Where to begin?
Having measured all sides of the site using a tape measure or using the diagram obtained in the BTI as a basis, begin to draw a detailed plan on a sheet of graph paper. The most suitable scale for a small garden (this is considered to be a plot of no more than 20 acres in size) is 1:100, that is, 1 cm of paper will be equal to 1 m of land. Take photographs of the most important parts of the site, this will help when developing a plan.
Mark the cardinal directions on the site plan, mark the entrance and entry points, draw on a scale all existing buildings indicating the location of doors and windows, reservoirs, wells, hatches, sewer and other communications, as well as existing trees and hedges, if there are no serious reasons for their removal.
Having organized the garden space using a large-scale grid, connect the functional zones with garden paths to each other, to the house and other buildings, gates and wickets, and also provide paved areas - patios, around the pool, in front of the garage, etc.
Regardless of the material from which they are made, garden paths should be such that they can be used in any weather: during prolonged rains, early spring, and icy conditions. The driveway or entrance road is most often straight; walking paths should be located so that they allow you to admire the beautiful corners of the garden. The width of the path depends on its purpose: the width of the main paths should be 1.0-1.5 m; auxiliary - 60-80 cm. The minimum width of a path that allows two people walking towards them to pass each other freely is 70 cm. It is unreasonable to save garden space at the expense of the width of garden paths.
Paths are not just strips of land that are convenient to walk on, but also a decorative element that emphasizes the style of the estate or even in some cases dictates it. Consider the direction and location of garden paths at your summer cottage, providing the shortest routes to important objects on the site and harmoniously linking them with walking routes.
How to lay rubber tracks at your dacha with your own hands
Rubber tiles for paths in the country have many advantages over other types of products.
In particular:
- environmental friendliness and safety of the material;
- anti-slip effect;
- preventing the formation of puddles and ice crust;
- resistance to temperature changes and chemicals;
- ease of installation;
- wear resistance;
- reducing injuries from falls;
- the presence of various color variations and textures.
It is easy to transport from the store. But it is not applicable near a recreation area with an open fire and is quite expensive.
There are several types of tiles in thickness.
In summer cottages, products are used for a sand or soil base from 30 mm with end grooves.
Tools and materials, in addition to the tile itself:
- sharp knife (jigsaw, hacksaw);
- polyurethane adhesive for rubber surfaces;
- rubber borders for the integrity of the composition;
- broom or vacuum cleaner;
- ruler or building level;
- chalk, spatula and roller;
- turpentine (acetone);
- notched spatula;
- foam sponges or brushes;
- rubber hammer.
Lay rubber tiles as follows:
- Concrete screed. A smooth surface without cracks or roughness is cleared of debris.
- Priming with a mixture of turpentine and polyurethane glue in equal proportions. About 300 g per sq.m. is used. Dries within an hour.
- Limit the perimeter with a cord to ensure clear edges.
- Rubber-bitumen mastic (glue) is applied to the entire surface, leveling it with a roller or spatula.
- The laying of non-rectangular paths begins from the center, having previously completed a sketch and made landmarks with pegs and ropes.
- Having laid the slab tightly, it is tapped with a hammer, “expelling” the air;
- Curb installation.
The nuances of installation are the presence of a slope for rainwater drainage, as well as the air temperature during installation - not lower than 5 degrees Celsius. After 2-3 days you can already walk on this structure.
We use rubber tracks in rolls at the dacha
There are other variations with rubber on the market. For example, roll options are installed using almost the same principle, but much faster and easier due to the integrity of the structure.

The length and width of the roll varies from manufacturer to manufacturer, but is usually 3 m by 30, 60 and 100 cm.
Convenient rubber options do not rot and perfectly prevent the spread of weeds.
What to pave with?
It is very stylish if the material of the house itself is partially used in paving paths around the house. If you have a brick house, it will be great if the path or area near the house combines, for example, brick with concrete tiles or brick borders with natural stone paving. But only clinker bricks can be used; ordinary building bricks will crumble in a couple of years.
The base of the house, lined with stone, suggests the use of stone in covering the adjacent paths. Running from the building into the garden, from one zone to another, the garden path can be transformed: paving stones are replaced by flagstone, and this, in turn, is replaced by a gravel embankment. A soft flow of coatings can be achieved by combining them at transition points, as well as by repeating elements of the previous coating in the next.
It would be wrong to think that a plot with a wooden house should be paved only with wood. Wood materials combine well with natural stone, gravel, concrete or porcelain tiles. If you have a luxurious stone house in the English style, and you would like to design your garden in the same style, make gravel paths. It will be very English!
Indoor transport network
In accordance with the traffic rules, when moving through the courtyard area, pedestrians can move not only on sidewalks, but also on the roadway. Pedestrians have the right of way, i.e. a driver in a residential area must give way.
The maximum speed is limited to 20 km/h, however, in reality, traffic police officers rarely look into the courtyards of residential buildings, so no one monitors compliance with the rules there. This leads to drivers forgetting the correct driving order in residential areas.
We offer the following technical methods for regulating the speed of vehicles in yards:
1. Installation of a “Residential zone” sign at all entrances to courtyards and neighborhoods.

2. Installation of a video surveillance system to record traffic violations not only on the roads, but also in courtyards.
3. Anti-parking bollards are a universal tool for calming traffic in yards. They are clearly visible to drivers and allow them to reduce speed in advance, but for pedestrians they are not an obstacle and do not spoil the appearance of the yard as a whole.
The following options for their use are possible: - narrowing the roadway at intersections with the pedestrian network; — reduction of rounding radii on turns; — narrowing the roadway as a whole and allocating space for pedestrians in courtyards where it is impossible to organize a separate sidewalk; - creating a chicane, i.e. a sequence of tight, twisting turns to deliberately slow down cars; — protection of sidewalks from illegal parking.

4. Another means of slowing down traffic, by analogy with pedestrian crossings, is raising the level of the roadway to the level of the sidewalk at the intersection with pedestrian paths, opposite the exits from the entrances of residential buildings, kindergartens, schools, playgrounds and sports grounds, and other infrastructure facilities in the residential area . This measure will force the driver to slow down and will protect, for example, a child running out of the entrance or school.
A single level with the sidewalk makes it possible to implement the principle of a barrier-free environment for people with limited mobility, and also makes the courtyards convenient for cyclists. In fact, this is an analogue of a speed bump, but also with an important functional and ideological component. It is much more convenient for people to move along such a crossing, and its raised design reminds drivers of the priority of pedestrians. Such intersections will not be flooded by rain; they will always be clean and dry.
Read also: How to properly prune actinidia in the fall

This solution can be implemented without significant costs, since there is no need to change existing sidewalks. In this case, installing a pair of anti-parking bollards will help prevent vehicles from driving onto the sidewalk.
5. Construction of an artificial road hump (“speed bump”) on the streets leading to the territory designated by the road sign “Residential zone” in front of children’s and youth educational institutions, playgrounds, places of mass recreation, shops and other objects of mass attraction for pedestrians .
A properly planned network of pedestrian paths in a garden plot is an important part of creating a beautiful and comfortable garden. We walk along them, enjoying the beauty of the garden, we push a wheelbarrow along them or walk with a bucket and shovel at the ready. Paths are main, walking and secondary, working. Depending on their purpose, we will build them from different materials. The size of the garden dictates its width: the main route paths are from 0.8 to 1.5 m, auxiliary paths are from 0.4 to 0.8 m, the optimal width is 0.6 m.
The design of the paths can be built on geometric or free landscape lines; a reasonable game of contrast between the forms of strict geometry and smooth lines is also acceptable, for example, a combination of straight and picturesque lines, diagonals, circles, etc.
Paths and paths divide the area into different zones and at the same time unite the garden into a single space. This is achieved not only by the general design of the paths, but also by the use of carefully selected paving materials. There are several rules for the selection and use of decorative materials that are applicable not only to creating a network of paths in the garden, but also to any other work on the design of our environment.
Rule 1. The paving of paths adjacent to the house must involve the material used in finishing the house itself, be it the facade, basement or porch. That is, the same material should move from the vertical plane of the house wall to the plane of the garden and spread throughout it, which significantly enhances the feeling of the common space of the entire estate. This material should not dominate the paving of the local area, otherwise the house and garden will visually merge. It usually takes up about a third of the paving area.
Let's look at a fairly common option. The house is built of red brick, has white window sashes, a concrete blind area and a porch. It would be appropriate to decorate the front area with paving made of concrete paving slabs, combining it with a pattern of clinker bricks. The light gray color of the concrete mutes the brightness of the red brick, making it calmer and more pleasant to perceive, harmonizing with the white color of the window frames, which, in fact, also work to smooth out the color of the walls. In this case, we choose clinker brick because its strength is close to natural stone, while ordinary brick in paving is fragile and begins to crumble quite quickly, especially if it is laid flat and not placed on its edge. But there can be a great variety of combinations and patterns of clinker and concrete tiles, just try to choose clinker and concrete tiles of more or less the same size. In this case, paving made from mixed materials will be stronger.
Rule2. The further from the house, the less home decoration elements are used in the path design. Let's say the path near or around the house will be laid out from concrete paving slabs with the inclusion of clinker or finishing the side line from it. Then we will move to paving with only concrete slabs, perhaps of a different size or shade with occasional clinker inlays, and then, as we move into the forest area, we will finally remove clinker from the paving, reduce the proportion of concrete slabs and introduce gravel backfill. In some areas of the path remote from the house, you can make a gravel backfill with the inclusion of separate concrete slabs of a different tone. As you move deeper into the forest, concrete may completely disappear from the road surface.
However, the materials with which we lay out the paths near the house will appear again when, on a forest path, we come across a bench on a small rest area or a fountain with cool water. We can pave such an area with concrete paving slabs with a clinker pattern, reminiscent of paving a local area, but simpler. Or we can simply make a gravel backfill over the entire site and edge it with one or two rows of clinker. The opposite solution is also possible here: if the brick walls of the house and the fence remain in the distance, then brick can be used as the basis for the paving, and concrete tiles or gravel backfill can be introduced only as a small memory of the path traveled.
Thus, combining carefully selected paving materials is an effective technique that unifies the entire composition of the garden. Moreover, in each zone of the garden, the paving must correspond to the purpose and style of the zone itself, be it a forest gazebo or a utility area.
Secondary or utility paths in the garden can be made of concrete paving slabs measuring 30x30 cm, laid in two rows, or two types of tiles, for example, in the first row of the path two tiles measuring 25x25 cm are laid, and in the second row only one tile measuring 25x50 cm, and these rows alternate. If you need to reduce the width of the secondary path, then 25x25 cm tiles in the first row are laid out side by side, as in the previous version, and in the next row the same tiles are laid, but in the middle, etc., that is, the tiles are laid according to the principle of brickwork, when one upper brick rests on two lower ones. The last two options for laying tiles do not have cross-shaped seams.
It’s worth taking a closer look at this method of paving. Most sites in the Moscow region are located on watered medium and heavy loams. The soil is constantly saturated with water, which does not leave. When frost sets in, the water in the soil freezes and, as you know, expands. The soil expands accordingly. Such soils are called heaving soils; they cause a lot of trouble for builders, landscape designers, and site owners. It is clear that such soils can lift tiles laid in a path, and it is the tiles that have cross-shaped joints that are most easily lifted, and paths with other types of joints are deformed to a lesser extent.
Read also: How to cook noodles at home
There are a sufficient number of developed types of layout of rectangular tiles. The most decorative is the so-called Roman masonry, in which tiles of several sizes are used, they are laid out in a free pattern, but without cross-shaped seams. In Western Europe, this type of masonry is extremely popular and is made from rectangular and square stone slabs.
Secondary paths can be laid using the step-by-step path technique, when the slabs are laid with breaks corresponding to the length of the step. The gaps between the slabs are filled with turf or bulk decorative materials. It is convenient to walk on such a path, you can transport a wheelbarrow along it, without harming the lawn.
Rule 3. In the design of paths and areas in the garden, you can use no more than three different but compatible materials and no more than two or three of their shades. At the same time, the methods of arranging these materials can be very diverse. Indeed, the monotony and uniformity of paving must be broken by interspersing tiles that are different in tone and texture, or by introducing green islands of unpretentious ground cover plants that are resistant to trampling, which look great on the paving.
From these rules it becomes clear that materials for the decorative and functional design of a site cannot be chosen at random.
Another standard option, which requires the selection of completely different materials, is a wooden house, and it can be an old village house, a house on a garden plot, or a modern cottage made of laminated or rounded timber. In this case, one of the materials for decorating the site will be wood. These are all kinds of decking, walkways, boards of various sizes, garden parquet, step-by-step paths from saw cuts of various sections and diameters, tinted timber and simply old railway sleepers, sunk into the lawn or gravel backfill and, finally, decorative backfills made of tree bark and wood chips.
Wood as a material for creating paths is still rarely used in our garden design. Usually preference is given to natural stone. However, wood is the main building material and is not such a clear leader in garden landscaping. There are no rock outcrops in nature in the Moscow region, so the excessive use of stone in decorating gardens is not entirely natural.
Tinted wood is beautiful, durable, environmentally friendly, pleasant to the touch, quickly absorbs solar heat, dampens the sounds of footsteps and makes the pedestrian look at his feet and admire the simplicity and naturalness of the material, familiar to us from childhood. We all remember the silver-gray picket fence of our grandmother’s fence from bad weather, but it will only stir up long-forgotten memories of low, similar dachas with carved platbands, painted shutters and an octagonal attic window in old dacha villages left over from a bygone era... And in other countries, progressive designers artificially age, bleach the wood, giving it exactly that unique silver-gray shade, using complex tinting compositions, or specially display garden furniture in gardens without any protective coatings and wait several years for it to acquire exactly that very shade...
Long-term use of wooden decks and walkways in the open air is possible subject to a number of rules. Firstly, you can purchase products from Western companies that produce wood materials with a ribbed non-slip surface, from which they make decks, patios, walkways and square panels, placed in a step-by-step order. They are extremely durable, since in the factory, antiseptics are driven into this wood under high pressure. However, such wood is very expensive. Among the available species we can name larch. It is durable, but not cheap. Oak is not suitable for such purposes for everyone, since it is also expensive and does not last longer than pine. Most consumers buy pine. With proper wood processing and preventive maintenance, such floorings can withstand 8-10 years without major repairs. For decking, boards with a thickness of 15-30 mm and a width of 200-250 mm are usually used. The entire surface of the wood is treated with an antiseptic, and those parts that will come into contact with the ground are coated with bitumen. Wood flooring and walkways must be maintained with constant ventilation, i.e. lift it off the ground, placing it on its feet. The legs are timber with a cross section of 40x80 mm. Of course, the legs are treated with bitumen. Typically, wooden walkways are two boards connected by transverse slats and placed on legs. A gap of 20-25 mm is left between the boards, which promotes additional ventilation. The surface of the boards must be well treated; the parts of the walkways are connected using galvanized bolts with recessed heads. You can walk on this flooring barefoot without fear of getting hurt. It dries quickly and heats up under the sun, giving pleasant warmth to your feet. Garden elements made of wood require annual treatment with antiseptic agents; if possible, it is advisable to put them indoors for the winter. Such walkways are placed on a gravel backfill. They are often spanned across a dry stream, led from one wooden deck to another, and are widely used in natural or native gardens. Wooden boards and walkways often lead to ponds and even extend out onto the surface of the pond on supports.
The same rules apply to the construction of a path from wood ends. Typically, the beams are cut 15-20 cm long, impregnated with an antiseptic, the part that will be in the ground is treated with bitumen and installed in a road bed on a layer of compacted sand. The gaps between the segments are filled with sand and compacted. Smaller diameter pieces can be driven into large gaps by first sharpening the lower end. You can decorate the gaps with tree bark or wood chips.
When working with wood scraps, you can use the following technique: in a predetermined place, not short scraps are buried, but elements 0.5 m long - such protruding processed logs can serve as seats or a support for a bench on a forest walking route. If you bury a group of logs 1.0-1.5 m high, you can get a decorative wall or garden sculpture that fits organically into the plane of the path and seems to “grow” out of it.
Read also: How to properly arrange the inside of a garage
Despite the fact that decorative wood materials are quite diverse, it is not entirely correct to use only them when decorating a site with wooden buildings, especially if the site is large enough. Wood materials combine well with natural stone, warm-colored gravel, artificial tinted concrete and porcelain tiles.
Nina Tomilina, landscape architect (Based on materials from the magazine “Bulletin of the Florist”, No. 3, 2005)
Concrete, stone, paving stones
Most often, concrete slabs of various shapes and colors are used for paths, which are laid on a sand cushion - this is the most inexpensive way to construct paths, and it is the most common. The external neutrality of this material allows it to be adapted to any tone and design style of the site, as well as combined with other types of coatings.
Another way to solve a path or site is a concrete or cement monolith. This coating is highly durable, but looks dull. However, a monolithic path or platform can be decorated, for example, interspersed with pebbles, colored glass, and ceramics. It’s quite simple: arrange a sand cushion in the place that you intend to decorate with concrete, make the paving lines you have chosen from strips of plywood and fill them with cement with a layer of 7-10 cm, leaving gaps about 7 cm thick between individual fragments. When the cement sets , press pebbles or other decorations into it. In the spaces between the “slabs” you can plant a suitable ground cover plant.
Good for paving and, of course, much more interesting are slabs made of natural stone no thinner than 5-6 cm - they are also laid on sand without concrete. Thinner stones (layers at least 4 cm thick are suitable for paving paths) need to be concreted.
In addition to flagstone, paving stones are the most famous paving material. Its high cost is compensated by its sophistication and quality. When laying paving stones or stone paving, it is necessary to maintain a slight slope in the transverse profile of the path, which allows for active drainage of water from the surface. A slope of 2–3 cm per linear meter of the width of the path, measured from its longitudinal axis, is ensured by constructing a base of the appropriate shape or during the process of laying paving stones on a dry mixture. Fixation of the road surface is ensured by the outer tiles laid on cement mortar. It is advisable to arrange the edges of the paths flush with the soil level, without fear of possible contamination of the surface of the path with fertile soil - over time, the lawn forms a powerful turf that firmly binds soil particles.
Do-it-yourself concrete paths at the dacha
Inexpensive paths in the countryside from scrap materials can also be made from simple concrete. The simplest option is a concrete screed. The foundation is being prepared for it. We will also use a special layer of film that does not allow vegetation to pass through and strengthens the structure, as well as an embankment of sand and small gravel on compacted soil.
But it also has a number of disadvantages. In particular, sliding, the creation of an ice crust, less durability due to instability to temperature fluctuations and mechanical damage.

But concrete can also be used to make luxurious shaped structures. Simple squares, circles or rectangles are poured yourself or purchased in stores. You can also diversify the surface of the path with different patterns or prints, for example leaves. Installation is not labor intensive:
- a trench is dug 2-3 cm below the height of the slab concrete;
- filled with sand a few cm;
- the tile is installed by pressing it with a rubber hammer;
- the edges are filled with crushed stone, gravel or soil.
Such paths look very impressive and allow you to easily create round, zigzag shapes. The material is fire resistant and suitable for barbecue areas.
Wooden paths
Nowadays, wooden paths and floorings have begun to be actively used in Russian gardens, as non-slip options have appeared. The best material for our climate zone is non-rotting larch. Wooden decks are easier and faster to build than pavement for the same area. Wood is warm, and it is much more pleasant if the area for sun loungers around a well-shaped pond is paved not with tiles, but with wood. And in the forest zone of the garden, it will look much more logical and natural not to have paved paths, but paths made of wooden flooring, placed on bars, and thus raised above the ground. The bars, in turn, are installed on the gravel. The boards in the flooring are installed with a gap of 1–2 cm for ventilation. It is best to use larch.
Once upon a time in Siberia, entire roads were paved with checkers from the ends of its logs. This species is distinguished by its great strength, moisture resistance, and unique wood grain. It is used to make “garden parquet” - square and triangular sections (the basic element has a size of 50x50 cm), assembled from wide slats. And for wooden sidewalks, boards with a “corduroy” profile are used, which prevents slipping in rainy weather. “Garden parquet” should be laid on a small (up to 15 cm) gravel bed.
Wooden paths can be made from round stumps laid vertically, or from wooden rectangular blocks, as well as from cross sections of thick trees 10-12 cm thick. To protect the tree, it is treated with an antiseptic. First, using pegs and rope, the boundaries of the path or site are marked, then a bed of appropriate depth is dug (most often 25-30 cm), the bottom is sprinkled with sand, which is leveled and compacted, gravel is laid on top of it, which is carefully leveled, watered abundantly and compacted well. Then they begin laying round timber, lumps or saw cuts, which are tightly fitted to each other; smaller ones are “squeezed” into the gaps between the large pieces. After this, gravel is poured on top so that all the gaps are filled, and it is compacted well, pouring water on it.
Concrete slabs as a path in the country: casting process
This method of creating functional and presentable paths is usually considered expensive due to the additional costs required for laying under the tiles. But there is an installation option using a ready-made mold, ordinary sand and cement, and the tile itself can be cast with your own hands.
For production you will need:
- cement;
- sand;
- superplasticizer (strength enhancer and resistance to low temperatures);
- dye (if desired).
For strength and visual naturalness, fine gravel, chips or granite screenings are added “under the stone”.
Forms can be created from wooden beams, and unnecessary containers will also work, but they are lighter and not so expensive; they can be purchased at any hardware store. It should be noted that the material of the acquired forms directly determines the number of possible ebbs. The most durable are rubber (500) and plastic (250), and polyurethane provides up to 100 units. tiles

Garden paths in the country from concrete tiles are cast as follows:
- We prepare the place for the path. Pour fine stone or sand, screenings (or slag) onto a flat prepared surface and level and compact. The depth of the “pillow” is 3-5 cm.
- Mix the solution according to the proportion: 1 part cement, 1.5 parts sand and 1.5 parts screenings, also a superplasticizer. The dye is optional, but the color will still include shades of gray. It is advisable to stir the dry mixture until smooth, and add water gradually so as not to overdo it. If it is not possible to mix the components of the future tile in a concrete mixer, then mix all the components manually.
- Before use, it is advisable to lubricate the mold with machine oil or regular dishwashing liquid. Place the mold on a compacted “pillow”. To save solution, the mold cavities can be filled with small stones.
- We fill the mold with the prepared solution. Use a spatula to level the surface. Remove excess solution.
- After a few minutes, carefully remove the mold, grease it again if necessary, and place it in a new place. We repeat the process.
- After a few days, fill the gaps between the tiles with sand.
Self-cast tiles will definitely become a source of pride for the owners, and at the same time you can be sure that they comply with the technological manufacturing parameters that affect their service life and strength. The installation process is quite quick and simple, which is suitable even for novice summer residents.
Cobblestone and gravel
The path paved with cobblestones looks good. The foundation for it is a layer of gravel with a layer of sand and clay poured on top of it. Laid out randomly or in a pattern, the cobblestones will become a spectacular decoration of the landscape. The combination of wooden flooring and cobblestones will enhance the Japaneseness of the Japanese garden you create.
Gravel paths are universal in use; they can be installed both at the entrance to the house and in the most remote parts of the site. They are beautiful in their naturalness, inexpensive, and easy to make into any shape. They are made slightly deeper than the soil surface. Under the gravel path, dig a trench 15-20 cm deep and compact its bottom well. To prevent the germination of weeds and the “leakage” of gravel into the ground, geotextiles are laid at the bottom. Gravel paths require curbs, otherwise the loose coating will “scatter” into flower beds and lawns. The gravel is poured in thin layers with each layer compacted tightly.
As you move away from the house, for example in the walking part of the garden, use completely different materials. This will emphasize that this is a different zone. Combining paving materials is a very interesting technique; if used skillfully, it will emphasize the style of each zone and at the same time combine the composition of the garden into one whole. Just don’t use more than three paving materials at the same time.
Garden paths - diagrams
There are a lot of modern methods for laying paths in private areas, it all depends on the chosen material. High-quality paths on the site must comply with the following rules:
- The layout should provide for their width.
- It is not recommended to place paths in the center of open lawns or fields.
- When creating a pedestrian garden path, it is important to include turns in the route that will help you examine the landscape from all sides.
- To prevent water from stagnating on the paths, it is worth making a slight slope of up to 3º.
- On a relief section, paths are made at a slope of 10 cm for each meter of path.
- When the angle is greater than 12º, it is recommended to make a step 10-15 cm high.
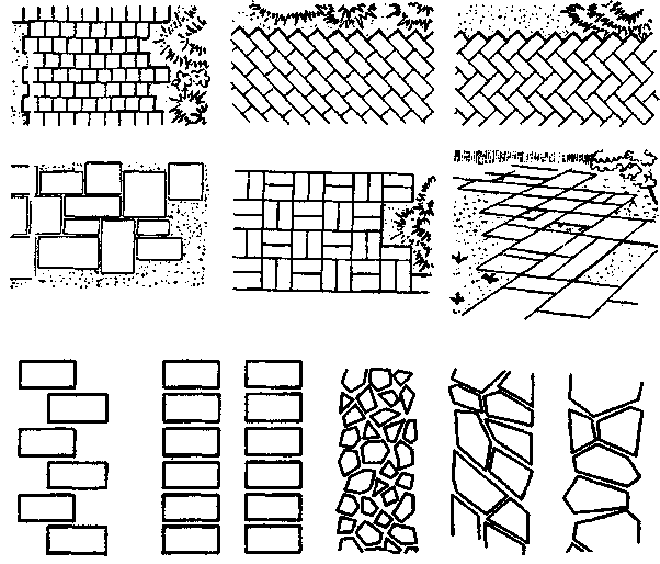
The following installation methods are used:
- column;
- brickwork;
- Christmas tree;
- squares;
- a combination of the above schemes.
We use lawn grates
Nowadays, paths and playgrounds are often made using lawn gratings and honeycomb panels made of high-density polyethylene. The lattice installed on the prepared base is covered with fertile soil and sown with grass. The result is a lawn with high mechanical strength (withstands loads of up to 200 t/sq. m), which can serve as a parking lot, driveway or pedestrian path.
The important thing is that, unlike a regular lawn, you can walk on it in early spring and in any weather.
Lawn grates are modular designs, they are equipped with a reliable connection with latches and are easy to install. The necessary bends of the tracks are made using cutting tools. The thickness of the base for the gratings is determined by the nature of the load on the surface. For example, the sand and gravel cushion at the entrance to the garage should be 20-25 cm thick, and at the parking lot - 30 cm.
With the help of lattice cells, you can not only grow a lawn that is resistant to mechanical stress, on which you can walk at any time of the year in any weather. If you fill the cells with fine gravel, you will get a gravel pad, driveway or parking lot.
If there is a forest area in the garden, then it will look logical and natural not to have paved paths, but to have wooden flooring, as well as paths made of gravel or wood chips.
PEDESTRIAN WAYS IN THE DEVELOPMENT TERRITORY
The network of pedestrian paths should connect the most attractive points for the population within the shortest distances. Therefore, when designing them, it is necessary to take into account the most appropriate directions of pedestrian flows and their rational organization. They should provide convenient approaches from any entrance to public transport stops, educational, children's, commercial buildings, cultural and public service points.
In residential groups, paths should be laid to sports and utility areas, as well as to recreation areas. The width of the tracks must be constant throughout their entire length, and for transit tracks it is 2.5. 3.0 m, for walking - 1.5 and for paths - 0.75 m.
To install rest benches on the paths, you can widen them by 1.5 m.
For pedestrian paths and paths, the following maximum longitudinal slopes are allowed: for paths 3.2.5 m wide - 6.8%, 1.5 m wide - 8.10%, for paths - 10.12%. If the terrain exceeds these slopes, it is necessary to arrange steps, ramps, and serpentine descents.
The transverse slopes allowed when constructing paths, paths and platforms are as follows: for gable paths 3 m wide - 2.3%, for single-pitch paths 3 m wide - 3%, for paths 2.25 m wide - 3.4%, for walking paths paths (single slope) - 4.5%, for sites for various purposes - 2.3%. Sites for various purposes should be designed with shallow drainage.
Types of road surfaces. The surface of the driveways must have a special coating that facilitates the passage of vehicles. Road pavement must be sufficiently strong and durable, waterproof, consistent with the nature of the movement, and ensure wheel adhesion to the road surface, i.e., be rough. In addition, road pavement is subject to the requirements of industrialization and mechanization of work, sanitary and hygienic requirements for operation and cleaning (dust-free, quiet during traffic, the possibility of mechanized cleaning).
In neighborhoods and microdistricts, the following road pavement designs are used for the carriageway: asphalt; crushed stone and gravel, treated with binding materials; prefabricated from cement-concrete slabs (Table 1).
Table 1.
Type of path, platform
Garden path design
It is difficult to find modern summer cottages without equipped quality paths. The choice of shape and materials for garden paths must be approached responsibly. Designers advise following a single style in the design of the site, with the exception of areas larger than 30 acres, where it is possible to divide into different zones. Paths on the site can be made using different stylistic solutions:
- Japanese garden or mysterious forest alley. The paths are based on the material of the blind area and finishing of the house.
- Rural style. A log house with a bathhouse will be complemented by paths made of stone or wood cuts.
- It is better to complement the English garden with brick paths, which will look natural among the greenery and wildflowers.
- Scandinavian style combines simplicity and expressiveness. The ideal option for this is natural materials.




Unusual garden paths
The organization of paths on the site is limited to a large extent by human imagination. Among the unusual garden paths are the following:
- Paths made from stones with an uneven structure blend perfectly with any landscape.
- Large flat concrete discs can not only serve as a path, but also act as steps.
- Using multi-colored stones, you can create garden paths with any pattern.
- Concrete is poured into the mold and the resulting products are placed in a chaotic order, filling the remaining space with fine gravel.
- Illuminated concrete blocks will decorate any interior.
- The combination of large concrete pancakes with small stones will fit perfectly into any design.