Practical benefits of plants for a pond
It doesn’t matter what size the country pond is. A mini-pond will decorate a small garden; on a larger plot, a man-made lake will look picturesque. To design the water surface and shores, you will need natural materials: sand, stones, pebbles. But in order to give an artificial reservoir the most natural look possible, you cannot do without aquatic and coastal plants.
A deserted water mirror surrounded by the same shore looks boring. Aquatic plants for a pond are not only an opportunity to show your imagination and turn a plastic container dug into the ground into a pearl of the garden. The decorative purpose is important, but if you choose the right flora, you can also solve important practical problems:
- Saturate the water with oxygen, create a habitat suitable for aquatic fauna (fish, snails).
With an emphasis on cereals Source yandex.net
- Maintain the ecosystem by preventing mud from growing and helping the water stay clean.
- Protect the water column from excessive penetration of ultraviolet radiation.
Therefore, pond plants are conventionally divided into two groups: ornamental crops and health plants. The former are distinguished by their spectacular appearance, large floating leaves and bright flowers. These include water hyacinths, lilies, and lotuses. The latter are not so impressive, but without them it is impossible to maintain the health of the reservoir. The water remains clear thanks to swampweed, hornwort, and elodea.

With a waterfall Source diz-cafe.com
Plants and animals of rivers, lakes, ponds. Educational complex "Planet of Knowledge", 4th grade, The world around us. - presentation

Plants of rivers, lakes, ponds.
ROGOZ - grows along the banks of fresh water bodies. A plant with thin slender stems and long leaves. At the top of the stem there is a dark brown cob. Its stems are very flexible and strong, and the leaves inside are empty and filled with air.
REED – tall as a cattail. The leaves are thinner and narrower, the stem is empty inside. At the top of the stem there is a dense panicle of dark purple spikelets.
WATER LILY - it is easily recognized by its white flowers and round shiny leaves floating on the surface of the water. Water lily flowers turn to follow the sun all day long, and in the evening they close and fall into the water. In the morning the buds emerge and open. After pollination, the flower fades, and in its place a fruit appears - a black berry. This is a rare and protected plant.
In summer, the ponds are covered with a green cover of duckweed. It consists of a small flat circle - a stem, floating on the surface of the water, with a root hanging down. Duckweed blooms very rarely, and reproduces mainly by pieces of the stem. In the fall, it sinks to the bottom and spends the winter there, and in the spring it floats to the surface again.
There are plants that are completely submerged in water. One of them - ELODEA - is a small plant with a branching stem that is covered with small leaves. Elodea grows very quickly, often forms large clusters and displaces other plants.
There is a lot of various ALGAE in the water.
Animals are inhabitants of rivers, lakes, and ponds.
Fresh water is a habitat for various insects. Most of them are MOSQUITOES. Their larvae develop in water.
Many DRAGONFLY live among the coastal plants. Their larvae also develop in water. Dragonflies are predators and most often feed on mosquitoes, which they catch in flight.
On the surface of the water you can see predatory water striders. They glide along the smooth water surface on long thin legs.
Wiggle beetles - spin on the surface of the water in search of prey. In case of danger, they quickly dive into the water or scatter in different directions.
Adult swimming beetles and their larvae are voracious predators. They attack insects, fish fry and tadpoles.
WATER BEETLE - swims slowly, most often crawls on aquatic plants. They feed mainly on plants. In case of danger, they throw out a black thick liquid and squeak frighteningly.
Crayfish live at the bottom. Eating the remains of dead plants and animals, they act as orderlies.
Pond snails are herbivorous snails that attach to aquatic plants. Their body is located in a spirally twisted shell and consists of a head, torso and legs.
Toothless live at the bottom, buried in the ground. Their shell consists of two valves. They are called living filters. By passing a large amount of water through their body, they purify it of various impurities and make it transparent.
Permanent inhabitants of fresh waters are FISH. CRUCCIAN CARESAN BREAM
PIKE GENDOW
Frogs feed in the coastal area. Frogs are hunted by snakes.
Wild GEESE and DUCKS build nests in the thickets on the shore. They feed on green parts of plants, seeds, snails and insects.
HERON is a large bird with a long sharp beak - it hunts frogs, fish, and snakes.
MUSKMARK OTTER OTTER BEAVER BEaver Among the aquatic inhabitants there are also animals: BEAVERS, MUSKRATS AND OTTERS. They swim and dive well, they have thick, greasy fur that does not let water through. Between the toes of the hind legs there are swimming membranes. The tail acts as a rudder during swimming.
Flora diversity
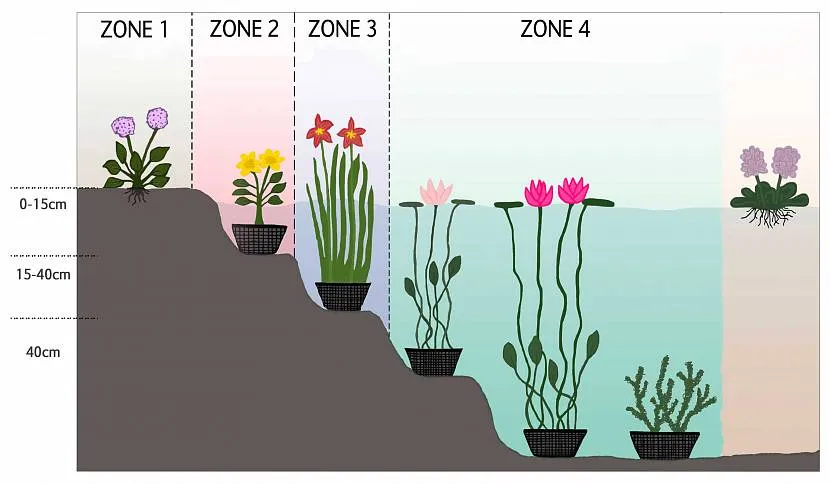
Plants with different functionalities are used to decorate a pond. Understanding their characteristics allows you to zone the pond and plant certain specimens taking into account the depth. There are several groups based on the accommodation area.
Oxygenators
These pond plants are valued for their developed ability to extract carbon dioxide dissolved in water and return oxygen. Oxygenators are needed in every body of water, since they are the ones who prevent the water from blooming. You can’t do without them if there are fish in the pond: underwater greenery will serve as food for them and provide shelter during spawning.
Most of the oxygenating plants are hidden under water; it is convenient to use special plastic containers for planting them. The disadvantage of this method is obvious: the container is visible in the water column, which spoils the overall impression. Owners who want to use container planting should also think about masking the plastic; gravel, pebbles or soil are suitable.
Zone planting Source aqua-store.fr
Some types of oxygenators are finicky and do not always tolerate domestic climatic conditions well. Therefore, to be on the safe side, it is recommended to plant two or three types of oxygenating plants.
Plants for a water purification pond include the following:
- Elodea . A perennial aquatic grass native to the North American continent, it has a decorative appearance. The main disadvantage is that the stems grow very quickly (another name is water plague), regular thinning is necessary; no other care is needed.
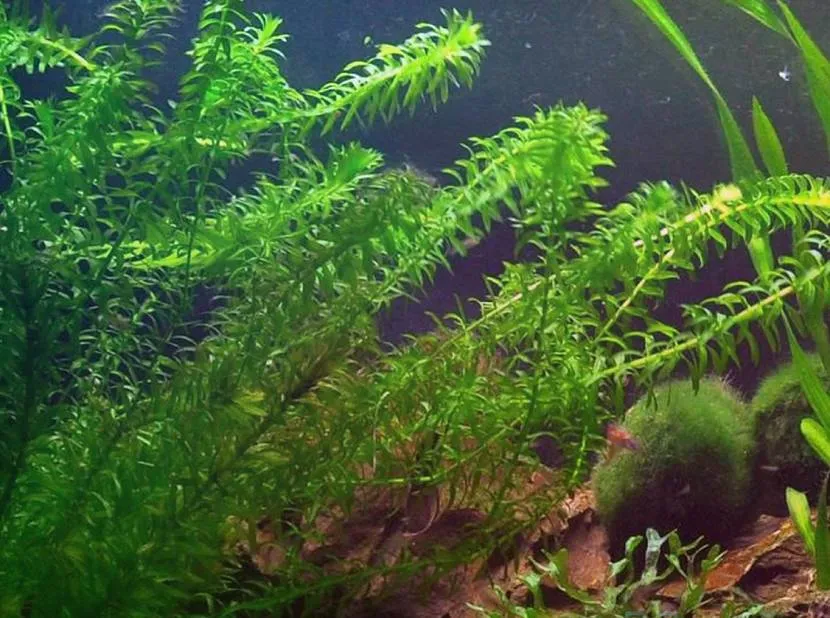

Elodea - water plague Source vaquariume.ru
- Rdest . A perennial species with a well-developed root system, it forms thickets in standing water. Unpretentious, tolerates wintering well. Serves as food for fish, shellfish, insects; fish spawn in the thickets of pondweed. Forms inflorescences in the form of a spike, seated with small yellowish flowers.
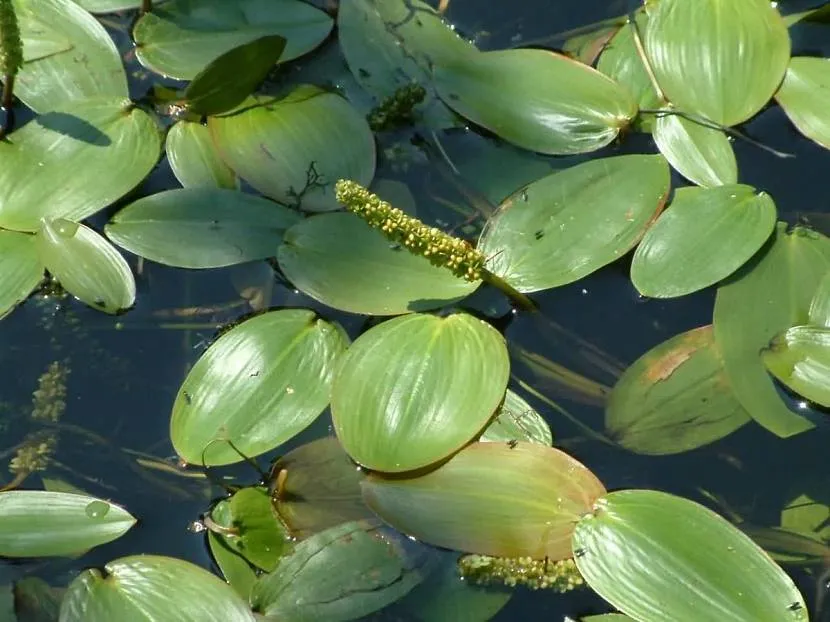

Perennial pondweed Source shopify.com
- Water buttercup (mulberry) . Unlike ground buttercups, it does not contain toxic substances and is propagated by cuttings. Numerous white flowers will decorate any pond.

See also: Catalog of companies that specialize in landscape work of any complexity
Floating
They, like oxygenating plants, prevent the water from overheating and blooming. In floating pond plants, the root is never connected to the soil, and the flowers and leaves are held above the surface of the water. They grow quite quickly, and if you don’t watch them, they will quickly fill the entire surface of the reservoir. They adapt floating species by simply lowering them into water; most require no maintenance.
The most famous floating species is duckweed, which forms a picturesque emerald carpet. Another species is Azolla, a genus of floating ferns that resembles moss in appearance.

Azolla - floating fern Source pinimg.com
Eichornia (water hyacinth) looks harmonious, with its emerald leaves and pale lilac flowers reminiscent of orchids. A small pond will be decorated with Pistia (water cabbage) with funny rosette leaves. Both plants are native to the tropics, so they do not tolerate cold and overwinter in the aquarium.

Eichornia (water hyacinth) Source sornyakov.net
Deep-sea (hydatophytes)
Hydatophyte plants are planted in containers in a deep place, closer to the center of the reservoir. They are completely hidden in the water; the stems grow to the surface, where leaves float and flowers appear. Most hydratophytes bloom very beautifully, which makes them an important decorative element.
Among the deep-sea species that grow in reservoirs, the lotus and nymphea (water lily) are especially impressive. The nymph is called the queen of the pond. It has oval, heart-shaped leaves and large, pink or white flowers. Despite its tropical origin, winter-hardy varieties of nymphs have been bred. They bloom luxuriantly from May to September, bloom in the early morning and close in the evening, and cope well with climatic vicissitudes.
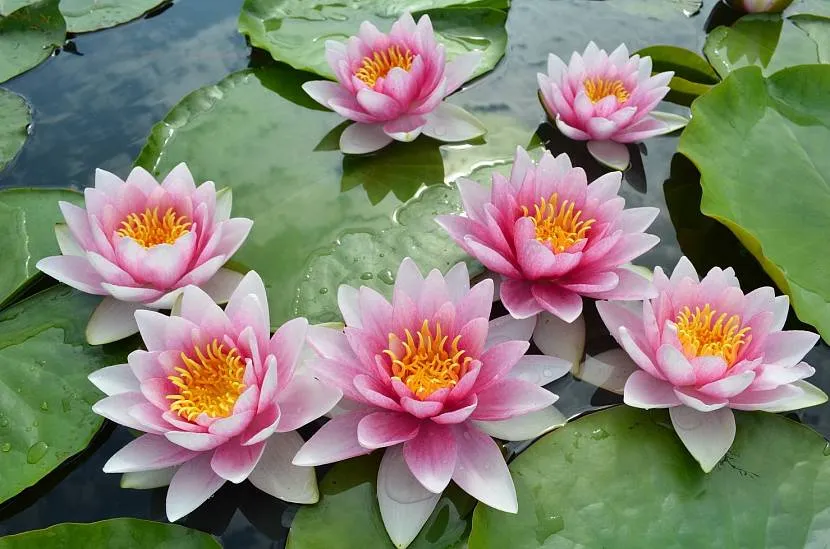

Nymphea in a pond Source twimg.com
Tropical varieties of nymphs are delicate and capricious, more suitable for breeding in an aquarium. If the pond is shallow (0.5-1.5 m), small and medium varieties of nymphs with red, pink or peach flowers are planted. To ensure that nymphs survive the cold, closer to winter they are taken out of the pond and stored in a damp basement with a temperature range from 0 to +10°C.
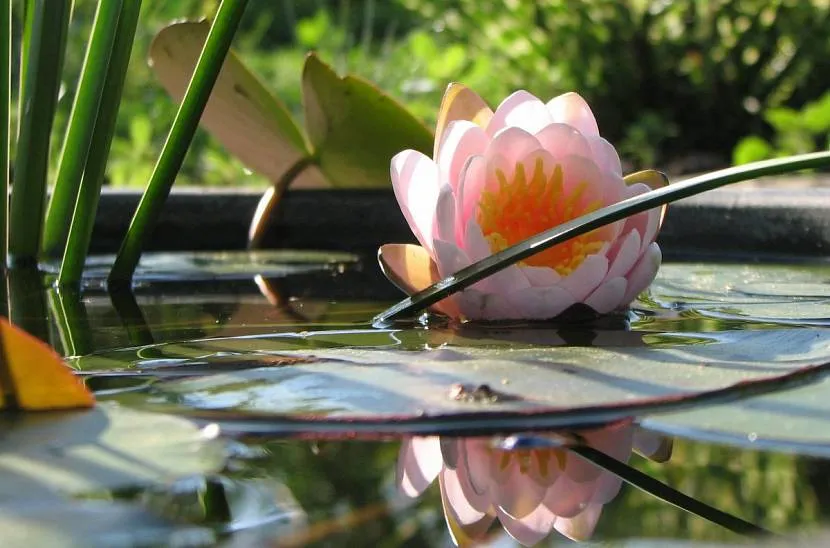

Pink miracle Source botanichka.ru
Plants of fresh water bodies photo
Photographs, pictures of medicinal freshwater plants, or plants growing in or near freshwater bodies could always provide much more information about a plant than its detailed written description. Not every person will be able to correctly draw a picture from the proposed description, at the same time, photographs and pictures of lake and river plants and plants can give a comprehensive idea of the appearance and certain characteristics of the plant.
This page contains all photographs, pictures and photos of medicinal fresh water bodies of plants and names
listed in our Encyclopedia of Medicinal Plants. By clicking on any plant (listed below) that interests you, you will find: photographs of marsh plants in nature, photographs of flowers of fresh water plants, photographs of leaves of lake plants, river plants and other parts of plants.
- Photos of fresh water plants on A
- Calamus marsh
photo - Althaea officinalis
photo
- Photos of fresh water plants on B
- Ledum marsh
photo - Common sheep
photo
- Photos of fresh water plants in B
- Water lily
photo - Water pepper
photo - Black crowberry
photo
- Photos of fresh water plants on G
- Pepper Knotweed
photo - Snake knotweed
photo - Knotweed
photo - Bird's knotweed
photo
- Photos of fresh water plants on D
- Elecampane tall
photo
- Photos of fresh water plants on I
- White willow photo
- Illy root photo
- Photos of fresh water plants on K
- Swamp marigold photo
- Lake reed photo
- Swamp cranberry photo
- Yellow egg capsule photo
- White water lily photo
- Photos of plants of fresh water bodies on L
- Potentilla gossamer photo
- Photos of fresh water plants on M
- Bear ear photo
- Photos of fresh water plants on P
- Moss club-shaped photo
- Photos of fresh water plants on R
- Cervical cancer photo
- Broadleaf cattail photo
- Small duckweed photo
- Small duckweed photo
- Photos of fresh water plants in C
- Swamp dry grass photo
- Marsh grass photo
- Photos of freshwater plants on T
- Bearberry photo
- Common reed photo
- Photos of fresh water plants on X
- Horsetail photo
- Horsetail photo
Additional photographs of medicinal plants
Medicinal plants home
Encyclopedia of medicinal plants Photos of medicinal plants Photos of Red Book plants and their names Photos of indoor plants and their names Photos of house plants and their names Photos of meadow plants and their names Photos of plants from ponds and their names Photos of forest plants and their names Photos of swamp plants and their names Photos of lake and river plants and their names Photos of mountain plants and their names Photos of steppe plants and their names Photos of poisonous plants and their names
| Share this article with your friends! |
Plants around the pond
In order for the pond to fit organically into its surroundings, the usual deciduous trees and shrubs, conifers, herbs and flowers are planted around it. Typically, trees are placed away from the water surface, flowers and herbs are planted at the water's edge, and bushes are planted in between. This is done for two reasons: the pond remains open for admiring, and falling leaves do not clog the water. Among the pond plants planted in the coastal zone are the following species:
- Caragana tree (yellow or Siberian acacia) . Deciduous shrub with lacy foliage and small yellow flowers of the moth type. The bush is undemanding to soil quality and tolerates frost well.
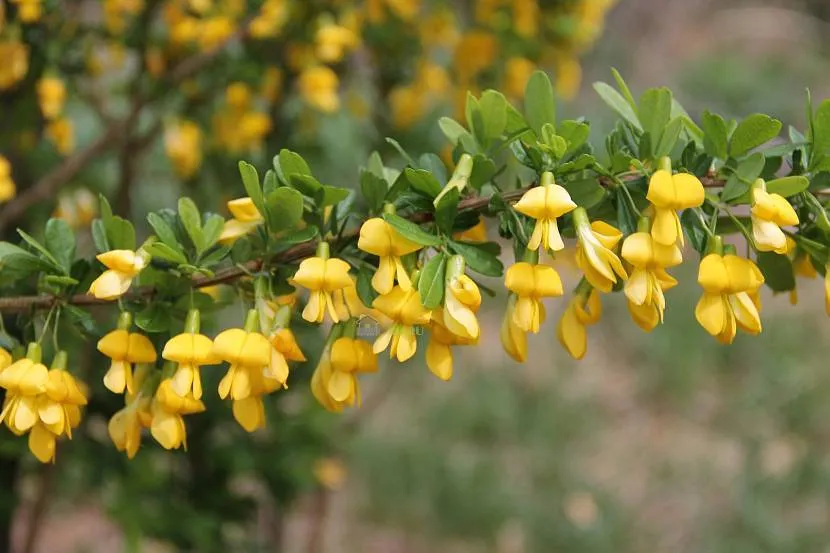

Siberian acacia Source 1d.ru
- Shaggy plum Pendula . Weeping, slow-growing tree; Blooms profusely pink before the leaves emerge.

Shaggy plum Source sadrium.ru
- European larch . Standard varieties with a weeping crown (Puli, Kornik). A small tree with soft needles that fall off in winter, it is frost-resistant, but needs sun and loves fertile soil.

European larch Source romashkino.ru
Near-aquatic
Submerged or semi-aquatic plants are common in the wild and are available for cultivation in artificial ponds.
Examples of aquatic plants growing in shallow or near water:
- Swamp iris - distinguished by bright yellow flowers with a brown pattern, prefers sunlit areas and fertile soil, stem height up to 1.5 m, suitable for ponds, planted to a depth of 40 cm.
- Smooth iris - blooms from June to October with blue or purple flowers, up to 1 m high, and goes well with other aquatic plants.

Briefly about the main thing
A pond in the garden is not only water and stones; Plants become an important decorative detail. They help to fit an artificial reservoir into the landscape and perform other functions: they purify the water, protect it from sunlight and saturate it with oxygen.
Plants are planted in zones, taking into account their characteristics. Oxygenating plants are natural purifiers; they are entirely hidden in the water column. Floating species make the surface of the pond picturesque; hydratophytes with their large and bright flowers become the highlight of the landscape. Plants in the coastal zone should be selected especially carefully, taking into account their size and moisture-loving properties.
Ratings 0
Oxygenators
One of the most important types of underwater plants that supply the entire body of water with additional oxygen. Many of them are also used as food for fish. Their advantage is also the improvement of sanitary conditions and biological purification of water.
Names of aquatic plants-oxygenators:
- Common marsh grass (Callitriche), also called water star.
- Urut (Myriophyllum) belongs to the perennials of the Slanoyagodnikov family; it has shoots rising above the water and a creeping rhizome. Long stems (up to 1.5 m) are covered with thin leaves and form an elegant lace of thickets under water, for which it is called “pinnate”. It is grown as a coastal plant, propagated vegetatively, its parts can be planted directly into the ground to a depth of 1.2 m in the spring and summer. Looks great in small ponds, where it forms beautiful patterns under water.
Creating a reservoir: rules
Using aquatic plants to decorate an artificial pond in a garden plot or on the territory of a country house will create a unique natural landscape and provide the opportunity to admire beautiful leaves and flowers throughout the warm season.
Regardless of the size of such a reservoir, it is necessary to select several types of plants with different flowering periods, sizes and shapes of leaves, also taking into account their height and planting depth. The main rule is to maintain biobalance in an artificial pond, in which, for the safe coexistence of all plants, fish and microorganisms, it is necessary to ensure that the vegetation covers the water surface by half or more.
The center of the pond is given over to beautifully flowering plants - water lilies, the variety of which is selected based on the area of the pond. Coastal species (arrowhead, calamus, susak) are planted along the edge; forget-me-nots or marigold are planted in shallow water; moisture-loving plants (sedges, irises, daylilies) with a strong root system can be placed on the soil along the edge, which will help preserve the shore from erosion.
Free-swimming species (duckweed, teloris, vodokras) under favorable conditions multiply very quickly and can occupy the entire surface, so they must be periodically removed with a net.










