Extraordinarily decorative spirea bushes are widely used in the design of urban and residential areas. The plant is loved for its unpretentiousness, resistance to frost and drought, varied and original shape of the bush and inflorescences, and ability to bloom until frost. In addition, the flowering shrub is an excellent honey plant, a source of medicinal raw materials and strengthens the soil. The appearance of the plant, the color and shape of the flowers depend on the variety, so descriptions and photos of spirea varieties will help you make the right choice.
Description
Spiraea or meadowsweet belongs to the Rosaceae family. This shrub is widely used in landscape design, because it can decorate any garden, yard, flower garden, and also become part of attractive compositions in combination with other plants.
Spiraea japonica is the Latin name for the Japanese dwarf or lilliputian spirea, characterized by a miniature spherical bush. This type of plant is a summer flowering plant. From June to August, beautiful inflorescences of small flowers appear on its shoots. They can be soft pink and red.
Did you know? Spiraea shoots contain salicin glycoside, which can be converted into aspirin.
The leaves of this type of spirea are also very beautiful. Most often they are colored in various shades of yellow, and depending on the time of year they can acquire a slightly reddish or orange color.
Due to the fact that this plant adapts well to different climatic conditions and is unpretentious in choosing soil for growth, it is very popular. And, despite the name, this type of spirea grows not only in Japan, but also in many other countries around the world.

Use in garden design and combination with other plants
Gray spirea and its varieties are perfectly combined with almost all types of plants that are used for landscaping and decorating gardens, parks, and personal plots. For single and group plantings, neighbors are selected taking into account their size, shape, flowering time, color palette of foliage and flowers, using spirea bushes as the center of the composition and for arrangement.
The combination of spirea with conifers and evergreen shrubs, such as juniper, will introduce oriental motifs to the ensemble of these plants. The spirea bush will look even more elegant against the background of viburnum, lilac, and broom. In flower beds of all formats in front of municipal buildings and in city squares, spirea bushes next to different types of roses or any other flowers, for example, tulips, crocuses, alyssums, visually add volume and expressiveness to them. The combination of species and varieties of spirea with different flowering periods allows you to admire flowering plants for 4 - 5 months in a row.
In order to hide a fence or other outbuildings on a summer cottage from view, dense and tall bushes of gray spirea are one of the best options. They are able to add splendor to any mixborder, enhance the festive beauty of borders and alleys, and emphasize the romantic power of giant trees. But a dwarf or low-growing variety of gray spirea is perfect for arranging an alpine hill and rock garden. And, of course, flowering spirea branches are an excellent material for floral arrangements and bouquets.
Landing rules
Gardeners and landscape designers love Japanese dwarf spirea for its unpretentiousness and ability to grow on any soil. The main thing is to choose a well-lit place so that the bush receives as much sunlight as possible. It is advisable to plant spirea in the fall, immediately after leaf fall. It can also be done in the spring, before the first buds bloom.

Seedlings are selected that are healthy and without damage. When planting, it is advisable to shorten the shoots by about a third, and also trim off too long and weak roots. If the rhizome is very dry, it should be soaked in water overnight. Spirea should be planted early in the morning or evening, and even better in cloudy weather or on days when it rains.
Important! Holes for Japanese spirea must be prepared in 2
–
3 days before landing.
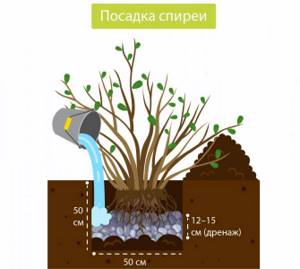
Holes for bushes must be made twice as large as the length of the rhizome, and their walls must be strictly vertical.
Planting spirea should be done in the following sequence:
- Dig holes at a distance of 50 cm from each other in advance and leave to ventilate.
- After a couple of days, make drainage by pouring broken bricks or large stones onto the bottom.
- Add a mixture of soil with peat and sand on top.
- Place the seedlings in the holes, sprinkle with the remaining soil mixture to the level of the root collar.
- Gently compact the soil so as not to damage the rhizomes.
- Water the young plants well using 2 buckets of water.
- Mulch the soil around the bushes with peat.
Botanical characteristics
Spiraea is a deciduous perennial plant 0.15-2.5 m high. It is nourished by a fibrous superficial rhizome. The shoots grow straight, spread along the ground or rise. Over time, even upright branches bend under their own weight. The color of the branches is light brown or dark brown. The bark peels off in longitudinal plates.
The alternate short-petioled leaves have no stipules and are distinguished by a narrow-lanceolate shape with a distinct relief pattern of the central and lateral veins. The edges of the foliage are serrated or toothed. Coloring can be quite varied. Some plants have green leaves throughout the season, while others change foliage several times from red to yellow, green or orange.
The first weak flowering begins in the second or third year of the spirea's life. In mid-spring or already in summer, many umbrella or paniculate inflorescences bloom in the axils of the leaves. Small corollas with a diameter of 6-10 mm, located close to each other, have a disc-shaped shape. Flowers with five individual rounded petals and a lush core (up to 60 stamens and about 5 ovaries) can be white or pink.
After pollination, lanceolate, flat, brown seeds ripen in multi-seeded leaflets. Their length is only 1.5-2 mm. Ripe fruits crack at the seams on their own.
How to care
Despite the fact that this shrub is often chosen for landscaping because of its ease of care, there are still rules that must be followed when growing dwarf meadowsweet.
Important! Excess moisture for Japanese spirea is as dangerous as drought, so it should be watered in moderation.
In order for the bushes to grow well, look beautiful and healthy, you must remember to do the following simple actions:
- Water the plants , especially during the periods when they take root and bloom, as well as after pruning. During the dry summer months, you need to pour 1-2 buckets under each bush twice a month.
- Fertilize after planting with mineral fertilizers, as well as peat and humus before and after flowering. In summer, feed with mullein solution to which superphosphate is added. And after pruning and for the winter, apply organic fertilizers to restore strength.
- , trim off the tops of shoots that have frozen over the winter, as well as dry and diseased branches. Periodically trim the bush, getting rid of old shoots. In summer, cut off dry inflorescences so that the plant does not waste energy on them.
- Weed the soil around the bush, loosen it and mulch it so that the rhizome receives a sufficient amount of oxygen and moisture is retained as long as possible.

All varieties of Japanese Lilliputian spirea are suitable for creating a unique landscape, because they have high decorative properties, are unpretentious in care and take root well on any soil. They can be used individually or in group plantings, as ground covers for flower beds, green hedges, and alpine slides.
Advantages of spirea sulfur
Gray spirea belongs to the group of early-flowering spring spireas. The plant has a number of advantages, thanks to which it is loved and in demand by gardeners and landscapers. Let's list the main ones:
- High decorative qualities throughout the year.
- An easy plant to reproduce.
- Easy to care for (watering, fertilizing, haircut).
- Cold resistance. Even if the ends of the young shoots freeze in a particularly cold winter, this will not affect the decorative appearance of the bush after pruning.
- Rapid growth and duration of abundant, picturesque flowering.
- Sanitary and hygienic role for the environment, thanks to the phytoncides that the plant secretes.
- Resistant to heavy gas pollution and smoke.
Spreading
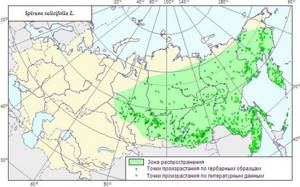
Various types of spirea can be found in forest-steppe, forest, semi-desert zones and in the subalpine mountain belt of the Northern Hemisphere . In Asia, the shrub can be found farthest south in the Himalayas. In North America - in Mexico.
Most representatives of the genus are drought- and frost-resistant and prefer to grow on fertile soil.
Reproduction methods
Spiraea can be propagated by seeds or vegetatively. For hybrid species and ornamental varieties, seed propagation is not suitable. In the spring, boxes are prepared with a mixture of leaf soil and high-moor peat. The seeds are evenly placed on the surface and covered with a layer of peat 1 cm high. Shoots appear in 1-1.5 weeks. Even at an early stage, they are treated with foundationazole or potassium permanganate. After 2-3 months, the roots of the grown seedlings are cut and transplanted into open ground in a training bed. They are located in partial shade or shade. Plants are watered abundantly and the soil is mulched.
The most reliable method of propagation is rooting cuttings. In the spring, before the leaves appear, the lower shoot is bent to the soil and fixed, and sprinkled with earth on top. The top is tied to a support. In the summer, not only the bush is watered, but also the cuttings. It will take root this year, but separation and transplantation are planned for next spring. For better development, flowers are removed in the first year.

During spring and summer, cuttings about 10 cm long are cut from semi-lignified and green branches. The lower cut is treated with “Kornevin” and then immediately planted in containers with loose garden soil. After 2-3 months, 50-70% of the cuttings will develop a full-fledged root system. Planting in open ground is carried out next spring.











