Why is vaccination needed?
The main purpose of grafting is to more rationally use tree resources. After all, fruiting of certain crops often stops not because of the trunk and root system of the tree. The formation of the crown of old trees is difficult; young shoots practically do not form on them and the yield is significantly reduced.
Successful result of apple tree grafting
At the same time, the root system of the tree works more and more efficiently every year (since it is constantly increasing in size). This results in a paradoxical situation: the roots supply the plant with nutrients, but the plant cannot use them anywhere due to the degradation of the crown.
It is at this moment that vaccinations come to the aid of the gardener. In place of the old crown, young cuttings take root, which, thanks to the feeding of a powerful root system, develop very quickly. Literally after 2-3 years the tree begins to produce stable yields. At a normal pace, this process would take much longer.
The same or another variety or species can be used as a grafting material. This does not play any role - the nutrients extracted by the root system from the soil are absolutely the same for all plants.
Grafting with a cutting into the butt

This method is used when the rootstock is noticeably thicker than the grafted cuttings. The rootstock is shortened to the desired height. On one side, use a knife to carefully cut off a strip of bark with a thin layer of wood. The width of the cut should correspond to the diameter of the grafted cuttings, and the length should be at least three times its diameter. Step back a third from the top of the cut and make a shallow cut.
The cutting is prepared in a similar manner to the improved copulation and compared to the cut on the rootstock, ensuring that the cambial layers are accurately aligned.
Remember: for better fusion of the graft, the top cut of the cutting should be slightly higher than the cut of the rootstock. The grafting site is tied with tape, being careful not to displace the cambial layers.
Then the cuttings are cut above the 3rd - 4th bud. Cuts on the cuttings and rootstock are covered with garden varnish.
General concepts

Typical method of rejuvenating old wood
Grafting involves two different types of biological material: scion and rootstock.
- A scion is a cutting or branch that is grafted onto an already formed root system or tree.
- The rootstock is the part of the plant to which the desired variety is grafted.
The rootstock can be:
- a young tree of a variety or species well adapted to the area
- old tree in need of renovation
- adult plant used as a “donor”
- a damaged or injured plant that you would not want to uproot
Despite the fact that the scion after the procedure will determine the varietal characteristics of the plant, it does not have its own roots and receives all the necessary elements from the rootstock.
This means that it is the rootstock that will determine the yield, the duration of the growing season and flowering, resistance to bad weather, the lifespan of the plant and many other factors.

Growing walnut rootstocks
Therefore, in order for the future garden tree to develop correctly and evenly, it is necessary that the rootstock has the following qualities:
- was well adapted to the climatic conditions of the growing region
- was compatible with the scion
- had a reliable and extensive root system
It is advisable to vaccinate in the spring. It is in the spring, during the period of maximum sap flow, that the survival rate of the scion is maximum.
Scion cuttings should be collected in early spring, as soon as the snow melts. The collection procedure must be completed before the first vegetative buds open.
Cuttings. Where is the best place to cut them?
Note: Ripened shoots should be taken from the outer parts of the crown of mature trees, well illuminated by the sun. Such shoots are characterized by short internodes (gaps between the buds) and highly developed eyes in the leaf axils. They have a high ability to assimilate and perceive organic substances, which the cutting needs for its rapid fusion with the rootstock and the formation of new shoots.
Cuttings for grafting are cut from fruit-bearing trees that have been tested for yield and grade.
Note: Cuttings should not be cut short (8-10 cm); thin, crooked, damaged ones, from overgrown branches, or from “tops” are also not suitable.
You should not cut off the scion and shoots that have grown in dense areas and on the north side, or parts of the crown of which are woven into a neighboring tree, as well as from trees of unknown varieties.
Timely preparation of cuttings for grafting is of great importance. Cuttings should be taken only from pure-quality mother plantings and from trees characterized by high productivity and stability. The cuttings should be 30-40 cm long, with well-developed growth buds. Thin, poorly formed shoots with underdeveloped buds are not suitable for grafting. In this case, it is better to use cuttings from the previous year’s growth, which has growth buds.

Preparation of scion cuttings

Soaking cuttings before grafting
In order for the vaccination to give a guaranteed result, it is important to obtain good graft material. There are many ways to obtain cuttings from varietal trees. From a banal purchase to self-production.
If you obtain cuttings yourself, you can use the following recommendations:
1You should choose cuttings from a proven and well-bearing tree. The cuttings are directly cut from the outer crown located on the south side
2 It is believed that the best scion is one-year shoots with a diameter of no more than 5-6 mm, equipped with at least 3 buds
3The length of the cutting should not exceed 40 cm
4Do not use frozen or dried cuttings. The criterion for a cutting to be unsuitable for grafting is its brown or gray core
5The number of cuttings prepared should be at least 10-15 pieces for one variety. Such a number of cuttings will not only increase their survival rate during storage, but will also allow you to select the most suitable cutting in diameter

Grafting of fruit trees
It is recommended that the buds be located quite compactly (at least 1-2 pieces per 15-20 cm of cutting). It is believed that greater distance of the buds from each other will lead to too different nutritional conditions for them. It is best to cut cuttings using pruning shears and then trim them with a grafting knife.
You can store cuttings in wooden boxes in a cellar or basement without access to light. However, they must be in a damp environment (for example, wet sawdust or a rag moistened with water). Cuttings should be removed from storage no earlier than one day before grafting.
If, for some reason, grafting is carried out in the summer, then the process of preparing cuttings is significantly simplified - they are cut immediately before grafting. Another advantage of summer grafting (besides the absence of the need for storage) is that only two buds are enough on the scion, and they may already be in bloom.
When is budding performed?
Depending on the timing (or rather, in which season) this procedure is carried out, it is customary to distinguish between budding:
- - so-called “sleeping” eye (summer);
- - “sprouting” eye (spring).
It is impossible to give specific dates for carrying out the described procedure, since the rate of maturation of wildflowers and cuttings is determined, first of all, by the peculiarities of the local climate. It is also important to take into account that in old and transplanted rootstocks, sap flow ends earlier, so they are budded first, after which they move on to young and untransplanted wild ones.
In most regions of the middle zone, budding of fruit trees with a dormant eye is carried out in the second half of summer - from approximately the third decade of July to mid-August (i.e. throughout the entire period of summer sap flow). The eyes for this procedure are taken from the current year's growth.
In turn, budding with a germinating eye is carried out during spring sap flow, when the bark is easily separated from the branches. In this case, eyes from last year's growth are used. The preparation of scion material for spring grafting begins in the fall or early spring. The awakening of the eyes occurs approximately two weeks after the procedure.
It is important to note that plants that have undergone spring budding are noticeably behind in development by the end of the growing season - compared to summer budding and plants grafted from cuttings. For this reason, experienced summer residents recommend budding fruit trees in the spring only for fast-growing species and only when traditional spring grafting with cuttings is not possible for some reason.
Optimal timing for vaccination

Spring grafting
The most suitable timing and methods of vaccination for various crops are given in the table:
| Culture | Vaccination dates | Vaccination method |
| Apple tree | March, April | Grafting with cuttings |
| end of April – beginning of May | Budding, eye grafting | |
| Pear | early spring | Vaccination for bark |
| beginning of sap flow | Bridge grafting | |
| first ten days of April | Into the cleft | |
| end of April - May | Side cut | |
| Cherry | spring | Any way and time |
| August | Grafting into cleft | |
| Cherries | spring | Any way |
| Aug. Sept | Into the cleft, behind the bark | |
| Plum | March, April | Budding or copulation |
| April May | For the bark | |
| Peach | 2nd ten days of March – end of April | Split with covering of the grafting site with film |
| May | Any method, covering the graft with paper |
Preparation of grafting material
For grafting, annual, or less often biennial, growths are used. Cuttings are harvested during the dormant period of plants and are kept in a dormant state until the operation begins. It is best to cut the cuttings at the end of November - December, when the temperature reaches below zero, and store them in a cool room (about °C) or bury them in a snow pile, which can be placed in the shady part of the garden. To prevent the snow in the piles from melting ahead of time, it is sprinkled with a layer of sawdust or shaded with covering material folded in two or three layers. To maintain high humidity, the cuttings are wrapped in a cloth moistened with water or covered with wet sawdust and covered with plastic wrap.

At the end of winter, the blanks are taken out of storage, their external condition is assessed and cuts are made with pruning shears: moldy cuttings or those with darkened wood are not suitable for grafting. If necessary, new material is prepared and put back in a cool place until the grafting time.
You can take cuttings in early spring, before the buds swell. However, if the winter is harsh, annual growth may be damaged by frost.
Tree grafting methods

Budding
There are several practically standardized methods of grafting fruit trees, which are traditionally used in spring. It is in the spring that the choice of vaccination method can be any. In the summer, there are certain restrictions on the methods of grafting plants.
Copulation

Preparation for grafting by copulation
Copulation The simplest method of grafting. It is carried out using a cutting with 2-3 buds. Traditionally, this grafting method is used in early spring before sap flow begins. Both the scion and the rootstock are cut at the same angle and connected to each other using any fixing material.
PROS:
- Possibility of grafting onto a rootstock of small thickness; this cannot be done in any other way
- relative ease of joining the material of the rootstock and scion
MINUSES:
- the reliability of the mechanical connection leaves much to be desired
- the cut is very fragile; there is a high probability of it breaking in the first year after vaccination
Successful copulation is only possible if the diameters of both the scion and rootstock match.
Vaccination for bark

Vaccination for bark
Grafting behind the bark In this case, the scion cutting is installed between the bark and the wood of the rootstock. A fairly reliable and safe method of grafting, since fixation is carried out by the bark.
The main advantage of this method of merging plants over others is the use of both scion and rootstock of different thicknesses. Actually, here it’s even the other way around: the thicker the rootstock and the thinner the scion, the better.
It is believed that the best time to carry out such a procedure is the beginning of May, when sap flow is maximum even for spring. In order to understand whether the optimal time for grafting has arrived, it is necessary to make a cut on one of the branches of the rootstock and check how well the bark separates from the wood. If this is done easily, you can start vaccinating in this way.
PROS:
- ease of implementation and high reliability
- More than 80% of cuttings take root
MINUSES:
- justified only in a narrow period of time - at the peak of sap flow, when the bark is easily separated from the wood
- there are restrictions on the diameter of the scion
Grafting into cleft

Grafting into cleft
Cleft grafting The most common method of grafting. It is used in cases where the diameters of the rootstock and scion differ by 2-3 times.
Technically it is carried out as follows:
- the branch or trunk of the rootstock is cut at a right angle
- cut (split) the saw cut in the middle to a depth of 3 to 5 cm
- the scion is cut into a wedge shape
- insert one or more scion cuttings into the split and securely fix the rootstock around the perimeter using electrical tape or a simple rope
PROS:
- very good mechanical contact between the rootstock and scion material
MINUSES:
- the method is relatively labor intensive
- difficult implementation with large diameters of rootstock and scion
- if there is a large amount of scion material, it is not used - for a reliable connection, a maximum of two cuttings can be placed in one split
Budding

Grafting by budding or eye
Budding This method of grafting is also called eye grafting. In this case, a T-shaped cut is made on the bark of the rootstock, into which the scion bud is inserted, like into a pocket. In this case, it is necessary that the wood of the cuttings be exclusively under the bud.
After the bud is installed, it is necessary to carefully wrap all the cut areas in the rootstock bark. The winding must be made in such a way that the kidney remains entirely in the air.
PROS:
- Almost all graft material takes root
- does not require a large amount of scion
MINUSES:
- relatively difficult to implement method
- not suitable for very thin bark
Bridge grafting

Bridge grafting
Bridge grafting This grafting method is carried out when it is necessary to save a tree with circular damage to its bark. This can happen when the trunks are frostbitten or during years of special activity of various rodents, for example, hares.
In fact, bridge grafting consists of several bark grafts made around the perimeter of the plant trunk. In this case, shoots of the same tree are used.
They are prepared immediately before grafting.
Grafting budding of fruit trees and its advantages
Among the many advantages of this method, first of all, the following should be noted:
- — economical consumption of scion material (up to five buds can be cut from one cutting, suitable for budding the same number of rootstocks);
- — high survival rate of eyes (buds);
- - simplicity and ease of implementation;
- - rapid healing of wounds on rootstocks.
In addition to vaccinating young game birds, this method can also be applied to overgrown game birds with strong trunks and mature crowns. However, only those trees whose thickness of branches in the crown does not exceed a centimeter in diameter are suitable for the procedure (for trees with thicker branches, another grafting method is used - “cutting”).
If you are planning to get winter-hardy, hardy and long-lasting fruit trees yourself, try using this method. The technique for implementing it is quite simple and can be mastered even by novice gardeners.
Important points

Treatment of cut sites near the grafting
With any method of plant grafting, you should remember a number of rules that will allow you to carry out this procedure with greater efficiency:
1Approximately 10-15 days before the planned grafting, you should loosen the soil around the rootstock and water it
2Immediately before grafting, you need to prepare the tool and cuttings. The tool should be cleaned of dirt and disinfected over fire or alcohol. The cuttings need to be soaked in water at least a few minutes before grafting.
3All cuts and cuts must be made exclusively with a sharp tool, at the correct angles and the required length. Torn edges of wood on cuts and cuts must be smoothed using a knife
4After the grafting has been carried out, the scion is additionally strengthened and partially isolated with a bandage (in the form of a rope, electrical tape, film, etc.), it is necessary to treat all open areas with damaged wood using a garden varnish. If you don’t have any varnish at hand, you need to at least use oil paint
By following these simple recommendations, you will be able to significantly increase the percentage of surviving scion.
For the vaccination to be successful
- The instrument must be in excellent condition. Well sharpened. The knife is adjusted every 15-20 cuts.
- All cuts are done the first time. You can't compare anything. It's better to make a new cut.
- The cuts should be smooth, without burrs of the bark.
- Before working with valuable varieties, it is better to practice on unnecessary branches.
- Only healthy plants can be used.
- The scion must be at rest.
- The cuts should fit each other perfectly, without gaps, and the cambial layers should match as much as possible.
- The strapping should securely fix the grafted components and protect the grafting site from drying out. To avoid overtightening and breakage of the graft, the binding must be removed in a timely manner.
- If your goal is not an experiment, but the desire to get a long-lasting plant, you need to graft only closely related species, selecting proven combinations of varieties and rootstocks.
Grafting into cleft

This method is usually used for regrafting mature trees.
The regrafted branch is cut or cut down at the desired height and split in the middle. To prevent the gap from closing, it is fixed with a small wedge. Symmetrical cuts are made on both sides of the grafted cutting and inserted into the split from one edge, aligning the cambial layers. The wedges are removed, the graft is tied, the cutting is cut under the 3rd - 4th bud. The gap on the rootstock is closed with a small splinter so that the garden varnish does not get into the split; all cuts are carefully covered.
If the diameter of the rootstock is more than 4 cm, then for better overgrowth two cuttings should be grafted. In the future, only one, the strongest, is left.
Secrets of success
For the vaccination to be successful, some requirements must be met:
- choose young shoots for budding whose diameter does not exceed 10-11 mm;
- the bark on the knot should be smooth and elastic;
- you should not plant an eye on the southern side of the crown - the sun will dry out the rootstock area;
- for guaranteed success, you can graft two buds at once on both sides of the rootstock, but they should be tied at the same time;
- To perform the method, no putty is required; polyethylene is sufficient;
- on one shoot you can plant several eyes in a row, only the interval between them should be 15-20 cm;
- the lower bud should be grafted at least 20-25 cm from the fork of the trunk;
- It is strictly not recommended to breed in rainy weather;
- In summer, for grafting, choose a cloudy, cool day or do budding in the morning or evening;
- a couple of weeks before the summer grafting, it is recommended to water the tree to activate the sap flow process in it;
- Fully mature, large eyes located in the middle part of the shoot take root best;
- Only well-ripened cuttings are suitable for bud grafting, which can be recognized by the characteristic cracking sound when bending.

Attention! The method under consideration is suitable for grafting absolutely any plants: fruit trees, berries and ornamental shrubs. Therefore, every self-respecting gardener should master it.
We are preparing to carry out work - what needs to be done?
A couple of days before budding, you need to do some preparatory work. If the weather is warm, then the grafted trees need to be watered, which will lead to increased sap flow, in addition, in this case the bark will better lag behind the tree, which will greatly facilitate the work. In areas of budding on the plant, you need to remove interfering side stems and leaves, if any.

On the day of grafting trees from the plant for budding, we cut the ripened stems with the formed “eyes”. Do not forget to remove the top from the shoot, remove the leaves, leaving only short (up to 1 cm) petioles. Since you will not carry out the work immediately after cutting the shoots, do not forget to wrap them in a damp cloth or immerse them in a container of water and place them in a cool place. Next, we proceed to prepare the vaccination site. On the trunk of the rootstock at a height of about 20 cm, we select a place for budding.

Wipe it with a damp cloth, and also clean the moss from the bark - it should be smooth and clean. If you work on the side branches of an adult plant, then it is better to choose biennial shoots, and it is better to carry out budding in the upper part.
How to do?
Having chosen one of the methods, you need to be informed how this is done correctly. So, let's figure it out.
The budding method requires preparation of the tree. 2 weeks before the start of the process, the rootstock tree must be prepared. The soil around the trunk is loosened and, if necessary, moistened. If it is decided to graft the tree into the neck of the trunk, then hilling should be carried out to the intended connection point. 24 hours before grafting, the soil is raked.
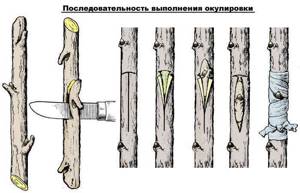
Budding sequence
Grafting is carried out in several stages:
- The scion and rootstock are connected;
- A T-shaped cut is made on the scion. The corners in the resulting compartment bend outward. A bud with a bark shield is attached inside the compartment;
- The scutellum is tightly connected to the educational layer of active cells ─ cambium. All this is pressed against the bark and secured with insulating film (polyethylene, electrical tape);
- The grafted kidney should remain exposed to air.
Grafting using cuttings is carried out as follows:
- First, you will need to make a 30-degree cut on both the scion and the rootstock;
- Next, the connection is made. They will be able to grow together, provided that the educational layer of their active cells has the same structure;
- After this, the junction is secured with the same film, and, if necessary, treated with garden healing agents;
- To improve fusion, it is advisable to make a non-ideal cut, but a zigzag shape (notch), so that the scion and rootstock are combined into a puzzle.
in spring
If the gardener decides to graft a fruit tree in the spring, then it is better to use the following methods:
- Carry out grafting using the splitting method. In this case, the cut on the cutting should be slightly larger than the cut on the rootstock. The old tree is cut off, leaving the stump about 6 cm high from the surface of the ground. Using an ax, a split is made in the middle. Cuttings with two buds are inserted into the gap. The lower buds should protrude from the depths of the hole. From the supporting buds, downward, oblique cuts are made, resulting in a kind of blade. The cut of this blade should be inserted into the hole in the stump so that their cambium is connected. The contact point is secured and lubricated with garden varnish.
- Grafting method using a side cut. In this case, the cut is made with a distance of 20 cm from the ground. At the base of the root neck, an incision is made in the bark, touching the wood. A cutting with two buds is cut on both sides with oblique lines, so that the buds are higher. The resulting cut of the cutting is inserted into the hole in the bark and secured.
In summer
Vaccination in the summer requires adherence to the calendar. All processes are carried out no earlier than the end of July and before the onset of autumn. The best survival rate is guaranteed if the kidney grafting method is used.
It would be useful to familiarize yourself with a number of rules and subtleties for the successful implementation of the procedure:
- Grafting begins with trees such as apple and pear, then they begin to renew apricot and cherry.
- Peach and cherry trees tolerate grafting well with the onset of the first cold weather, ideally at the end of August.
- For better separation of the bark, half a month before grafting, the soil needs to be loosened and moistened.
- A few days before the start of procedures on the clonal rootstock, it is necessary to cut off the branches leading to the side, so that the length remains no more than 25 cm.
- Cuttings are pruned immediately before grafting itself, this is approximately 14 days.
in winter
In order to reduce the time for seedling growth, many gardeners pay attention to the copulation method in winter.
This method will allow you to obtain a one-year-old seedling with a strong root system by autumn. Another advantage is the fact that all work is performed without being on site; everything is easily done while sitting at a table in a warm house.
Work must be carried out from mid-December to early April.











