Geogrid is a new, but already popular material for strengthening embankments and slopes. Without it, the lines quickly lose their clear outlines, the dug up soil crumbles
Geogrid is a polymer fabric with cells in the form of a honeycomb made of non-rotting material. They have a flat or three-dimensional structure. This is clearly visible in the photo of the geogrid.
Can be made from: polypropylene, high-density polyethylene, polyester, carbon fiber, innovative synthetic raw materials, metal-plastic.

On top it is covered with polyvinyl chloride, which protects it from destruction under ultraviolet radiation. This is important when the canvas is not completely covered with substrate or grass.

Also, the geogrid is resistant to destruction by frost, humidity, microorganisms, acids, and alkalis.
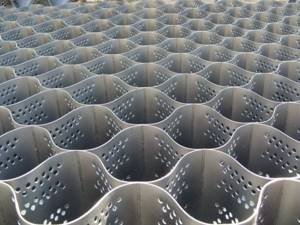
The synthetic material does not decompose and can last at least 50 years.
Due to the manufacturing and design features of the geogrid, it has high tensile strength. The scope of application of the geo-fabric is wide - it strengthens pits, various slopes, strengthens roads, coastal zones, slopes, and helps in the formation of garden designs.

When creating artificial reservoirs, the geotextile also helps strengthen the bottom. In general, any earthen area that experiences high loads should be reinforced with geogrid.

The strengthened soil does not settle over time, it does not form holes, surface curvatures, etc.

Geogrid is a strong competitor for strengthening slopes with concrete geoplates. Geoplates are more expensive and have difficulties in transportation and installation.
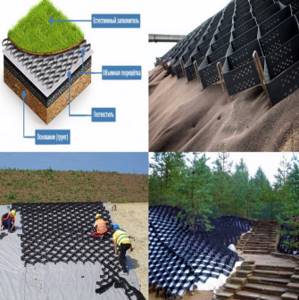
Laying
Laying a geogrid is incredibly simple - take the required part of the canvas, stretch it, lay it on the base, and pour any substrate into the cells for fixation - soil, sand, pebbles, crushed stone.

Purchase and inspection of land
How to make drainage on a site - the secrets of a master on how to make drainage to drain water yourself!
- How to clean a pond: a detailed description of how to clean a pond quickly and easily with your own hands (130 photos + video)

Planting fast-growing plantings with a branched root system that does not go far into the depths will help to quickly strengthen the soil in the geogrid.

The size of the geogrid cells is selected depending on the base that needs to be strengthened. There are canvases with cell sizes from 160*160 to 410*410 and heights from 50 mm to 20 cm.

Geogrid laying technology
- When performing work to strengthen sedimentary sediments (road pavement), five main types of this work should be considered: Work to strengthen the lower layers of sedimentary sediments on temporary roads. In these cases, the geogrid is laid under a base layer of granular materials (transitional type coating). The geogrid here performs the tasks of reinforcement and provides protection against mutual penetration of layer materials into each other. Those located above the geogrid, and located below it. The use of a geogrid increases the service life of the subsector between repairs;
- Work to strengthen the lower layers of sediments, classified as capital, carried out on roads with intense and heavy traffic. The geogrid is also laid under the carrier base layer, made of granular materials. In these cases, the geogrid is assigned the task of protecting materials of different layers from mutual penetration, as well as increasing the service life of the subsidiary;
- Strengthening of transitional type DOs, which play the role of a primary structure in the early stages of construction. Geogrids are placed there and solve the problems of protecting against interpenetration, strengthening BS at the first stage of construction work, as well as increasing the service life of BS;
- Strengthening roadsides. The geogrid is spread under the layer of reinforcement of their bulk materials. Problems to be solved: protection and strengthening, as well as increasing the period of operation;
- Strengthening ABP (asphalt concrete pavements). The geogrid is laid directly under the ABR layer, which improves the performance of the coating in terms of “stress/strain” in areas where return cracks occur, performs waterproofing functions, and increases service life.
Lawn grate
A more modern and durable version of the geogrid is the lawn grid. Eco-parking areas are being created on its basis. This eco-parking looks very neat and modern. It is a grass flooring similar to a lawn.

The grass grows through the laid volumetric geogrid and is fixed with lawn soil. It is easy to care for – the grass is prevented from growing by a car driving over it.

Decorate the site according to Feng Shui: location features, design elements, Feng Shui zones. How to work with a ba gua diagram? Secrets of garden decoration
How to arrange a plot in the Russian style: the best ideas for creating a beautiful and cozy plot (145 photos and videos)

Do-it-yourself pond on a summer cottage: detailed description of the construction of a decorative pond, design and design options (110 photos and videos)

Moreover, it creates and protects the soil ecosystem with minimal maintenance - the lawn only needs to be watered systematically.
Production Features
Geogrid for slopes is made of synthetic materials that are resistant to adverse external factors.
During the production process, strips of polyester, polyethylene or polypropylene can be used. All fragments are connected using high-strength welds. When the working surface is stretched, a strong frame is formed. The material protects slopes and slopes from crumbling and destruction. Our company produces geogrids suitable for solving most problems related to strengthening. Our products are resistant to various substances, do not rot, and are easy to install. Its service life is more than 50 years. To increase friction between the cell walls and the filler, the surface of the material is textured. This gives them a rough appearance. This is important if concrete mixture or fine-grained sand is used as filler.
Composite geogrid
Composite geotextile is used for the same purposes. Its difference is that this variety combines geogrids and geotextiles.

The function of geotextiles is additional and secondary. A composite geogrid combines the roles of a separator and a filter, which increases adhesion to the surface.

Laying a composite geogrid solves the issue of strengthening the asphalt concrete layers of roads, parking lots, and gas stations.

Where are geogrids used?
The advantages of geogrids and geogrids are highly appreciated by landscape designers. The material can completely change the visual perception of the external decor of the site, by changing the relief, arranging and landscaping lawns. A coating made of durable and rigid modules is recognized as the optimal solution for cases where increased demands are placed on the load-bearing capacity of the base.
Volumetric geogrids are most widely used in strengthening coastal zones of natural and artificial reservoirs, protecting road and hydraulic structures from water and wind erosion, arranging supporting walls, and fixing the soil foundations of road embankments. Despite the apparent simplicity of the laying technology, in order to obtain positive results, it is necessary to follow a certain sequence of work operations.
Strengthening slopes of varying degrees of steepness
Gentle slopes up to 8° do not require reinforcement. They are well strengthened by germinating plantings. Their roots grow deep and are fixed to stones in the soil. This is enough to prevent the slope from settling.


Stone retaining walls are options for constructing and arranging areas with a slope. 115 photos of landscape design ideas
How to arrange a summer cottage - design options, beautiful ideas and stylish design solutions (90 photos + video)
- How to make a well with your own hands - design ideas and recommendations on how to beautifully design a well (110 photos + video)
On moderately gentle slopes of 8-15°, plants appear naturally, but can be washed out by rainfall, so it is advisable to strengthen them with geogrid, especially slopes of complex shapes.

Steep slopes of 15-35° definitely need reinforcement. It is very important to supplement the reinforcement with geotextiles - a non-woven material that will prevent soil erosion.
- when the angle of inclination exceeds 45°, use a cell edge measuring 200 mm;
- up to 45° – 150 mm;
- up to 30° – 100 mm;
- up to 10° – 50 mm.

Advantages of using geogrid

- Durability , resistance to mechanical damage and environmental factors (temperature fluctuations, moisture, mold, insects and rodents) and chemical agents (oil, gasoline, fertilizers and weed killers);
- Preservation of water purity (polymer materials do not emit harmful substances and are suitable for use in nature reserves, when improving reservoirs for fish farming);
- Environmental friendliness (the structure and material of the geogrid does not interfere with the natural growth and development of the root system of plants);
- Simplicity and high speed of installation (does not require special skills or the use of heavy equipment);
- Versatility in use (suitable for reservoirs with standing water, medium and fast current, can be used on both stable and poorly cohesive soils);
- Wide possibilities of landscape design (planting of clay banks, creating terraces and approaches to the water, decorative decoration with pebbles and marble chips);
- Invisibility (after filling with filler and germination of plants, the geogrid cells become invisible even at close range, which allows the reinforced area to look natural);
- Low cost (in comparison with materials such as concrete piles and hardwood timber, geogrids are much more affordable and much easier to transport).
Photo of geogrid for strengthening slopes
Did you like the article? Share


0