Why does a house need a drainage system and is it possible to do without it?
A drainage system is necessary to collect water from the roof and drain it away from the facades and blind area. If there is no drainage system, then over time the blind area may be destroyed, as a result of which water will enter the soil near the foundation, and in the absence of proper waterproofing, it will gradually begin to be washed away. In addition, rainwater can cause serious damage to facades. For example, many years of experience in inspecting buildings shows that it is the absence of a drainage system that leads to delamination of brickwork, peeling of the plaster layer, and destruction of the cladding.
Consequences of the absence of a drainage system on a brick house
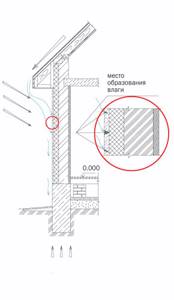
Consequences of the absence of a drainage system on a house with a plastered facade
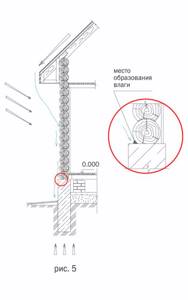
Consequences of the absence of a drainage system on a log house
Types of drainage systems
Types of drainage systems depending on the base:
- plastic,
- metal (galvanized, aluminum, copper).
To know how to choose the right drainage system, you need to take into account the type of roof, resistance to mechanical and temperature influences, the price of individual elements, and the complexity of installation.
Plastic drainage systems
Advantages:
- corrosion resistance,
- UV and chemical resistance,
- light,
- easy to install,
- has noise-absorbing properties.
Flaws:
- fragility (service life is 15-20 years),
- unstable to sudden temperature changes.
Metal drainage systems
Galvanized drainage systems with a polymer coating, based on steel, aluminum or copper, have the following advantages:
- resistance to temperature changes,
- suitable for use in harsh conditions,
- resistance to corrosion and deformation,
- long service life (25 -100 years depending on the metal).
Among the disadvantages of metal structures, high cost and installation difficulties are noted.
Installation of a drainage system
General instructions for installing a drainage system:
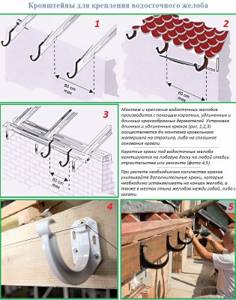
- Installation of horizontal elements (gutters, drains). In areas not intended for draining water, plugs are attached. The gutters are connected to each other by special couplings. The joints should be coated well with silicone or roofing mastic. At the end of the gutter, a funnel is installed through which water from the gutter enters the pipe.
- Pipe installation. First, you need to mark on the wall the places where the holes for the bracket dowel will be drilled. Afterwards, we mount the brackets themselves without clamping the clamps. We lean the pipe, and, making sure that everything is smooth and done correctly, we fasten the clamps.
- Installation of bends. The first outlet is mounted to the gutter funnel. We cut a pipe to fit it to size, which will play the role of a connector between the gutter and the vertical pipe at the distance of the eaves overhang. An outlet is also attached to the end of this connecting pipe, to the tail of which the main drain pipe is adjacent.
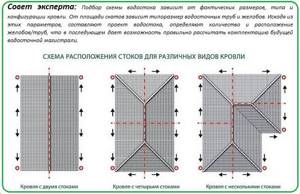
Rules for installing a drain
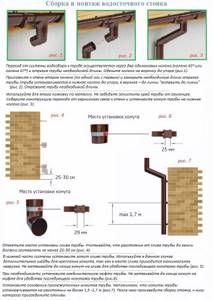
- First, the brackets are installed. They are screwed to the starting board of the roof slope, or to the front board. Install the brackets so that they are on a slope. For example, if the length of the slope is 6 meters, then it would be more appropriate to take one side as “0”, and from this zero, gradually lower the brackets so that the last brackets are 3-5 cm lower than the first. Then the water will flow to this side and leave as it should. If the length of the slope is greater, for example, 18 meters, then point “0” should be taken from the center of the slope and slopes in both directions. In this case, the water will move away from the center along different edges of the slope.

- For plastic drainage systems, the brackets are attached at a distance of 40 - 60 cm, for metal ones - 60 - 80 cm. Be sure to install the brackets on both sides of the corners of gutters and funnels.
- The gutters are laid on brackets. The parts of the gutter are connected with an overlap of 25-30 mm, or into the grooves of the connector itself (if provided by the manufacturer). At the connection points, it is important not to break or lose the rubber seals that go in the connector (coupling) itself.
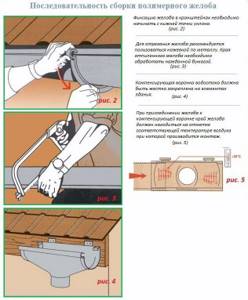
- The drip line is attached to the roof on top of the brackets. One side is nailed to the roof (to the sheathing or plywood, depending on the type of roof), and the second is lowered into the gutter so that the water flows into it and does not flow past.
- Drainpipes are mounted at a distance of 3-8 cm from the wall, this distance is adjusted with a pipe bracket. If you screw it all the way in, the distance will be shorter; if you screw it in halfway, the distance to the wall will be greater. You always need to consider whether façade work will be carried out and adjust the distance based on this. So, if in the future the house will be sheathed with foam plastic 50 mm thick and plastered, then the distance from the pipe to the wall should be at least 9 cm. The same must be taken into account in the distance from the ground: if a blind area is made, then take a reserve, relying on its future height.
When installing a drain yourself, it is important to correctly calculate the angle of the roof and the slope of the water, so that moisture does not get into the cracks and joints. Despite the simplicity of the work, you may encounter errors:
- insufficient slope of gutters, which will complicate the operation of the drain. The gutters will become clogged and fail to perform their function;
- insufficient number of risers, which will lead to water overflow;
- displacement of the risers during installation, which leads to a violation of the design slopes and the position of the water intake funnels.
To place an order or consult, call us at:
+7 495 642-42-07
Mon.-Fri. from 8-00 to 18-00
What you need to know about gutters
What you need to know about gutters
A drainage system for a home is not just an aesthetic detail. First of all, it is a means of protection against the destructive effects of precipitation. When there is no properly organized drainage, rain and melt water flows down the walls. This leads to the appearance of stains and smudges, cracks and potholes in the brickwork or plaster, and destruction of the facade cladding. Water destroys the blind area and washes away the foundation, causing soil subsidence and skewing of the building. A properly installed drainage system prevents all of these negative scenarios. But, having decided to install a drainage system on your country house, you immediately ask yourself a number of questions. What types of drainage systems should you pay attention to? What does the drainage system consist of? What difficulties may arise during its installation?
Materials for gutters
Today the market offers a wide range of drainage systems, differing in design parameters and materials. In general, this wide selection can be divided into two large groups: metal (galvanized, galvanized with coating or copper) and plastic gutters.
For those who care about quality and durability, it is recommended to install metal gutters that can withstand high snow loads and temperatures from -500C to +1100C.
Choosing a metal drain
The drainage system is selected according to several criteria: area of application, cost, durability of the material, aesthetic preferences.
Galvanized steel gutters are used mainly in industrial buildings and housing and communal services facilities, but sometimes they are also found in private households. The main role is played by the low price, while no attention is paid to the low corrosion resistance. It is obvious that galvanization is not durable: “Soviet” galvanization of class 1 with a coating thickness of up to 40 microns is practically not found today, and galvanization of class 2 has a layer of zinc only 5-9 microns thick, so rust will appear on it within 10 years. Galvanization is almost impossible, so it will not be possible to extend its service life or update its appearance in this way. A good roof will last 50 years, i.e. saving on the quality of the drainage system, you will have to change it at least ten times.
Copper gutters are wear-resistant, have the highest level of corrosion protection, but are the most expensive. In addition, copper oxidizes unevenly and dark and green spots appear on gutters.
Gutters made of galvanized steel with a polymer coating have a level of corrosion protection comparable to their copper counterparts, and they are resistant to mechanical damage. They attract consumers with a variety of colors and allow you to choose the gutter to match the material and color of the roof or walls.

Metal drainage structures
Structurally, the factory variety of modern drainage systems for private construction can be reduced to two types: round drains, the so-called “Scandinavian” type, and rectangular drains, “American” type. In Central Russia and the northern regions, gutters with a round cross-section are more in demand, since with this shape, ice is squeezed upward when freezing, without deforming the gutter. In southern regions with high rainfall, rectangular gutters are preferred - such a gutter can hold a larger volume of water and avoid overflow. The choice depends only on the customer's preference.
Drainage systems Metal Profile
Having analyzed the needs of the market, Metal Profile Company will develop and produce drainage systems for all categories of buildings. These are the drainage systems “MP Modern”, “MP Prestige” and “MP Project”. Each of them has its own design features and scope of application.
The drainage systems "MP Modern" and "MP Prestige" are used mainly for private houses and small industrial buildings. "MP Prestige" is a circular cross-section system of the "Scandinavian" type, with a gutter with a diameter of 125 mm and pipes with a diameter of 100 mm. The system elements are made of galvanized steel 0.5-0.6 mm thick with a double-sided, most durable polymer coating “plastisol” of 100 microns on each side or with a branded PURMAN® coating in elegant black color. The double-sided coating reliably protects the inner surface from damage by ice and debris, and the outer surface from damage during transportation and installation.

“MP Modern” is an “American” type drainage system, with a complex shaped gutter with a cross-section of 86x120 mm and rectangular pipes of 76x102 mm. The material is galvanized steel 0.5 mm thick with a plastisol coating 200 microns thick on the outside and protective varnish on the inside.
The round drainage system "MP Project" is intended for multi-storey residential and industrial buildings, its gutter has a diameter of 185 mm, and the pipe has a diameter of 150 mm. The drainage system is intended primarily for the budget segment; it is made of galvanized steel with an inexpensive polyester coating.
Which gutters are suitable for the harsh Russian climate?
For most drainage systems, Metal Profile Company uses plastisol-coated steel, which is resistant to corrosion and mechanical damage. Unlike Europe, where 2 mm thick holders are used, Metal Profile Company products produce 4 mm thick holders in galvanized steel with powder coating. Such holders are able to withstand loads ranging from 50 to 100 kg, i.e. The drainage system can withstand even an avalanche of snow from the roof.
Tags: #Drainage system
Return to list