evenly spaced along the periphery of the crown. When pruning, low-growing rose hips are pruned much more strongly than vigorous ones.
Rose hips bush a lot, so after some time it is necessary to thin out the bushes. To do this, almost all old branches are cut down to soil level and 5-6 healthy strong shoots are formed again. At the end of flowering, rosehip shoots are shortened. For tall bushes with bare branches, each branch is cut to half its length. In the middle zone, it is best to do this in April.
Types of tools
To ensure that pruning garden trees and berry bushes does not cause severe harm to the condition of your crops and is as comfortable as possible for you, you should use a high-quality cutting tool. The main tool for proper pruning is a pruning shear. If you are the owner of a young garden, then at first this will be enough. In order to rejuvenate trees and shrubs, and cut branches with a thickness of over 50 millimeters, we recommend purchasing a garden saw. Another name for it is a garden hacksaw. To carry out the intended actions in hard-to-reach places, inside bushes, we recommend having a lopper on the farm.

The requirements for working tools that will be used to trim fruit bushes are not complicated. They must be sharp enough to make even cuts. Safety and comfort during operation are important. Secateurs or loppers should have tapered ends that will help you reach branches that are too far and high. Having a low dead weight, the tools must withstand any force. The handle should not be slippery to the touch, preferably.
Secateurs are used to cut branches up to 25 millimeters. There are two types of them - the bypass one has a convex blade that slides over the surface of the concave one, the anvil pruner has a wedge-shaped working blade with double-sided sharpening, it works on the principle of an ax. Secateurs of the first type are recommended for cutting living wood, the second - for dried branches. Thanks to the long handles, a lever is formed that allows you to cut high branches without a ladder.
Spring pruning of perennial flowers
If you did not cut off the faded stems in the fall, you can trim them after the young shoots emerge from the ground. Until then, the old stems will serve as beacons so as not to accidentally weed out the plants or plant something in their place. This measure is especially relevant for those plants that emerge late after winter (for example, hosta, platycodon).
By its nature, lavender is a subshrub, but due to its external characteristics it is perceived by many as a beautifully flowering perennial
It is important to prune this plant every year in the spring, cutting off the tops by one third of the length, and you can also give the plant a spherical shape
Without pruning, the lower part of the lavender will become bare, resulting in unattractive “bare legs” on the bushes.
Occasionally, lavender can be given a more radical pruning, but it is important not to cut off the woody parts of the stem, as the bushes will then branch poorly
A close relative of lavender, Perovskia, also needs spring pruning. During the winter, the branches of this plant are almost completely frozen, so in the spring you need to prune when the plant begins to grow. When pruning, leave 6-8 centimeters from the ground, but if the stem is completely frozen, then it is cut off at soil level, and young shoots will appear from the root.
For evergreen plants (bergenia, chistets, heuchera and others), only the old leaves that died during the winter are removed. You cannot completely cut off the bushes; this will weaken the plant or even lead to its death.
Don't throw away last year's bergenia leaves. From the foliage of this plant that has turned brown over the winter, you can prepare a very tasty tonic drink called “Mongolian tea.” The taste of bergenia leaves, which have undergone natural fermentation in winter, resembles exquisite varieties of black tea, while they do not contain tannins, but have a number of beneficial properties and are indicated for certain diseases. However, the drink has a number of contraindications, so you should consult your doctor before drinking it.
It is important to prune lavender in the spring to give the plant a spherical shape. Oxford Pruning Company
Spirea pruning
When is the best time to prune?
The timing of autumn pruning of spirea depends on the timing of its flowering:
- Kobeya: growing from seeds, types and varieties
- For varieties of spirea that bloom in late spring or early summer, pruning in September is optimal if you did not do this in the summer, immediately after flowering. Early flowering species include spirea Vagutta, sharp-toothed, medium, Nippon, oak-leaved;
- Late-flowering spirea, which includes Japanese spirea, Boumalda, Douglas, Billiard, willow-leaved, birch-leaved, is pruned in the spring.

Autumn pruning tips
After the early-blooming spirea has faded, trim off the faded tips of the shoots to preserve the natural contours of the crown until the end of summer. With the onset of autumn, so that the bush does not lose its decorative value in the future, a fourth or fifth of all shoots are removed from it at the root - this measure stimulates the growth of shoots next year. If possible, remove all faded shoots, leaving young shoots. Spirea bushes are thinned out every two to three years, cutting out crooked, too thin and weak branches.
Once a decade, unless there is a need to do this earlier, the spirea is pruned thoroughly, leaving only 5-7 young strong branches on the bush.

Pruning and shaping the crown of shrubs on a trunk
It is not difficult to form a bush on a trunk. Of course, by their nature they are not inclined to grow into one trunk, and will try with all their might to “convince” you of this. But there are plants with which it is quite possible to carry out such manipulations.
When forming these shrubs on a trunk after planting, all existing branches are cut off. When young shoots grow, you need to choose one that is strongest and directed vertically; the rest - cut out completely. When the remaining branch reaches the desired size, it is cut off and a crown is formed.
For shrubs, it is enough to leave a trunk 70-100 cm high. In this case, all shoots and buds are removed from the trunk, except for the very top ones - from these the crown is formed by pinching growing shoots after 2-3 leaves. You should not leave a very large number of branches in the crown.
You can also obtain a crown at the desired height by grafting. Having received the standard in the manner described above, early in the spring, when the buds are just swelling, graft a cutting of the desired variety onto it. Take a cutting with 4-5 buds, all of them will germinate in the first season, and the crown will form quite quickly.
Japanese quince can also be obtained in standard form, but in this case the formation process has its own characteristics. It is unlikely that it will be possible to remove a standard from the branches of the shrub itself, so pear or rowan seedlings are used as a standard forming material. The seeds of these crops germinate well when sown in the ground in the fall and, with good care, grow quite actively.
Rowan seedlings grow faster than pears, and in the first year they can reach 40 cm or more. Depending on the desired height of the trunk, grafting can be done on one-year or two-year-old seedlings. The grafting is carried out with a cutting in the butt or in a side cut in the spring.
When is the right time to prune blackberries?
The purpose of pruning blackberries is the same as for raspberries. At the end of the season, all two-year-old shoots are pruned without leaving the ground. In the vacant space, young shoots are tied to the stems, ripening the berries next year. Young shoots are shortened by about a quarter. No more than 8 promising shoots are left for the winter, and weak and sick ones are cut off.
If there are few young shoots, you can leave a few old ones. Their side branches are pruned to a length of 2.5 cm. In autumn, cuttings appear on the sides of the bushes - blackberries tend to grow wide, this process must be stopped. In spring, you only need to trim overwintered shoots and damaged tissue to a healthy part.
About the procedure methods
Pruning shrubs involves 2 methods:
- Shortening branches. This method is used if there is a need to get rid of the upper part of the shoot. After this procedure, the diameter of the branches will increase, the shoots will begin to grow faster, and the development of buds will accelerate;
- Shrub thinning. This involves pruning all branches so that the bushes do not become dense. After this procedure, the plant is not afraid of diseases and pests.
Carrying out these pruning methods has a positive effect on the bush, because all the nutrients that the plant has begin to be redistributed along each branch. Spring pruning of shrubs has a beneficial effect on the plant, and its shoots begin to develop more intensively, the branches become stronger and gain healthy strength. After pruning, the number of buds decreases, and, consequently, the path of movement of nutrients from root to leaf becomes smaller, and crown growth increases significantly.
Formative pruning of shrubs
Shrubs that form hedges (barberry, privet, hawthorn, honeysuckle, cotoneaster, snowberry, hairy willow) need mandatory annual pruning to maintain an attractive shape. If you prefer to form a hedge in the spring, trim off those parts of the shoots that grew last season. If it is more convenient for you to form ornamental shrubs in July-August, then remove the current year’s growth.
Adult fast-growing specimens that have already reached the desired size need to be cut in both spring and summer. The plants will look neat.
One- and two-year-old plants can be trimmed with garden shears or an electric trimmer. And the branches of mature shrubs are tough only for pruning shears.
Shrub pruning: mistakes
It is only at first glance that it seems that cutting off an extra branch is a simple matter. However, gardeners often make many mistakes in the process of pruning crops. Let's look at the most common of them, perhaps this will help you avoid repeating them:
- Inappropriate tool. Some summer residents do not pay enough attention to what they are working with and cut down large (2 or more cm) branches. Sometimes completely unsuitable hacksaws are used for this.

Choose special tools for the job
- Incorrect cut processing. The cut area must not only be corrected with a sharp knife, but also treated with garden varnish (a layer of 3-4 mm). Otherwise, mushroom spores and a hollow will form at the cut site.
- Failure to follow pruning order rules. First, cut off most of the branch, leaving 30-40 cm from the base, and then carefully saw off the remaining part.
- Incorrect cut location. There is usually a slight “overflow” where one branch transitions to another. You need to cut the branch along its edge. No more, no less.
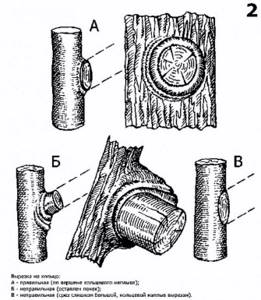
Scheme of cutting a branch with “influx”: right and wrong
- Inappropriate time and purpose of haircut. Before you start pruning, look at the bush carefully: what needs to be done? Carry out sanitary measures, form a crown or rejuvenate the crop? Perhaps the plant needs several types of pruning at once. In any case, before removing branches, decide on the type of bush, goals and timing of pruning.
Garden shrubs, beautifully flowering or decorative deciduous, are wonderful plants that can become the highlight of any site and even an element of its landscape design. But in order for the bush to have a neat appearance and grow well, do not forget not only about watering and fertilizers, but also about pruning. Proper and timely pruning of a crop is the key to its beauty, lush flowering and active growth. Don’t make mistakes, keep an eye on the green “residents” of the garden, and they will delight you for a long time.
Proper spring pruning of ornamental shrubs
How to prune a bush correctly and not harm it is one of the most common questions that arises among novice gardeners. The procedure for proper pruning is not very difficult if you follow the basic recommendations.
When pruning, you must follow certain rules:
- all dried and broken shoots should be removed immediately;
- stumps and cuttings should not be split;
- the correct cut, which does not leave a stump, should be made at an angle and not straight;
- the pruning tools used must be well sharpened and always clean;
- you should try to cause minimal damage to the treated shrub: branches whose thickness is less than or equal to 2 cm are cut with pruners, and in the case of thicker branches - with a hacksaw;
- in the process of work it is necessary to act pointwise, try not to catch nearby shoots;
- To stimulate the growth of weak branches, shoots should be cut shorter, but for healthy and well-growing branches, shortening too much is not required;
- The correct cut is characterized by a smooth surface and without various scraps of bark. In case of an uneven cut, you can use a garden knife, which will help achieve the required smoothness;
- Do not forget that it is better to pinch the shoot at the right time than to cut it off later.
We recommend reading these articles:
Fertilizer for raspberries in spring to increase yield
Why whitewash trees in spring?
Fertilizer for strawberries in spring to increase yield
Also, do not forget about care after pruning: all cuts are treated with garden varnish, and if the surface thickness is over 3 cm, using oil paint will be much more effective.
Do-it-yourself figured spring pruning of shrubs
The best examples of curly pruning of shrubs are considered to be the so-called living sculptures
To create various shapes from shrubs, it is very important to ensure that they are evenly covered from top to bottom with leaves or pine needles
In order to perform curly pruning of shrubs with your own hands, you need to choose the right plants and shape them accordingly.
The easiest way to have a living sculpture in your garden is to purchase shrubs in the sculptural form you desire. The best sculptures are made from evergreens such as boxwood, privet, holly, cherry laurel, and bay laurel. However, in central Russia, most species of evergreen plants in open ground freeze or die in winter. Therefore, only coniferous and deciduous shrubs are suitable for creating living sculptures in the garden. For small figures it is very good to use spirea, honeysuckle, elm, cotoneaster, barberry, mahonia, Japanese quince, etc.

Small-leaved linden, hawthorn, spruce, hazel, small-leaved elm, apple berry and some others are quite suitable for creating larger figures.

Figures formed from evergreens, and above all boxwood, look very beautiful. How to prune shrubs beautifully to create living sculptures from them? Plants should be formed in an appropriate container so that they can be transferred to heated rooms for the winter. The plants from which the sculptures will be formed are planted on fertile, permeable soils in bright areas of the garden. Do-it-yourself decorative pruning of shrubs to form living sculptures from deciduous plants is carried out in early spring or at the end of shoot growth.
Spring pruning of trees and shrubs must be done with well-sharpened tools (secateurs and saws) so that the cutting surface is smooth. After pruning, the wound should be treated with FUNABEN garden ointment or white emulsion paint with the addition of Topsin fungicide, which will protect against damage by pathogenic fungi.
Regular spring pruning, removal of dry, weak, damaged and excess branches, and proper formation of the crown of berry bushes allows you to rejuvenate and improve the health of these crops, increase their fruiting period, increase the quantity and improve the quality of future harvests.
What flowers and shrubs cannot be pruned in the fall?
In autumn, especially as long as this year, there is enough time to prune the garden. However, not all crops require this operation, and sometimes it can be harmful. Let's figure out which plants should not be pruned now.
For ornamental shrubs, a simple rule applies - if they bloom on last year's shoots, then you cannot prune them, otherwise you will not see flowering. There are many such crops; you probably have them in your garden.
Common barberry and Thunberg barberry are popular shrubs; numerous varieties with yellow and red leaf colors are often found in gardens. Barberry blooms in May-June on last year's shoots; it does not require autumn pruning.
Weigela flowering, hybrid, early, Middendorf and other species sometimes have two waves of flowering. They bloom profusely on last year's shoots in the spring, and then again in mid-summer. The main pruning is recommended to be done in the summer, and in the fall you can only remove damaged shoots.
Weigela early
The spectacular ferruginous cherry is a shrub that blooms profusely in May; it requires only spring sanitary and thinning pruning.
The most popular hydrangeas in our country are tree-like and paniculate, which retain lush inflorescences all winter. There is no need to trim them; dry corymbose or paniculate inflorescences will decorate the garden in the off-season and also preserve flower buds on the tops of the shoots.
Louiseania triloba (almond triloba) is distinguished by early flowering, some varieties bloom before the leaves bloom. Plants are pruned only in late spring or early summer, after flowering.
Luxurious clematis are pruned depending on their belonging to a particular group. There are several groups of varieties in which flowering occurs on the shoots of the previous year, or the flowers of the first wave are formed on the shoots of the previous year, then the second wave of flowering occurs on the shoots of the current year. These groups of varieties include – Lanuginosa (varieties Ballerina, General Sikorski, Diamantina), Patence (varieties Barbara Jackman, Miss Batman, Lord Nevill), Florida (varieties Mechta, Pink Perfection, Vyvyan Pennel), Montana (varieties Elizabeth, Freda, Rubens ). Such clematis should not be pruned in the fall; they are removed from their supports and covered; minimal pruning is carried out in the spring.
Clematis General Sikorski
Varietal vesicular carp viburnum with spectacular purple or golden leaves forms white or pink flowers in corymbose inflorescences on last year's shoots; minimal pruning is carried out only in the spring.
Diabolo
Lilacs lay flower buds on the tops of the strongest shoots of last year's growth; in the fall they are not touched or shortened. If necessary, at the end of the season, you can remove only broken and dry branches, and postpone thinning pruning until spring.
Spring flowering spirea - alpine, Vangutta, Nippon, sharp-toothed (arguta), gray, Thunberga and others form flowers on the shoots of the second year of life. If necessary, they can be pruned after flowering ends, from about mid-June.
In temperate climates, winter-hardy types of forsythia are most often grown - hybrid intermediate and oval (ovoid). Shrubs covered with yellow flowers open the spring season from the end of April; they are pruned only after flowering.
Forsythia oval
Chaenomeles japonica requires rare pruning, it is carried out once every 5-6 years after flowering; this operation is not required in the fall.
Fragrant snow-white species and varietal mock oranges traditionally grow in our gardens; their flowers form on shoots of the second year of life. Formative pruning is recommended to be done after flowering.
Perennial ornamental plants require selective pruning in the fall. Be sure to remove dried shoots from those species that suffer from diseases (delphinium, phlox), as well as from plants that produce abundant but undesirable self-seeding (lupine, goldenrod).
Plants with overwintering leaves should not be pruned; there are plenty of them in our areas. The powerful leaves of bergenia cordifolia tolerate cold well and remain decorative for a long time in the spring.
Bergenia cordifolia
The dark green cover of the small periwinkle under the snow does not suffer from frost.
Various varieties of heuchera and heucherella, painted in lemon, purple, and carmine colors, must be left to overwinter; they tolerate the cold period well and add decorative value to the flower garden after the snow melts.
Pachysandra apex, thanks to its tough, dark green leaves, creates a stable cover throughout the year. The leaves live for three years; the plant does not need pruning. There is also no need to trim the green leaves of the ground cover species of sedum, saxifrage, primrose, lungwort, creeping tenacious, and evergreen iberis.
Pachysandra apex
Southern lavender always leaves shoots with silver-gray leaves; in the spring they will gradually be replaced by young leaves. The winter-green leaves of these plants provide initial growth in early spring and then die back before needing to be removed.
Lavender angustifolia
There are a number of plants that die and dry out in the fall, but thanks to their tough, durable stems they retain their shape. These species can not be pruned, but can be used to create a winter flower garden.
It will attract attention in the off-season with panicles of cereals - Chinese miscanthus, blue moth, feather feather grass, gray fescue, maned barley. Dry capitate inflorescences of teasel, flat-leaved eryngium, common Echinacea, and Echinacea purpurea look impressive.
Common Mordovnik
Dry shoots and leaves of astilbe are best left until spring; they will create natural protection for the root system and help retain snow. It is also worth doing with perennials of southern origin that have adapted to wintering in northern latitudes. There is no need to prune perennial types of sage, fennel grass, oregano and lemon balm; with the remains of the shoots they will withstand the cold well, and in the spring it will be easy to remove them.
Oak sage Amethyst
You don’t have to cut off daylily and hosta leaves in the fall; they easily decompose under the snow, leaving virtually no messy marks. However, next to these powerful perennials, which grow later than other species, many gardeners place early small-bulbous flowers - crocus, muscari, scilla, chionodoxa, pushkinia. In this case, the flower garden needs to be cleared of leaves; this is easiest to do after the first frost. This is the only way you can admire the charming primroses.
When assessing the need for pruning of flower beds, keep in mind that it is imperative to remove leaves affected by diseases in order to prevent the spread of infection.
Calculate your strength and time. If you have to end the summer season early, then the easiest way is to leave all ornamental shrubs and perennials without pruning; this will not harm them in any way. It is quite possible to remove dry shoots of grasses in the spring, and at the same time it will be convenient to trim off shoots of shrubs that were damaged in winter.
Source
Pruning shrubs in summer and autumn
According to the rules for pruning shrubs, when caring for plants, you first need to remove old branches, which are already bearing less fruit. On red currants and honeysuckle, branches older than 7-8 years are removed. When pruning golden currant fruit bushes in spring, branches older than 10 years are removed. If it is a shaped hedge, then it needs to be trimmed to the desired shape.
During the summer, the garden should also not be left unattended. At this time, the tops of the trees are broken out, strongly growing shoots are pinched to form fruit formations from them, and severely damaged branches are cut out. Mature hedges are periodically trimmed.
In autumn, sanitary pruning of ornamental shrubs is carried out. This procedure should be planned for the end of October, when the plant goes into a dormant state. You should not prune other crops in the fall - this reduces their winter hardiness.
Which tool is suitable for pruning?
Successful pruning depends largely on the tool used for this operation. If the pruning shears or pruning shears are too small, you risk damaging them or the shoots and branches, leaving wounds and damage. The basic working garden tools needed to maintain a tidy garden are presented in the infographic:
Correct and timely pruning of fruit and ornamental plants allows you to avoid many problems that appear during the period of their growth, flowering and fruiting.
It is extremely important to carry out the “health improvement” of trees and bushes in a timely manner. This will help them live long, and you will enjoy lush flowering and a bountiful harvest.
Timing for pruning shrubs

Incorrectly chosen timing of pruning shrubs is dangerous for the health and development of the crop. Traditionally, three types of pruning are used:
- Spring pruning
. The most used type is after winter, when the danger of frost has passed, but before fruit buds set. Berry bushes are pruned first, followed by fruit trees and ornamental shrubs. - Summer pruning
. In the summer, the crowns are adjusted and pruned after the apple tree blooms. Evergreens also undergo summer pruning. In addition, in the summer it is necessary to prune plants that have active sap flow in the spring, for which spring pruning is contraindicated.

- Autumn pruning
. In autumn, berry bushes are pruned and begin a new vegetative cycle in early spring. Autumn pruning involves those crops in which it is customary to remove fruit-bearing shoots (raspberries, for example). - Winter pruning
. A rare exception relating to emergency methods of saving a plant. If there is no urgent need, it is necessary to postpone pruning until spring, since at low temperatures the shoots become fragile and the cut becomes brittle, leading to injury to the plant.
Pruning ornamental bushes
Autumn is the best time for pruning shrubs, since at the end of the growing season you are not pressed for deadlines, as is usually the case at the beginning, when the time interval between the onset of spring and the beginning of sap flow in the plants is too short, during which it is too late to prune. The only precaution that must be taken when pruning shrubs in the fall is to avoid carrying out the procedure at temperatures below -10 ºC, so as not to injure the wood, which is too fragile from frost.
How to prune fruit and berry bushes in autumn
Here is a rough list of the tools you may need to do the pruning:
- sharpened pruning shears with two blades. Ideally, the blades of this tool should be of such length that when they are fully extended, a branch with a thickness of one and a half to two centimeters can be placed between them. It's nice if the tool is equipped with such improvements as a gear amplifier, a rotating handle and ratchet wheels, with which you can cut old thick branches in three steps;
- lopper - a type of pruner with long handles, which is used for trimming large branches in hard-to-reach areas of the crown. It is also much more convenient to trim thorny bushes with a lopper and make cuts below the soil level. The more the blades taper towards the ends, the more versatile the tool;
- saws and hacksaws for removing large branches;
- putty to protect cuts from infection and drying out. You can use garden pitch or modern factory-made preparations containing physiologically active and disinfecting substances that promote rapid wound healing.

There are two types of pruning of flower bushes: shortening and thinning. Shortening the shoots helps create the shape of the bush, regulates flowering and limits too intense growth, and thinning is a sanitary or rejuvenating pruning necessary to extend the life of the bush. Autumn pruning of shrubs serves in most cases for sanitary purposes, and if the plant has reached an advanced age, pruning of branches is also done for the purpose of its rejuvenation. True, there are shrubs that are better to form in the fall rather than in the spring.
- Eleutherococcus











